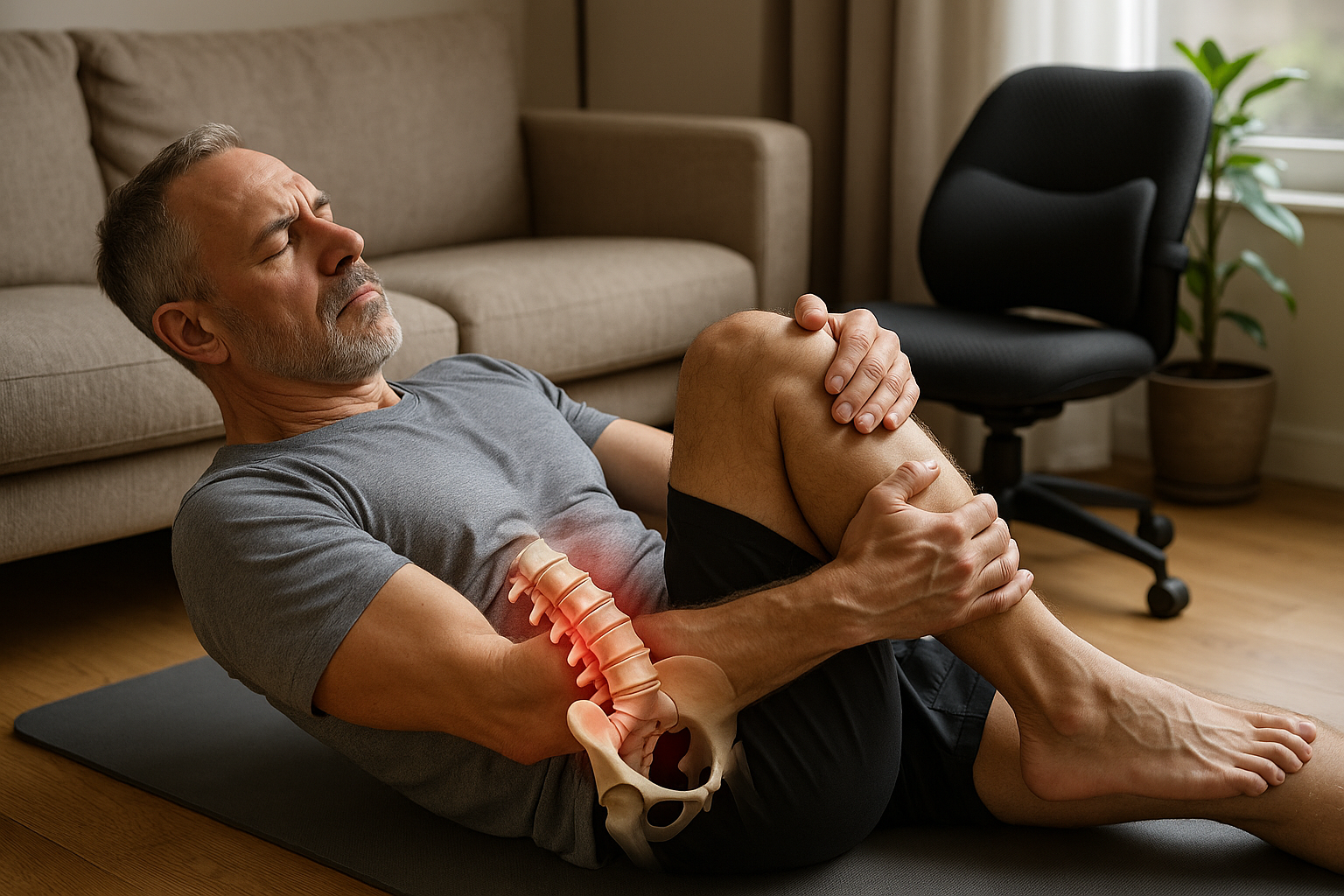
Back cramps, often referred to in medical terms as back spasms, are a common ailment that many individuals experience at some point in their lives. These cramps are characterized by sudden, involuntary tightening of the muscles in the back, which can lead to significant pain and stiffness. Although they can occur in any part of the back, it is important to differentiate between upper and lower back cramps, as they can have different causes and implications.
