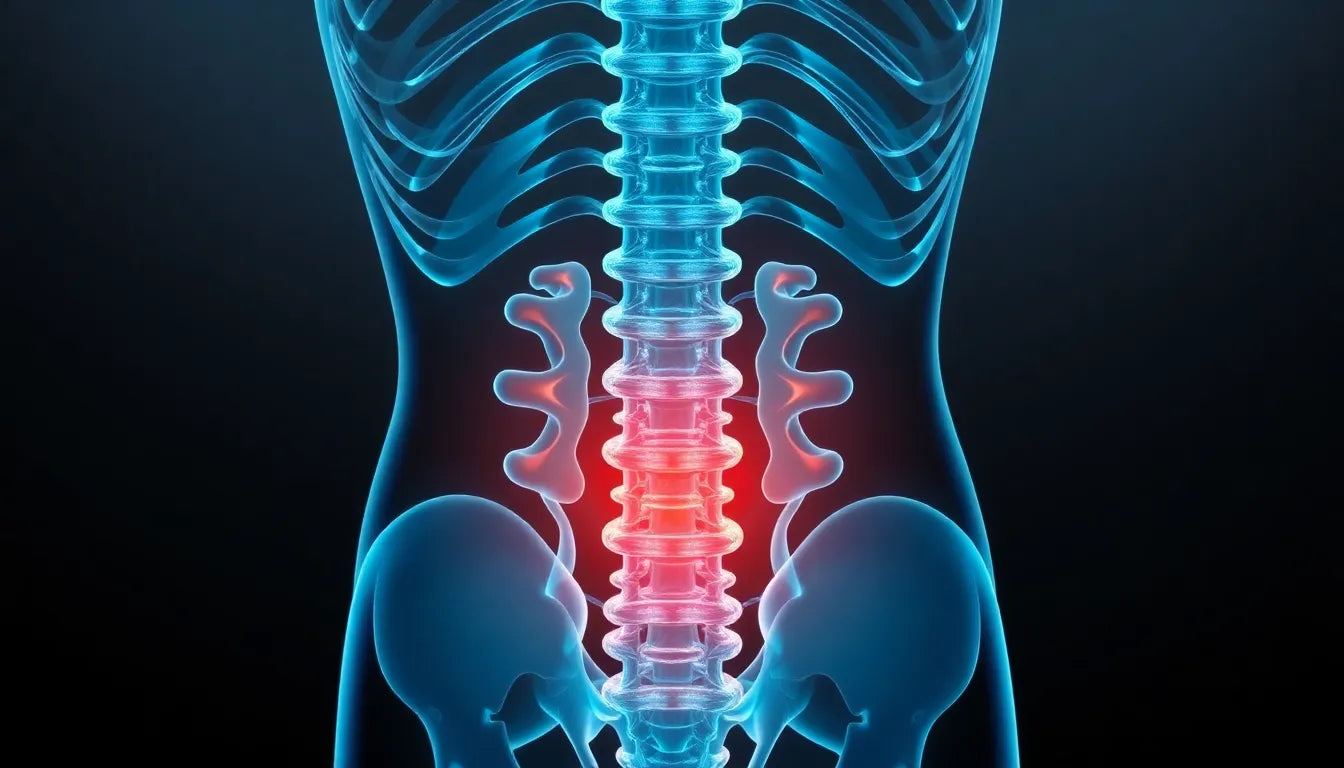
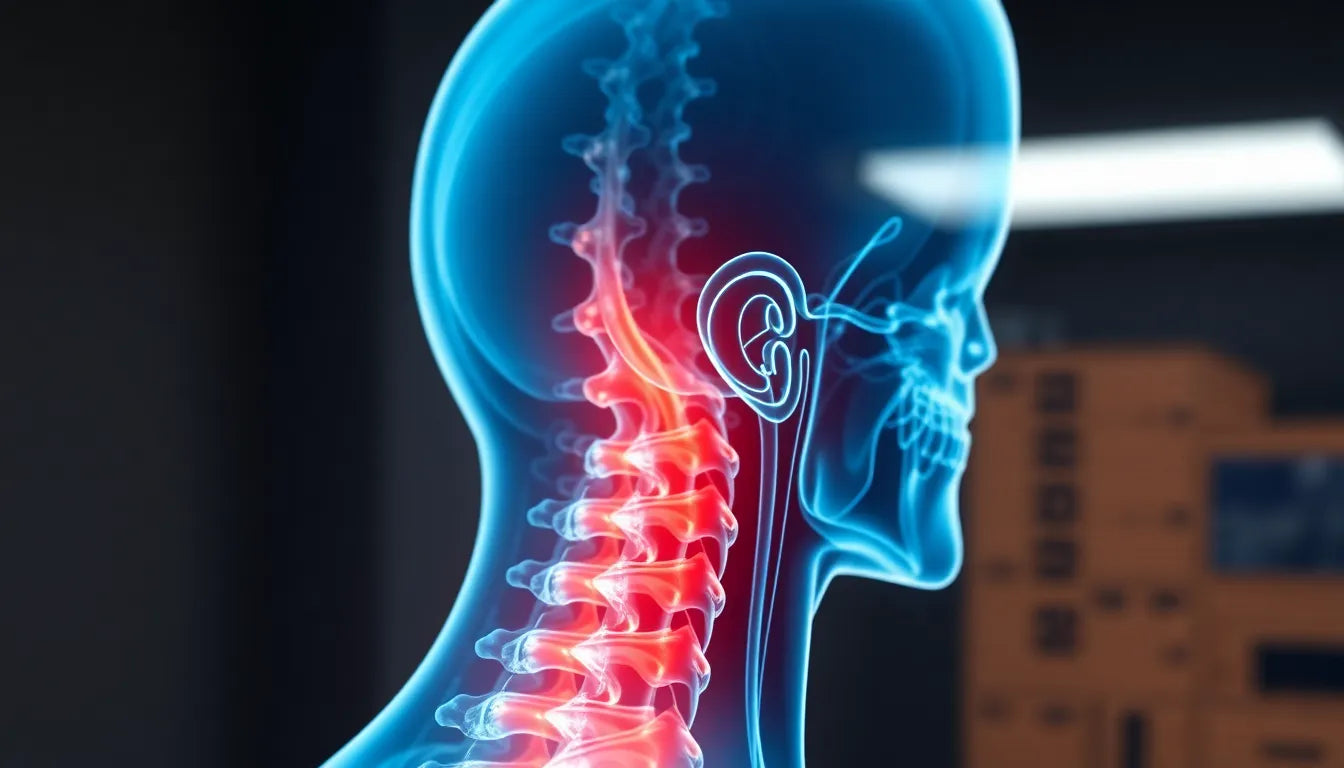
Living with spondylosis with radiculopathy can be a challenging experience, as it combines the effects of age-related spinal degeneration with nerve root compression. This condition is characterized by changes in the spine, known as spondylosis, which lead to radiculopathy—a condition where nerve roots are irritated or compressed. This can result in symptoms such as pain, numbness, tingling, or muscle weakness along the affected nerve pathway. The cervical (neck) and lumbosacral (lower back) regions are most commonly affected, making everyday activities difficult and impacting overall quality of life.
Understanding spondylosis with radiculopathy
Spondylosis refers to the degenerative changes that occur in the spine as we age. These changes can include the thinning of intervertebral discs and the formation of bone spurs, also known as osteophytes. When these alterations compress or irritate nearby nerve roots, radiculopathy occurs. This condition is prevalent among older adults, particularly affecting the cervical and lumbosacral regions, due to the high mobility and load-bearing functions of these parts of the spine.
