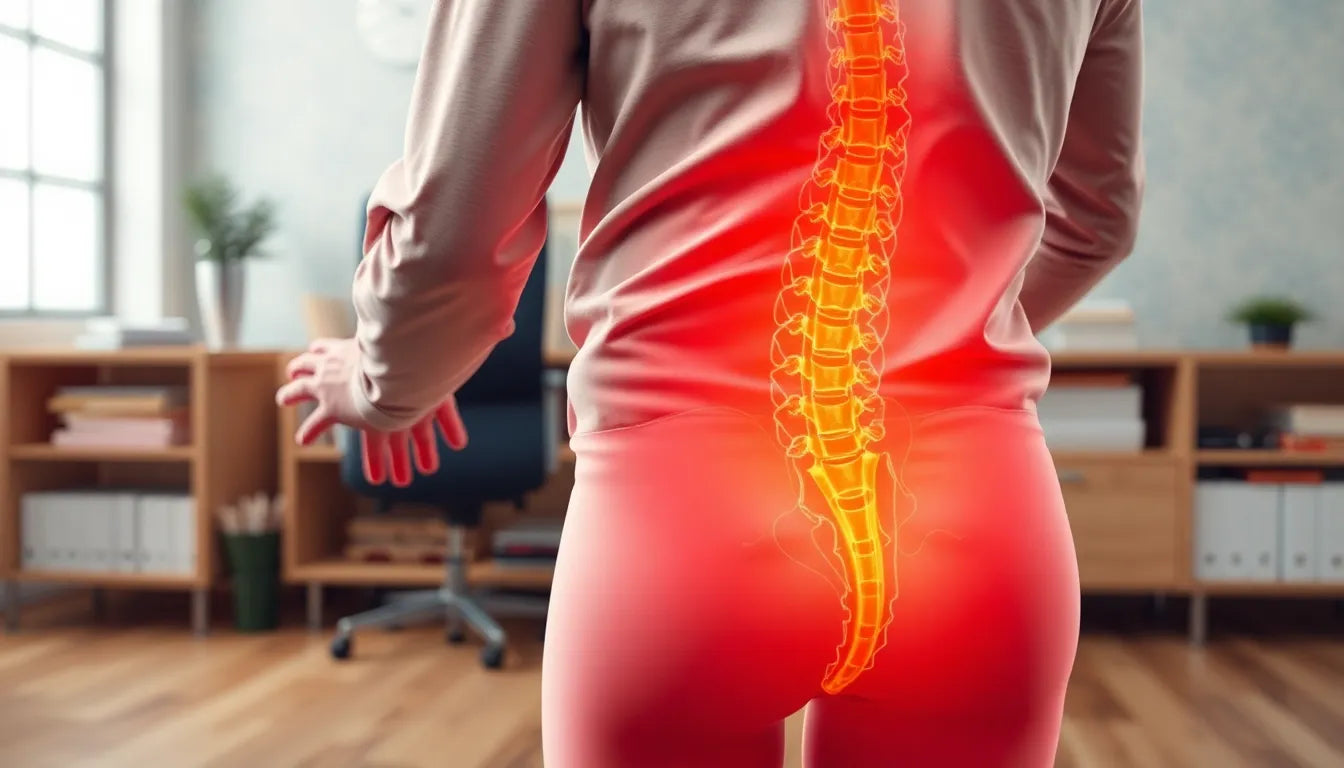
A herniated disc in the neck, also known as a cervical herniated disc, is a condition that arises when the inner gel-like substance of a spinal disc pushes through its tougher outer layer. This protrusion can irritate or compress nearby nerves, leading to a variety of symptoms. Understanding this condition is crucial, as the cervical spine plays a vital role in supporting the head and facilitating movements such as turning and bending.
the importance of early detection
Recognizing the signs of a herniated disc in the neck early on is vital for preventing further complications. Early detection allows for timely intervention, which can significantly reduce the risk of chronic pain or permanent nerve damage. When symptoms are identified and addressed promptly, individuals can explore a range of treatments that may alleviate discomfort and restore normal function.
commonality and concerns
Herniated discs are a prevalent source of neck pain, affecting a significant portion of the population at some point in their lives. The condition can be particularly concerning as it often interferes with daily activities, such as driving, working, and even sleeping. The impact on quality of life can be substantial, making it essential for individuals to be aware of the symptoms and seek medical advice if they suspect a herniated disc. By understanding the commonality and potential consequences of a herniated disc in the neck, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their health and well-being.
primary symptoms of a herniated disc in the neck
When it comes to identifying a herniated disc in the neck, several primary symptoms can serve as key indicators. Understanding these symptoms is crucial for early detection and effective management of the condition.
localized pain and tenderness
One of the most common symptoms is localized pain and tenderness in the neck area. This pain can vary in intensity, ranging from a dull ache to sharp, stabbing sensations. The discomfort often increases with certain movements or positions, such as turning the head or looking down for extended periods. This localized pain is a direct result of the disc pressing on nearby nerves, causing inflammation and irritation.
radiating pain
In many cases, the pain does not remain confined to the neck. Instead, it can radiate to other areas, such as the jaw, shoulders, arms, or even the hands. This radiating pain is typically due to nerve compression caused by the herniated disc. The pain may follow the path of the affected nerve, leading to discomfort that can be persistent or intermittent. It is important to note that this radiating pain can significantly impact daily activities, making it difficult to perform tasks that involve arm or shoulder movement.