Upper back cramps typically involve the muscles in the shoulder and neck region, often resulting from poor posture or repetitive motions. On the other hand, lower back cramps are more prevalent and can be attributed to a variety of factors, including muscle strain from heavy lifting, awkward twisting, or prolonged periods of sitting. Regardless of their location, back cramps can disrupt daily activities and significantly affect one's quality of life.
Understanding the impact of back cramps
Back cramps can have a profound impact on an individual's ability to perform everyday tasks. The pain and stiffness associated with these cramps can make it difficult to move, bend, or even stand for extended periods. This can lead to a decrease in productivity at work, limitations in physical activities, and overall discomfort in daily life. Moreover, recurring back cramps can contribute to a cycle of pain and restricted movement, further exacerbating the issue.
Addressing back cramps effectively is crucial not only for immediate relief but also for long-term prevention. This blog aims to explore practical solutions that can help alleviate the discomfort of back cramps and prevent them from recurring. By understanding the underlying causes and implementing targeted strategies, individuals can take proactive steps towards managing and reducing the frequency of back cramps.
In the following sections, we will delve deeper into the common causes of back cramps, ranging from muscle strain and overuse to structural issues and lifestyle factors. We will also discuss immediate relief techniques and when back cramps might indicate a more serious underlying condition. Ultimately, our goal is to empower readers with the knowledge and tools needed to achieve lasting relief from back cramps and enhance their overall well-being.
Exploring the causes of back cramps
Understanding the root causes of back cramps is crucial for effective management and prevention. One of the most common triggers is muscle strain and overuse. Activities such as heavy lifting, sudden twisting motions, or engaging in sports can lead to micro-tears in the muscles and tendons, resulting in painful cramps. These injuries are often seen in individuals who push their physical limits without adequate preparation or conditioning.
Conversely, underuse of muscles and a weak core can also contribute to back cramps. Prolonged periods of sitting, poor posture, and lack of exercise can lead to muscle imbalances, making individuals more susceptible to cramps. A sedentary lifestyle can weaken the abdominal muscles, which play a crucial role in supporting the spine. This lack of support can increase the strain on back muscles, leading to cramps.
The role of posture and ergonomics
Posture and ergonomics are vital factors in preventing back cramps. Slouched sitting, awkward sleeping positions, and repetitive tasks at work can all contribute to muscle fatigue and cramps. Maintaining a neutral spine is essential to reduce the risk of cramps. This involves aligning the ears, shoulders, and hips in a straight line, whether sitting or standing. Ergonomic adjustments, such as using a chair with proper lumbar support or adjusting the height of a computer monitor, can help maintain this alignment and reduce muscle strain.
Structural issues, such as disc problems, arthritis, or spinal stenosis, can also exacerbate back cramps. These conditions can put additional pressure on the muscles and nerves, leading to increased tension and spasms. It's important to address these underlying issues with the help of a healthcare professional to prevent further complications.
Other contributing factors
Beyond physical causes, other factors can contribute to back cramps. Dehydration and low levels of essential minerals like potassium and calcium can affect muscle function and lead to cramps. Additionally, stress and tension patterns can cause muscles to tighten, resulting in spasms. Managing these factors through proper hydration, nutrition, and stress-relief techniques can help reduce the frequency and intensity of back cramps.
Recognizing when back cramps may indicate a serious issue
While many back cramps are benign and resolve with self-care, certain symptoms may indicate a more serious underlying condition. Persistent pain, neurological signs such as numbness or tingling, recent trauma, or systemic symptoms like fever or unexplained weight loss should prompt a consultation with a healthcare professional. These red flag symptoms could signify issues beyond simple muscle cramps, such as nerve compression or infection, requiring further evaluation and treatment.