The symptoms of spondylosis with radiculopathy can vary depending on the location of the affected nerve roots. For instance, cervical spondylosis may cause neck pain and stiffness, radiating pain into the shoulders and arms, and numbness or tingling in the hands. In severe cases, it can even lead to coordination difficulties or bladder and bowel dysfunction. Meanwhile, lumbosacral spondylosis often presents as lower back pain and sciatica, which is characterized by radiating pain down the leg, along with leg weakness and numbness.
The importance of early recognition and management
Early detection and intervention in cases of spondylosis with radiculopathy are crucial to prevent further progression and alleviate symptoms. Recognizing the signs early can lead to more effective management strategies, which can significantly improve a person's mobility and quality of life. This blog aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the symptoms, causes, and potential management strategies for those dealing with this condition.
By understanding the underlying mechanisms and symptoms of spondylosis with radiculopathy, individuals can seek appropriate medical advice and explore various treatment options. These may include conservative approaches like physical therapy and medications, as well as interventional treatments such as steroid injections. In certain cases, surgical interventions might be necessary to relieve persistent nerve compression.
In the following sections, we will delve deeper into the specific symptoms associated with cervical and lumbosacral spondylosis, explore the primary causes and risk factors, and discuss both conservative and surgical treatment options. Our goal is to equip you with the knowledge needed to make informed decisions about your health and find a path to pain-free living.
Detailed symptoms of spondylosis with radiculopathy
Understanding the specific symptoms of spondylosis with radiculopathy is crucial for early detection and effective management. The manifestation of symptoms largely depends on whether the cervical or lumbosacral region is affected. Each region presents distinct challenges and impacts on daily life.
Cervical spondylosis symptoms
Cervical spondylosis with radiculopathy primarily affects the neck and upper body. Common symptoms include persistent neck pain and stiffness, which can be exacerbated by movement or prolonged postures. Patients may experience radiating pain that extends into the shoulders and arms, often accompanied by numbness or tingling sensations in the arms and hands. In severe cases, the condition can lead to difficulties with coordination, affecting fine motor skills and balance. Bladder and bowel dysfunction may also occur, indicating significant nerve involvement and requiring immediate medical attention.
Lumbosacral spondylosis symptoms
Lumbosacral spondylosis with radiculopathy affects the lower back and can manifest as chronic lower back pain. A hallmark symptom is sciatica, where pain radiates down the leg, often accompanied by leg weakness and numbness. This can severely limit mobility and make activities such as walking or standing for extended periods challenging. Understanding these symptoms enables individuals to seek timely medical advice and explore appropriate treatment options.
Causes and risk factors
The development of spondylosis with radiculopathy is primarily attributed to age-related degeneration of the spine. Over time, the intervertebral discs lose moisture and elasticity, leading to disc degeneration. This process can result in the formation of bone spurs, or osteophytes, which may compress nearby nerve roots, causing radiculopathy.
Several factors can contribute to the onset and progression of this condition. Genetics play a significant role, as a family history of spinal problems can increase susceptibility. Previous spinal injuries, a sedentary lifestyle, and poor posture are also contributing factors. These elements can exacerbate spinal degeneration, leading to earlier onset and more severe symptoms.
Conservative treatment approaches
For many individuals, conservative treatment methods can effectively manage symptoms of spondylosis with radiculopathy. Non-surgical approaches are typically the first line of treatment, aiming to reduce pain and improve function without the need for invasive procedures.
Non-surgical methods
Physical therapy is a cornerstone of conservative treatment, focusing on exercises that enhance strength and flexibility. A tailored physical therapy program can help alleviate pressure on the affected nerve roots and improve overall spinal health. Medications such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and muscle relaxants can provide pain relief and reduce inflammation.
Lifestyle modifications are equally important in managing this condition. Weight management is crucial, as excess weight can place additional strain on the spine. Ergonomic adjustments in daily activities, such as using supportive chairs and maintaining proper posture, can prevent further strain on the spine and reduce symptoms.
Interventional treatments
For individuals who do not respond to initial conservative measures, interventional treatments may be considered. Steroid injections can be administered to reduce inflammation around the affected nerve roots, providing temporary relief from pain. Selective nerve root blocks are particularly useful in cervical cases, targeting specific nerves to alleviate symptoms.
