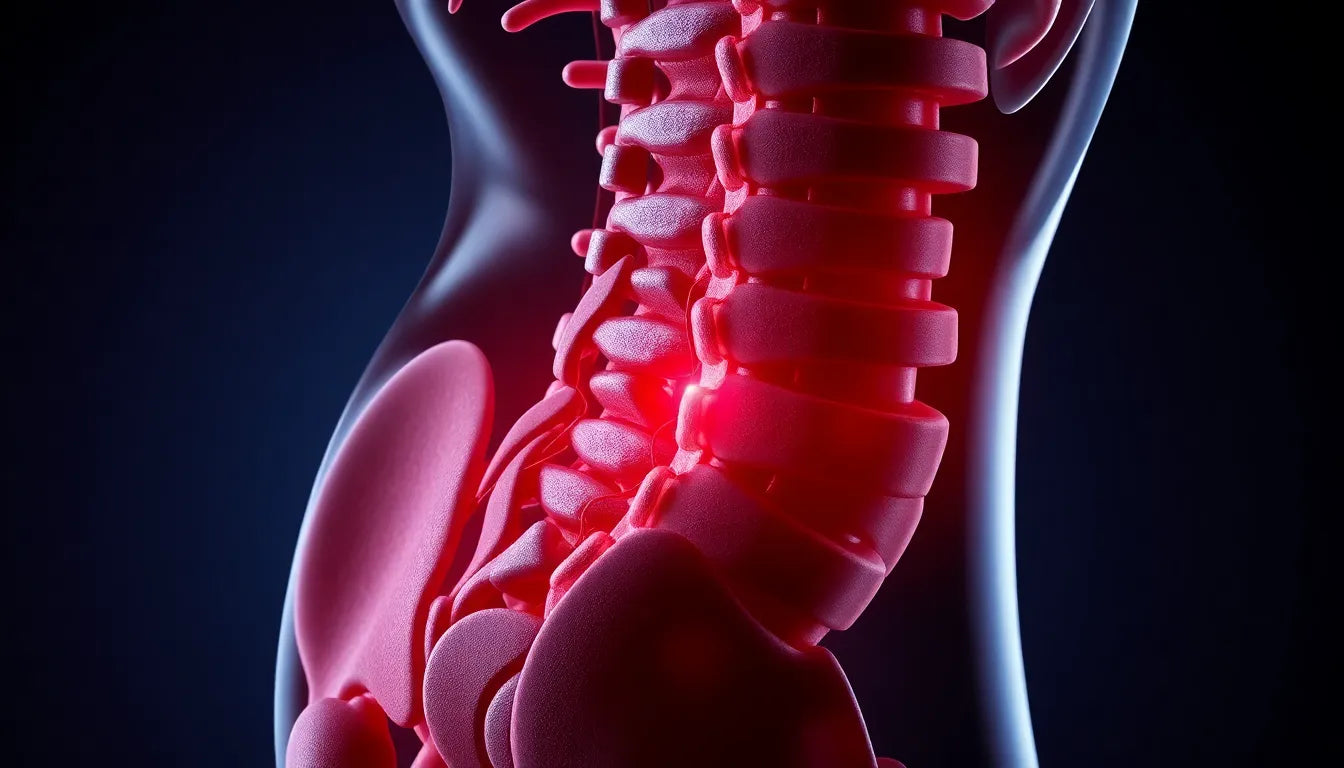
Experiencing lower back pain can be a common yet debilitating issue, often stemming from a herniated disc at the L4-L5 level of the lumbar spine. Understanding the anatomy of this region is crucial for grasping the impact of such conditions. The lumbar spine consists of five vertebrae, and the L4-L5 segment is particularly susceptible to disc herniation due to its role in supporting much of the body's weight and its involvement in a wide range of movements.
Disc herniation at the L4-L5 level is a prevalent condition that can significantly affect one's quality of life. This specific location is prone to wear and tear, making it a common site for herniation. When the disc material protrudes out of its normal boundary, it can compress nearby nerves, leading to pain, numbness, or even weakness in the lower back and legs. This type of pain can disrupt daily activities, hinder mobility, and reduce overall life satisfaction.
