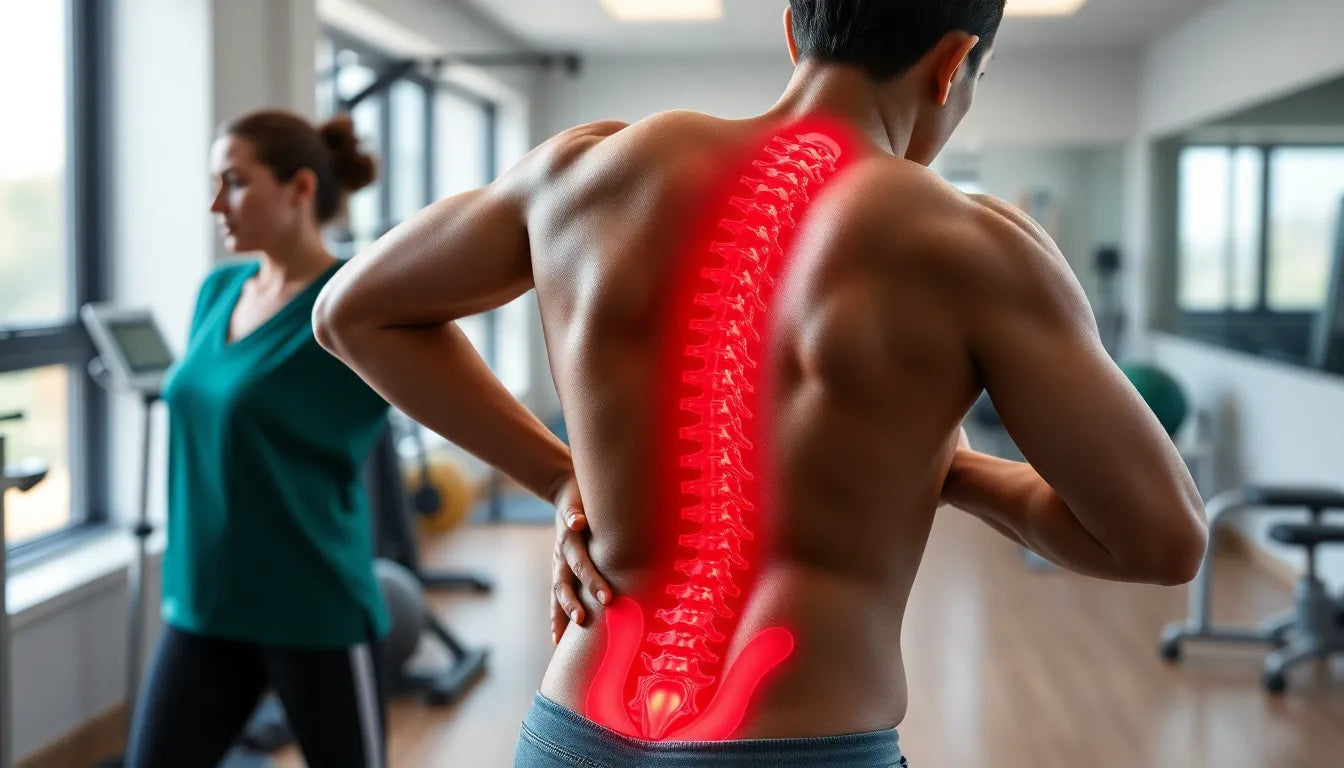
Are you experiencing unexplained lower back pain or shooting pain down your leg? It might be more than just a muscle strain. These symptoms could indicate a herniated disc in your lower back, a condition that is often misunderstood and misdiagnosed. Understanding the signs of a herniated disc is crucial for early intervention and preventing further complications.
A herniated disc, also known as a slipped or ruptured disc, occurs when the soft, gel-like center of an intervertebral disc pushes through a crack in the tougher exterior casing. This condition is most common in the lumbar region of the spine, which is the lower back area. The intervertebral discs act as cushions between the vertebrae, absorbing shock and allowing for flexibility in the spine. When a disc herniates, it can press on nearby nerves, leading to a variety of symptoms that can significantly impact your daily life.
Recognizing the symptoms of a herniated disc in the lower back is essential for seeking timely medical advice and avoiding potential complications. The most common symptom is lower back pain, which can range from a dull ache to sharp, throbbing pain. This discomfort may improve over time or persist intermittently, often being mistaken for other types of back pain.
Another hallmark symptom of a herniated disc is radiating pain, commonly known as sciatica. This condition manifests as sharp, shooting pain that travels from the lower back through the buttock and down one leg. Sciatica is typically caused by nerve compression and can severely affect mobility and quality of life.
In addition to pain, a herniated disc can cause numbness and tingling sensations, particularly in the leg or foot on the affected side. These changes in sensation can interfere with everyday activities and may be accompanied by muscle weakness. This weakness can make it difficult to walk or stand, and in some cases, result in a noticeable loss of reflexes, especially in the knee or ankle.
While these symptoms are common, it's important to be aware of more severe signs such as muscle spasms in the lower back and changes in bladder or bowel function. Although rare, these symptoms could indicate a serious condition known as cauda equina syndrome, which requires immediate medical attention.
Understanding the symptoms of a herniated disc in your lower back is the first step toward effective management and treatment. By recognizing these signs early, you can seek appropriate medical care and take proactive measures to protect your spine health.
Common symptoms of a herniated disc in the lower back
Understanding the full spectrum of symptoms associated with a herniated disc in the lower back is crucial for effective diagnosis and management. While lower back pain is often the first and most noticeable symptom, it is important to recognize other signs that could indicate the presence of a herniated disc.