These conservative and interventional approaches, when combined with lifestyle changes, can significantly improve quality of life for individuals with spondylosis with radiculopathy. By addressing both the symptoms and underlying causes, these strategies offer a comprehensive path to pain-free living.
Surgical interventions for severe cases
When conservative and interventional treatments do not provide sufficient relief, surgical options may be considered for individuals with spondylosis with radiculopathy. Surgery is typically reserved for severe cases where nerve compression has led to significant pain, weakness, or loss of function that impairs daily life. Common surgical procedures include discectomy, spinal fusion, and anterior cervical discectomy and fusion. These surgeries aim to relieve pressure on the nerve roots by removing or reshaping the affected structures.
While surgery can offer significant benefits, such as pain relief and improved mobility, it also carries risks, including infection, nerve damage, and complications related to anesthesia. It is crucial to have a thorough discussion with a healthcare provider to weigh the potential benefits and risks before proceeding with surgical intervention. Patients should consider all available information and explore how surgery fits into their overall treatment plan.
Ergonomic and lifestyle modifications for long-term relief
In addition to medical treatments, ergonomic and lifestyle modifications play a vital role in managing spondylosis with radiculopathy. Proper posture and an ergonomic workspace can significantly reduce strain on the spine, helping to alleviate symptoms and prevent further degeneration. It is essential to maintain a neutral spine position when sitting or standing and to use supportive furniture that promotes good posture.
Creating a spine-friendly environment at home and work involves using adjustable chairs with lumbar support, positioning computer screens at eye level, and taking regular breaks to stretch and move around. Incorporating daily exercises and stretches that focus on strengthening the core and improving flexibility can also help relieve pressure on the spine and enhance overall spinal health.
These lifestyle changes, combined with medical interventions, can provide a comprehensive approach to managing spondylosis with radiculopathy. By addressing both the physical and environmental factors contributing to the condition, individuals can improve their quality of life and find a path to pain-free living.
Frequently asked questions
What is the difference between spondylosis and radiculopathy?
Spondylosis refers to degenerative changes in the spine, such as disc thinning and bone spur formation, often due to aging. Radiculopathy, on the other hand, occurs when these changes lead to compression or irritation of the nerve roots, causing symptoms like pain, numbness, or weakness along the nerve pathway.
Can lifestyle changes really make a difference?
Yes, lifestyle changes can significantly impact the management of spondylosis with radiculopathy. Adopting ergonomic practices, engaging in regular exercise, and maintaining a healthy weight can reduce symptoms and prevent the progression of the condition.
When should I consider seeing a doctor?
You should consider seeing a doctor if you experience severe pain, numbness, or weakness, or if your symptoms interfere with daily activities. Early medical intervention can prevent further progression and improve your quality of life.
Are there any red flag symptoms to watch for?
Yes, certain symptoms, such as loss of bladder or bowel control and severe muscle weakness, are considered red flags. These symptoms require immediate medical attention as they may indicate significant nerve involvement.
How effective are surgical treatments for spondylosis with radiculopathy?
Surgical treatments can be effective for individuals who do not respond to conservative treatments. However, it is important to carefully consider the potential risks and benefits with your healthcare provider to determine if surgery is the right option for you.
Sources
- OWC Health. "Symptoms, causes, and treatments for lumbosacral spondylosis with radiculopathy."
- NIH/PMC. "Cervical spondylotic radiculopathy: diagnosis and nerve root block treatments."
- Frontiers in Surgery. "Surgical outcomes in cervical spondylosis with radiculopathy."
- Johns Hopkins Medicine. "General overview of radiculopathy."
- Cleveland Clinic. "Radiculopathy symptoms, causes, and when to seek care."
- Mayo Clinic. "Cervical spondylosis symptoms and serious complications."
- Penn Medicine. "Core symptoms of radiculopathy."