Immediate relief techniques for back cramps
When a back cramp strikes, immediate relief can be achieved through several methods. Ice and heat therapy can be effective in managing pain and inflammation. Ice is typically recommended immediately after an injury to reduce swelling, while heat can be used later to relax and soothe tense muscles. Applying either ice or heat for 20-30 minutes at a time can provide significant relief.
Gentle movement and stretching are also beneficial for alleviating cramps. Engaging in light activities, such as walking or gentle stretching exercises, can help improve blood flow to the affected area and reduce muscle tension. Over-the-counter pain relief options, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), can also be used to manage pain and discomfort temporarily.
By understanding the causes and immediate relief techniques for back cramps, individuals can take proactive steps towards managing their symptoms and preventing future occurrences. In the next section, we will explore strategies for long-term prevention and answer common questions related to back cramps.

Lumbar support belt
Provides support and relief for the lower back, ideal for pain and tension during daily activities.
Preventing Future Back Cramps
Preventing back cramps involves a combination of ergonomic adjustments, strengthening exercises, and lifestyle changes. Implementing these strategies can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of cramps.
Ergonomic Strategies
Proper ergonomics at work and home can play a crucial role in preventing back cramps. Ensure your chair, desk, and monitor are set up to promote a neutral spine position. For instance, your monitor should be at eye level, and your feet should rest flat on the floor. When lifting objects, use your legs rather than your back, and keep the load close to your body to minimize strain.
Posture and Support
Maintaining a neutral spine is essential to reduce muscle strain. This involves keeping your ears, shoulders, and hips aligned. Posture-support garments and braces can provide feedback and support, helping you maintain proper alignment during daily activities.

Men's Posture Shirt™ - White
Posture shirt with patented NeuroBand™ for improved posture and muscle support.
Strength and Mobility
Incorporating exercises that strengthen the core, glutes, and back extensors can enhance your body's ability to support the spine. Simple routines, such as planks and bridges, can be effective in building strength and mobility, reducing the likelihood of cramps.
Lifestyle Adjustments
Hydration, nutrition, sleep, and stress management are vital components in preventing back cramps. Ensure you drink enough water and maintain a balanced diet rich in essential minerals like potassium and calcium. Prioritize quality sleep and incorporate stress-relief techniques, such as yoga or meditation, to help relax tense muscles.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why do I get back cramps at night?
Back cramps at night can be caused by poor sleeping posture, an unsupportive mattress, dehydration, or muscle fatigue from the day's activities. Ensuring proper hydration, using a supportive mattress, and adjusting your sleeping position can help alleviate nighttime cramps.
Are back cramps normal during pregnancy?
Yes, back cramps are common during pregnancy due to hormonal changes, weight gain, and altered posture. Engaging in gentle exercises, maintaining good posture, and using supportive garments can help manage these cramps.
Can anxiety cause back cramps?
Anxiety can lead to muscle tension and stress, which may contribute to back cramps. Managing anxiety through relaxation techniques, regular physical activity, and adequate rest can help reduce the occurrence of cramps.
Is it safe to exercise with back cramps?
It is generally safe to engage in light exercises and gentle stretching when experiencing back cramps, as these activities can improve blood flow and relieve tension. However, avoid intense workouts until the cramps subside. Always consult a healthcare professional if you're unsure about your exercise routine.
Källor
- National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases. "Back Pain."
- CHRISTUS Health. "How to Know if Back Pain is Muscular or Spinal."
- Summit Health. "When Should You Worry About Back Spasms: Signs and Solutions."
- Hinge Health. "Lower Back Spasms."
- Main Line Health. "Back Spasms."
- Mayo Clinic. "Back Pain - Symptoms and Causes."
- MyHealth.Alberta.ca. "Back Spasm: Care Instructions."
- Kaiser Permanente. "Back Spasm: Care Instructions."
- Cedars-Sinai. "Back Injuries."