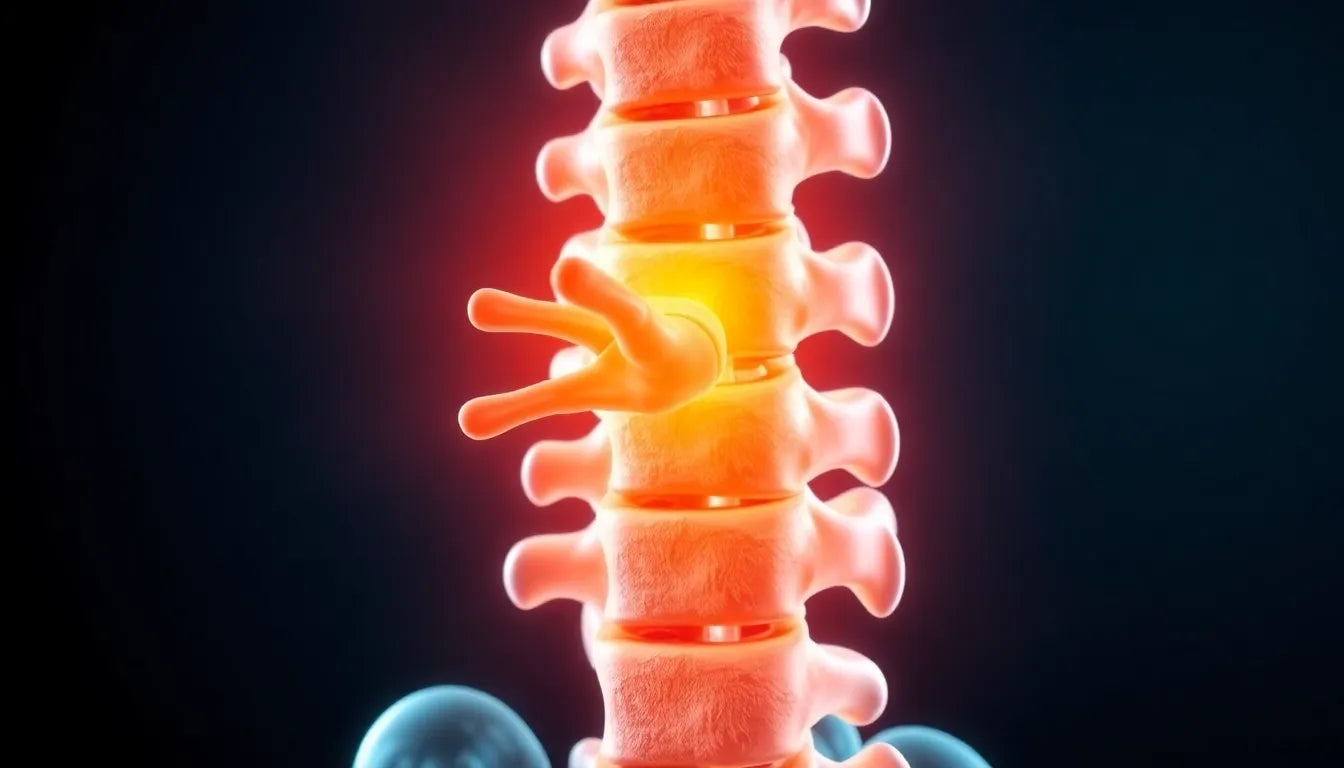
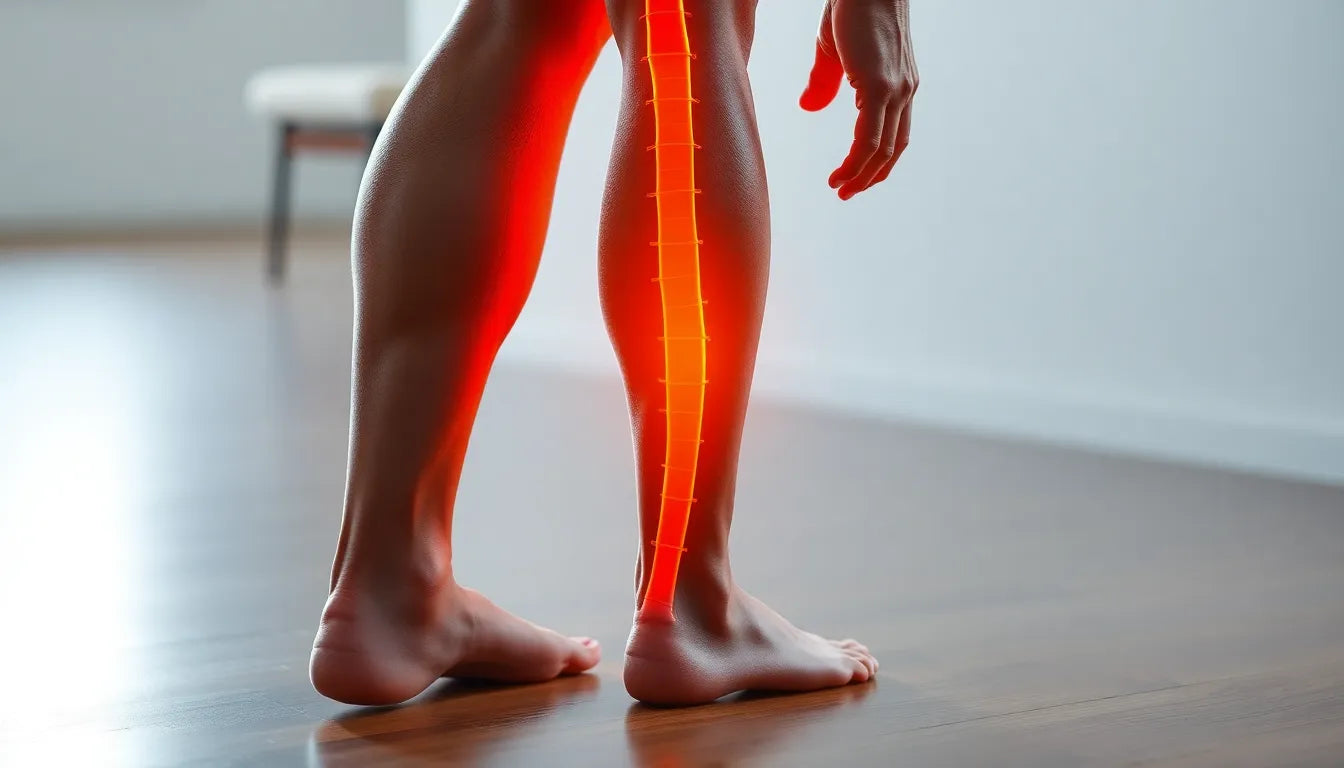
A herniated disc, often referred to as a slipped or ruptured disc, is a common spinal condition that can cause significant discomfort and disruption to daily life. It occurs when the soft inner gel of a spinal disc pushes through a tear in the tougher outer layer. This condition can result from age-related wear and tear, improper lifting techniques, or sudden trauma to the spine. The symptoms of a herniated disc can vary, but they typically include sharp back pain, numbness, tingling, and weakness in the limbs. These symptoms arise because the displaced disc material can press on nearby nerves, leading to inflammation and irritation.
Understanding painkillers for herniated disc relief
For those suffering from a herniated disc, effective pain management is crucial to maintaining a good quality of life. Painkillers play a pivotal role in managing the symptoms associated with this condition. They help alleviate pain, reduce inflammation, and improve mobility, allowing individuals to continue with their daily activities with less discomfort. The right pain management strategy can also support the body's natural healing processes and prevent further injury by reducing strain on the affected area.
The importance of effective pain management
Unmanaged pain from a herniated disc can have a profound impact on an individual's daily activities and overall well-being. Chronic pain can lead to decreased physical activity, which may further exacerbate the condition and lead to additional health issues. Moreover, persistent pain can affect mental health, leading to stress, anxiety, and depression. Therefore, the goal of pain management is not only to alleviate pain but also to enable the individual to engage in activities that promote healing and prevent further injury.