nerve sensations
The presence of nerve sensations is another hallmark of a herniated disc in the neck. These sensations often manifest as numbness and tingling, commonly felt in the shoulders, arms, or fingers. Such sensations occur because the herniated disc exerts pressure on the nerves, disrupting normal nerve function. In some cases, individuals may also experience a burning sensation in the same areas, adding to the discomfort and indicating nerve irritation.
muscle weakness and spasms
Nerve compression from a herniated disc can lead to muscle weakness or spasms, particularly in the shoulders or arms. This weakness may make it challenging to perform everyday tasks that require lifting or holding objects. Additionally, involuntary muscle contractions, or spasms, can occur, further limiting mobility and causing pain. Recognizing these symptoms early is essential for preventing further muscle deterioration and maintaining strength and function.
emergency signs that require immediate attention
While many symptoms of a herniated disc in the neck can be managed with appropriate treatment, certain signs require immediate medical attention. These emergency symptoms suggest significant nerve involvement and potential damage.
difficulty urinating or loss of bladder/bowel control
If you experience difficulty urinating or notice a sudden loss of bladder or bowel control, it is crucial to seek emergency medical care. These symptoms may indicate severe nerve compression, which can lead to permanent damage if not addressed promptly. Early intervention is vital to prevent long-term complications and preserve nerve function.
saddle anesthesia
Saddle anesthesia refers to a loss of sensation in the inner thighs and buttocks. This symptom is a red flag for potential nerve damage and requires immediate evaluation by a healthcare professional. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are essential to prevent further nerve injury and ensure optimal recovery.
Understanding these primary and emergency symptoms of a herniated disc in the neck empowers individuals to take proactive steps in managing their health. Early recognition and intervention can significantly improve outcomes and enhance quality of life.
Causes and risk factors of a herniated disc in the neck
Understanding the causes and risk factors associated with a herniated disc in the neck is essential for prevention and management. Several factors can increase the likelihood of this condition, making it important to be aware of them.
Degenerative disc disease
One of the primary causes of a herniated disc is degenerative disc disease, a condition that results from age-related wear and tear on the spinal discs. As we age, the discs in the spine lose hydration and elasticity, making them more susceptible to herniation. This natural degeneration process can lead to the weakening of the disc's outer layer, allowing the inner gel-like core to protrude.
Injury or trauma
Sudden impacts or accidents can also cause a herniated disc in the neck. Activities such as car accidents, falls, or sports injuries may exert excessive force on the cervical spine, leading to disc herniation. Even minor injuries can have significant effects if the discs are already weakened due to degeneration.
Lifestyle factors
Poor posture, repetitive movements, and a sedentary lifestyle can contribute to the development of a herniated disc. Maintaining good posture and incorporating regular exercise can help reduce the risk. Activities that involve repetitive neck movements or prolonged periods of sitting can place additional stress on the cervical spine, increasing the likelihood of disc herniation.
When to seek medical help
Recognizing when to seek medical help for a herniated disc in the neck is crucial for effective treatment and recovery. If you experience persistent or worsening symptoms, it is important to consult a healthcare provider. Early diagnosis and intervention can prevent complications and improve outcomes.
Severe symptoms, such as difficulty urinating, loss of bladder or bowel control, or saddle anesthesia, require immediate medical attention. These signs may indicate significant nerve involvement and potential damage, necessitating prompt evaluation by a healthcare professional.
Treatment options for herniated discs in the neck
Treatment for a herniated disc in the neck varies depending on the severity of the condition and the individual's overall health. Both non-surgical and surgical options are available to address symptoms and promote healing.
Non-surgical treatments
Many cases of herniated discs can be managed with non-surgical treatments. Physical therapy is often recommended to strengthen neck muscles and improve flexibility. Medications, such as pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs, can help alleviate symptoms. Lifestyle modifications, including posture correction and activity adjustments, are also beneficial in managing the condition.
Surgical interventions
In some cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to relieve symptoms and prevent further complications. Common surgical procedures for a herniated disc in the neck include discectomy, where the herniated portion of the disc is removed, and spinal fusion, which stabilizes the spine by joining two or more vertebrae. Surgery is typically considered when conservative treatments fail to provide relief or when severe symptoms are present.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between a herniated disc and a bulging disc?
A herniated disc involves the rupture of the disc's outer layer, allowing the inner core to protrude, while a bulging disc means the disc protrudes without rupture.
Can a herniated disc in the neck heal on its own?
In some cases, symptoms of a herniated disc may improve with conservative treatment, but a medical evaluation is essential to determine the best course of action.
How is a herniated disc diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination, medical history review, and imaging tests such as MRI or CT scans to assess the extent of the herniation.
Are there exercises to help with a herniated disc in the neck?
Yes, specific exercises can strengthen neck muscles and improve flexibility. However, they should be performed under the guidance of a healthcare professional to ensure safety and effectiveness.
What lifestyle changes can aid recovery?
Maintaining good posture, staying active, and avoiding activities that strain the neck are beneficial lifestyle changes that can aid recovery from a herniated disc in the neck.
Sources
- Cascade Orthopedics & Sports Medicine Center. "Four Warning Signs of a Herniated Disc."
- SEMrush. "SERP Analysis: What It Is & How to Do It."
- WebMD. "What Is a Herniated Cervical Disk?"
- Rock Content. "The Ultimate Guide to SERP Analysis."
- Florida Surgery Consultants. "5 Common Symptoms of a Herniated Disc in the Neck."