Exploring paths to relief
The journey to relief from L4-L5 herniated disc pain involves understanding the symptoms, exploring various treatment options, and making necessary lifestyle adjustments. Recognizing the symptoms early, such as persistent lower back pain, sciatica, or tingling sensations, is the first step in seeking appropriate care. Timely intervention can prevent the condition from worsening and improve recovery outcomes.
Treatment approaches for managing herniated disc pain at the L4-L5 level range from conservative methods like physical therapy and rest to more advanced options such as injection therapies or surgery. The goal is to manage pain effectively, restore function, and prevent recurrence. Lifestyle adjustments, including ergonomic improvements and regular exercise, play a vital role in supporting recovery and maintaining spinal health.
Reclaiming one's life from the grip of L4-L5 herniated disc pain is not just about addressing the physical symptoms but also about empowering individuals to live actively and pain-free. By understanding the condition and exploring comprehensive treatment strategies, it is possible to manage pain effectively and prevent future episodes, allowing individuals to regain control over their lives.
Understanding l4-l5 disc herniation in depth
The lumbar spine, a critical component of our skeletal structure, is designed to support significant body weight and facilitate a wide range of movements. At the heart of this structure lies the L4-L5 segment, which is particularly vulnerable to disc herniation. This condition occurs when the soft inner gel of a spinal disc pushes through a crack in its tougher exterior, often due to wear and tear or sudden injury. The L4-L5 level is a common site for such herniations because it endures substantial mechanical stress.
Several factors contribute to the development of a herniated disc at this level. Age-related degeneration is a primary cause, as the discs naturally lose water content and elasticity over time, making them more prone to rupture. Physical trauma, such as lifting heavy objects improperly or experiencing a fall, can also precipitate a herniation. Additionally, lifestyle factors like prolonged sitting, poor posture, and obesity increase the risk, as they place undue stress on the lumbar region. Genetic predisposition can further exacerbate susceptibility, with some individuals inheriting a tendency for disc degeneration.
Recognizing symptoms of l4-l5 herniation
The symptoms of an L4-L5 herniated disc can vary widely, depending on the severity and the extent of nerve involvement. Commonly, individuals experience lower back pain that may radiate down the leg, a condition known as sciatica. This occurs when the herniated disc compresses the sciatic nerve, leading to sharp, shooting pain along its path. Other symptoms include numbness, tingling, and muscle weakness in the legs, which can significantly impair mobility.
In severe cases, nerve compression can lead to more alarming symptoms such as loss of bladder or bowel control. This condition, known as cauda equina syndrome, requires immediate medical attention. Recognizing the severity of symptoms is crucial for determining the appropriate course of treatment. Below is a summary of symptoms and their potential severity:
| Symptom | Severity |
|---|---|
| Lower back pain | Mild to severe |
| Sciatica | Moderate to severe |
| Numbness/tingling | Mild to moderate |
| Weakness in legs | Moderate to severe |
| Loss of bladder/bowel control | Severe |
Exploring treatment options for l4-l5 herniated disc
Conservative treatments
Initial management of an L4-L5 herniated disc typically involves conservative treatments. Physical therapy is often recommended to strengthen the muscles supporting the spine, improve flexibility, and reduce pain. Rest and lifestyle modifications, such as adopting proper body mechanics and using ergonomic aids during daily activities, play a vital role in recovery. These measures aim to alleviate symptoms, improve function, and prevent further injury.
Injection therapies
For individuals who do not respond adequately to conservative measures, injection therapies may be considered. Epidural steroid injections can provide significant pain relief by reducing inflammation around the affected nerve root. These injections are typically used as part of a comprehensive treatment plan, offering temporary relief to facilitate participation in physical therapy and other rehabilitative activities.