Effective pain management for herniated discs often involves a combination of over-the-counter (OTC) and prescription medications. OTC painkillers, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like naproxen and ibuprofen, are commonly used to reduce inflammation and relieve pain. Acetaminophen is another option for those who cannot tolerate NSAIDs. In cases where OTC medications are insufficient, prescription options like muscle relaxants, nerve pain medications, and corticosteroids may be recommended by healthcare professionals.
By understanding the role of painkillers in managing herniated disc symptoms, individuals can work towards a comprehensive treatment plan that addresses both pain relief and long-term recovery. This approach not only improves the immediate quality of life but also supports a healthier, more active future.
over-the-counter pain medications for herniated disc relief
When dealing with the discomfort of a herniated disc, over-the-counter (OTC) pain medications are often the first line of defense. Among the most commonly recommended are nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), which include naproxen (Aleve) and ibuprofen (Motrin, Advil). These medications are well-known for their ability to reduce inflammation and provide pain relief, making them effective for those experiencing the acute symptoms of a herniated disc. Naproxen, in particular, is highlighted for its prolonged anti-inflammatory effects, which can offer extended relief with less frequent dosing.
Ibuprofen is another popular choice due to its availability and effectiveness in managing both inflammation and pain. It is often recommended for short-term use to alleviate the discomfort associated with herniated discs. While aspirin is also an NSAID, it is less commonly emphasized for herniated disc pain, although it can still be a viable option for some individuals.
For individuals who cannot tolerate NSAIDs due to gastrointestinal issues or other contraindications, acetaminophen (Tylenol) serves as an alternative. While acetaminophen does not possess anti-inflammatory properties, it is effective in reducing pain, making it a suitable option for those seeking relief from herniated disc symptoms without the potential side effects of NSAIDs.
limitations of otc medications
Despite their benefits, it's important to note that OTC medications primarily provide symptomatic relief. They do not address the underlying cause of the herniated disc nor promote healing of the disc itself. Therefore, while they can significantly improve comfort and mobility, they are best used as part of a broader treatment plan that includes other therapeutic modalities.
prescription medications for herniated disc pain
When OTC options are insufficient, healthcare providers may prescribe medications that offer more targeted relief. Muscle relaxants, such as carisoprodol (Soma), cyclobenzaprine (Flexeril), and metaxalone (Skelaxin), are commonly used to address muscle spasms associated with herniated discs. These medications help reduce muscle tension and improve mobility, thus alleviating some of the discomfort caused by muscle spasms.
Nerve pain medications, including gabapentin (Neurontin) and pregabalin (Lyrica), are specifically designed to target nerve-related pain. These medications can be particularly helpful for individuals experiencing tingling, numbness, or shooting pain, symptoms often associated with nerve compression from a herniated disc. Similarly, duloxetine (Cymbalta) is another option that targets nerve pain while also addressing mood, which can be beneficial for individuals experiencing anxiety or depression related to chronic pain.
Corticosteroids, available in both oral and injectable forms, provide potent anti-inflammatory effects. They are typically used for short-term relief to reduce inflammation and swelling around the affected nerve, offering significant pain reduction. However, due to potential side effects, their use is generally limited to short durations.
Opioids, while effective for severe pain, are prescribed with caution due to their potential for addiction and other serious side effects. They are usually considered a last resort when other medications have failed to provide adequate relief, and their use is closely monitored by healthcare providers.
non-medication approaches to pain management
In addition to medications, non-medication approaches play a crucial role in managing herniated disc pain. Physical therapy, injections, and surgery are often part of a comprehensive treatment plan. Physical therapy can help strengthen the muscles supporting the spine, improve flexibility, and reduce strain on the affected area. Injections, such as epidural steroid injections, can provide targeted relief by delivering medication directly to the site of inflammation. In severe cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to remove or repair the damaged disc material.
