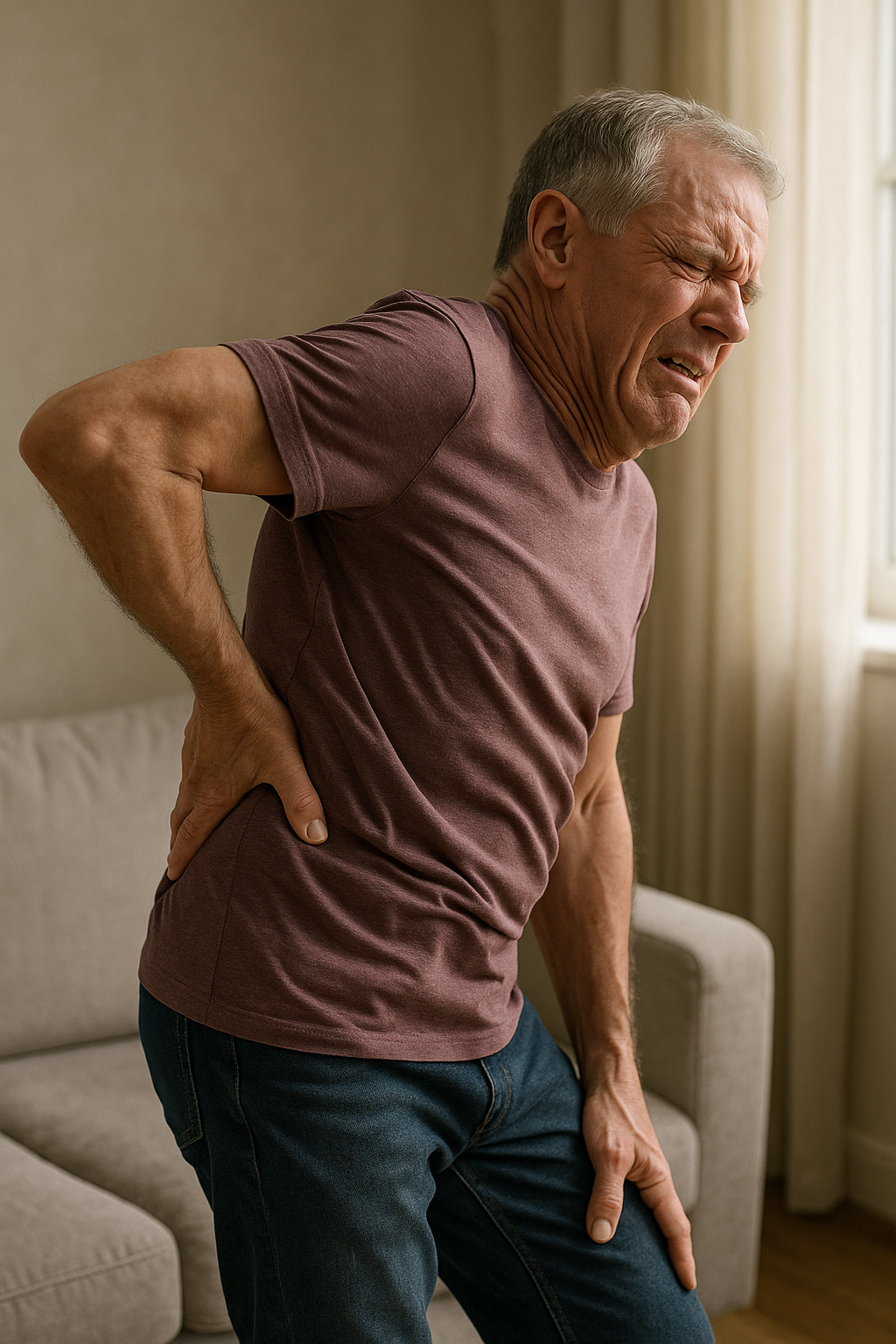
Facet syndrome, a condition impacting the facet joints situated between and behind adjacent vertebrae, is more prevalent than many realize. These small stabilizing joints play a crucial role in maintaining the spine's flexibility and stability. However, when they become inflamed or degenerate, they can lead to significant discomfort and pain, disrupting daily life. Understanding facet syndrome is essential for those experiencing unexplained back pain, as it often goes undiagnosed due to its subtle yet pervasive symptoms.