Lower back pain
The pain stemming from a herniated disc can vary in intensity and character. It might start as a dull ache and progress to a sharp, throbbing pain. This discomfort can be persistent or intermittent, sometimes improving with rest but often exacerbated by certain movements or activities. It's not uncommon for this pain to be mistaken for other types of back pain, which can delay proper diagnosis and treatment.
Radiating pain or sciatica
Sciatica is one of the hallmark symptoms of a herniated disc in the lower back. This condition is characterized by sharp, shooting pain that travels from the lower back through the buttock and down one leg. The pain is typically caused by compression of the sciatic nerve, which can lead to significant discomfort and mobility issues. Patients often describe this pain as electric or burning, and it may worsen with prolonged sitting or standing.
Numbness and tingling
Alongside pain, a herniated disc can cause numbness and tingling sensations, primarily in the leg or foot on the affected side. This sensation change occurs due to nerve irritation or compression and can interfere with daily activities. Individuals might experience a pins-and-needles feeling or a complete loss of sensation in specific areas.
Muscle weakness
Muscle weakness is another common symptom that can significantly impact one's quality of life. This weakness often affects the leg or foot, making it difficult to walk, stand, or perform tasks that require stability and strength. In severe cases, muscle weakness can lead to a condition known as foot drop, where lifting the front part of the foot becomes challenging, increasing the risk of tripping.
Loss of reflexes
A herniated disc can also lead to a noticeable reduction in reflexes, particularly in the knee or ankle. This symptom is a result of nerve compression and can be a critical indicator for healthcare professionals when diagnosing the condition. Reflex changes are often assessed during a physical examination and can help confirm the presence of a herniated disc.
Muscle spasms
Muscle spasms in the lower back are another potential symptom of a herniated disc. These involuntary contractions can be painful and are often triggered by sudden movements or prolonged periods of inactivity. Muscle spasms can add to the overall discomfort and limit mobility, making daily activities more challenging.
Bladder or bowel changes
Although rare, changes in bladder or bowel function can occur with a herniated disc and may indicate a serious condition known as cauda equina syndrome. This syndrome is a medical emergency and requires immediate attention. Symptoms to watch for include difficulty urinating, loss of bowel control, or numbness in the groin or inner thighs. Prompt medical evaluation is crucial to prevent permanent damage.
Recognizing these symptoms and understanding their implications is vital for anyone experiencing lower back pain. Early detection and appropriate medical intervention can help manage the condition effectively, reducing the risk of long-term complications. If you suspect you may have a herniated disc, seeking a professional evaluation is the best course of action to ensure proper care and treatment.
Diagnostic and self-check information
Identifying the symptoms of a herniated disc in your lower back can be challenging, especially since they often overlap with other conditions. A simple self-assessment can be a helpful first step. Consider if you experience persistent lower back pain, radiating pain down one leg, numbness or tingling in your leg or foot, muscle weakness, or reduced reflexes. If these symptoms are present, it is crucial to seek a professional medical evaluation.
Medical professionals typically use diagnostic procedures such as physical exams and imaging tests like MRI to confirm a herniated disc. During a physical exam, a doctor may assess your reflexes, muscle strength, and ability to walk. These tests help determine the extent of nerve involvement and guide appropriate treatment plans.
Practical advice for managing symptoms
Managing the symptoms of a herniated disc at home involves a combination of lifestyle changes and ergonomic adjustments. Implementing ergonomic solutions, such as using supportive chairs and maintaining good posture, can alleviate pressure on the spine. Products from Anodyne, designed with ergonomic support in mind, can be particularly beneficial in managing back pain.
Incorporating regular, gentle exercise can also help maintain flexibility and strength in your back. Activities like walking, swimming, or yoga can support recovery and prevent further injury. Additionally, applying heat or cold packs to the affected area can provide temporary relief from pain and inflammation.
Conclusion
Recognizing and understanding the symptoms of a herniated disc in your lower back is essential for timely intervention and effective management. If you experience persistent pain, sciatica, or other related symptoms, consult a healthcare professional to explore diagnostic and treatment options. Proactive management, including ergonomic adjustments and lifestyle changes, can significantly improve your quality of life and reduce the risk of long-term complications.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can a herniated disc cause leg numbness?
Yes, a herniated disc can lead to leg numbness due to nerve compression. This compression affects the nerves responsible for sensation in the leg, often resulting in numbness or tingling.
When should I see a doctor for lower back pain?
It is advisable to see a doctor if your lower back pain persists, worsens, or is accompanied by symptoms such as numbness, muscle weakness, or changes in bladder or bowel function. These could indicate a more serious condition requiring medical attention.
What are the treatment options for a herniated disc?
Treatment for a herniated disc may include physical therapy, medications to relieve pain and inflammation, and lifestyle modifications. In some cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to relieve nerve compression and alleviate symptoms.
Is it possible to prevent a herniated disc?
While it may not be possible to prevent all cases of herniated discs, certain measures can reduce your risk. Maintaining a healthy weight, practicing proper lifting techniques, and using ergonomic supports can help protect your spine and prevent disc herniation.
Sources
- Mayo Clinic. "Herniated Disk: Symptoms and Causes."
- Cleveland Clinic. "Herniated Disc: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment."
- Johns Hopkins Medicine. "Herniated Disk: Overview and Symptoms."
- University of Maryland Medical Center. "Herniated Disc: Diagnosis and Treatment."
- OrthoInfo – AAOS. "Herniated Disc: Symptoms and Diagnosis."