By combining medication with these non-medication approaches, individuals can achieve more effective and long-lasting relief from herniated disc symptoms, ultimately improving their quality of life and promoting recovery.
Limitations of medication-only approaches
While medications are pivotal in managing herniated disc pain, relying solely on them can lead to potential drawbacks. Long-term use of painkillers, especially prescription medications like opioids, can result in side effects such as gastrointestinal issues, dependency, and increased tolerance, necessitating higher doses for the same relief. Moreover, medications primarily address symptoms and do not facilitate the healing of the herniated disc itself.
Therefore, integrating other therapies and lifestyle changes is crucial for a holistic approach to pain management. Combining medications with physical therapy, ergonomic adjustments, and lifestyle modifications can enhance the overall treatment outcome, reducing reliance on medications and promoting natural healing.
Integrating ergonomic solutions with medication regimens
Incorporating ergonomic solutions can significantly complement medication regimens by addressing the root causes of discomfort associated with herniated discs. Ergonomic aids, such as supportive chairs, standing desks, and lumbar cushions, can help maintain proper spinal alignment, reducing pressure on the affected disc and alleviating pain.
Additionally, practicing good posture and using ergonomic tools can prevent exacerbation of symptoms during daily activities, allowing individuals to maintain a more active lifestyle. By integrating these solutions with medication, individuals can experience enhanced pain relief and support their recovery process.
Case studies and recommendations
Consider the case of John, a 45-year-old office worker experiencing chronic pain from a herniated disc. Initially relying heavily on NSAIDs, John found limited relief and began incorporating ergonomic solutions into his daily routine. By using a standing desk and lumbar support, he noticed a significant reduction in pain and reliance on medications. Similarly, Mary, a 50-year-old teacher, combined physical therapy with nerve pain medications and ergonomic adjustments, resulting in improved mobility and reduced pain.
For individuals with mild symptoms, starting with OTC medications and ergonomic changes can be effective. Those with moderate to severe symptoms may benefit from prescription medications, physical therapy, and specialized ergonomic solutions. It is crucial to tailor treatment plans to individual needs, ensuring a balanced approach to pain management.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the best painkillers for herniated disc relief?
The most effective painkillers for herniated disc relief include OTC options like NSAIDs (naproxen, ibuprofen) and acetaminophen. Prescription medications such as muscle relaxants, nerve pain medications, and corticosteroids may be recommended for more severe cases.
Can painkillers heal a herniated disc?
No, painkillers primarily alleviate symptoms and do not heal the herniated disc. They are used to manage pain and inflammation, allowing the body to heal naturally over time.
What are the risks of long-term painkiller use?
Long-term use of painkillers can lead to side effects such as gastrointestinal issues, dependency, and increased tolerance. It is essential to use medications as part of a broader treatment plan and under medical supervision.
How can ergonomic solutions help with herniated disc pain?
Ergonomic solutions, such as supportive chairs and lumbar cushions, help maintain proper spinal alignment, reducing pressure on the herniated disc. These aids can enhance pain relief and support recovery when used alongside medications.
When should I consider seeing a specialist?
If symptoms persist or worsen despite initial treatment, or if there are signs of significant nerve damage, it is advisable to consult a specialist. They can provide a comprehensive evaluation and recommend advanced treatment options.
Sources
- Mayo Clinic Staff. (2021). "Herniated Disk: Diagnosis & Treatment." Mayo Clinic.
- WebMD Editorial Contributors. (2020). "Herniated Disc Overview." WebMD.
- Sissons, C. (2021). "What to know about a herniated disc." Medical News Today.
- Performance Pain. (2021). "Herniated Disc Pain Relief." Performance Pain & Sports Medicine.
- Axion Spine & Neurosurgery. (2021). "Herniated Disc Treatment." Axion Spine & Neurosurgery.
- Spine-Health. (2020). "Pain Relief for a Herniated Disc." Spine-Health.
- ProHealth. (2020). "Prolotherapy for Herniated Discs." ProHealth.
- Cohen, S. P., & Raja, S. N. (2015). "Pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment of lumbar disk herniation." JAMA.