Surgical options
When conservative treatments and injection therapies fail to provide sufficient relief, surgical intervention may be necessary. Surgery is generally considered a last resort and is recommended only when symptoms are severe or worsening. Common surgical procedures for herniated discs include discectomy, where the protruding disc material is removed to relieve nerve pressure, and spinal fusion, which stabilizes the spine by joining two or more vertebrae. It is crucial to consult with a spine specialist to determine the most appropriate surgical approach based on individual circumstances.
Recovery and long-term management of l4-l5 herniated disc
Recovering from an L4-L5 herniated disc involves a journey that varies for each individual, depending on the severity of the condition and the chosen treatment path. Conservative treatments, such as physical therapy and lifestyle modifications, often lead to significant improvement within six to twelve weeks. However, for those requiring surgical intervention, recovery may extend over several months, with gradual resumption of normal activities.
Long-term management is crucial in maintaining spinal health and preventing future issues. Incorporating ergonomic aids, such as supportive chairs and adjustable desks, can significantly enhance comfort and reduce strain during daily activities. Regular exercise, focusing on strengthening core muscles and improving flexibility, plays a vital role in sustaining recovery and minimizing the risk of recurrence.
Preventive measures and lifestyle adjustments
Preventing future occurrences of L4-L5 herniated disc pain involves adopting a proactive approach to spinal health. Regular physical activity, including exercises that strengthen the back and core muscles, is essential. Activities such as swimming, walking, and yoga can improve flexibility and support spinal alignment. Maintaining a healthy weight reduces the stress on the lumbar spine, further decreasing the risk of disc herniation.
Creating an ergonomic workspace is another critical preventive measure. Ensure that your workstation promotes good posture, with your computer screen at eye level and your chair supporting the natural curve of your spine. Taking regular breaks to stretch and move can prevent stiffness and reduce the cumulative strain on your back.
Frequently Asked Questions
What causes an L4-L5 herniated disc?
An L4-L5 herniated disc can result from several factors, including age-related degeneration, which causes discs to lose water content and elasticity. Physical trauma, such as improper lifting or falls, can also lead to herniation. Additionally, lifestyle factors like prolonged sitting, poor posture, and obesity increase the risk, as do genetic predispositions.
How long does it take to recover from an L4-L5 herniated disc?
Recovery times vary based on the severity of the herniation and the treatment approach. Most individuals experience significant relief within six to twelve weeks with conservative treatments like physical therapy. If surgery is required, recovery may take several months, with gradual improvement over time.
Can ergonomic aids help in managing L4-L5 herniated disc pain?
Yes, ergonomic aids can play a significant role in managing L4-L5 herniated disc pain. Using supportive chairs, adjustable desks, and proper body mechanics can alleviate stress on the spine, reduce pain, and support recovery. These aids help maintain good posture and prevent further injury.
What are the signs that I might need surgery for my herniated disc?
Surgery is typically considered when conservative treatments fail to alleviate symptoms or if there is significant nerve compression causing severe pain, weakness, or loss of bladder or bowel control. Consulting with a spine specialist is essential to determine the necessity and type of surgical intervention.
How can I prevent future herniated discs?
Preventive strategies focus on maintaining a healthy lifestyle and proper body mechanics. Regular exercise, weight management, and creating an ergonomic workspace are key. Additionally, practicing good posture and avoiding activities that strain the back can help prevent future herniated discs.
By understanding the recovery process and implementing preventive measures, individuals can find relief from L4-L5 herniated disc pain and reclaim their lives with confidence and comfort.
Sources
- Deuk Spine Institute. "Herniated Disc Symptoms and Treatments."
- Spine-health. "Lumbar Herniated Disc: Causes and Treatment Options."
- Mayo Clinic. "Herniated Disk: Symptoms and Causes."
- Johns Hopkins Medicine. "Herniated Disk: Overview and Treatment."
- Spine-health. "All About the L4-L5 Spinal Segment."
- Kreiner, D. S., et al. (2014). "An Evidence-Based Clinical Guideline for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Lumbar Disc Herniation with Radiculopathy." The Spine Journal.
- WebMD. "Herniated Disc: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment."
- Dr. Kevin Pauza. "Herniated Disc Treatment: Non-Surgical Options."