Common causes and risk factors
The causes of facet syndrome are varied, with osteoarthritis being one of the most common culprits. As the cartilage within the facet joints wears down, the bones can rub against each other, causing pain and inflammation. Obesity contributes to this condition by placing additional strain on the spine, accelerating joint wear and tear. Smoking, known for its detrimental effects on bone health, can also exacerbate the degeneration of facet joints.
Trauma, such as whiplash from a car accident or a fall, can lead to acute facet syndrome by causing direct injury to the joints. Additionally, as we age, the likelihood of developing facet syndrome increases. The facet joints are constantly in motion, making them susceptible to degenerative changes over time. Poor posture and certain occupational hazards, such as repetitive heavy lifting or prolonged sitting, can also increase the risk of developing this condition.
Symptoms and diagnosis
Recognizing the symptoms of facet syndrome is crucial for timely diagnosis and treatment. Common symptoms include localized pain in the spine, which can radiate to the shoulders, legs, and even cause headaches. This referred pain is often mistaken for other conditions, such as herniated discs or muscle strains, leading to misdiagnosis.
Diagnosing facet syndrome typically involves a combination of physical examinations and imaging studies. During a physical exam, a healthcare provider may perform specific movements to pinpoint the source of pain. Imaging techniques such as X-rays, CT scans, or MRIs are employed to visualize the joints and assess any degenerative changes or inflammation. These diagnostic tools are essential in confirming facet syndrome and ruling out other potential causes of back pain.
Understanding facet syndrome's impact on daily life underscores the importance of seeking medical advice if you experience persistent back pain. Early diagnosis and intervention can help manage symptoms effectively, improving quality of life and preventing further joint damage. As we delve deeper into this condition, we will explore the various treatment options available to alleviate discomfort and restore mobility.
Detailed exploration of facet syndrome
Facet syndrome, while often overshadowed by more commonly discussed spinal issues, plays a significant role in spine health and functionality. The facet joints, small yet pivotal components of the spine, are integral to maintaining its stability and flexibility. These joints are located between and behind adjacent vertebrae, allowing for smooth movement and providing structural support. When facet syndrome develops, these joints undergo degenerative changes, often resulting in the formation of bone spurs and thickening of the ligaments. These pathological changes can lead to a narrowing of the space where nerves exit the spine, contributing to pain and discomfort.
The neurological aspect of facet syndrome is particularly notable. As the condition progresses, the nerves surrounding the facet joints become irritated, transmitting pain signals to various parts of the body. This pain can be diffuse and severe, often radiating to areas such as the shoulders, arms, legs, and even causing headaches. Understanding the anatomical and pathological nuances of facet syndrome is crucial for comprehending its impact on daily life and the importance of timely intervention.
Treatment options and approaches
Conservative treatments for facet syndrome
Managing facet syndrome often begins with conservative treatment approaches aimed at alleviating pain and improving function. Self-care strategies, such as applying heat or cold to the affected area, can provide immediate relief. Heat therapy boosts circulation and relaxes tense muscles, while cold therapy helps reduce swelling by constricting blood vessels. Over-the-counter medications like NSAIDs can be effective in managing inflammation and pain, while muscle relaxants and antidepressants may be prescribed to address muscle spasms and chronic pain, respectively.
Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) therapy is another non-invasive option that has gained popularity for its effectiveness in pain management. By delivering mild electrical impulses to the skin, TENS therapy can help disrupt pain signals and provide relief. Lifestyle modifications, such as weight loss and ergonomic adjustments, play a vital role in reducing strain on the spine and preventing further joint degeneration.
Interventional therapies for enhanced relief
For individuals whose symptoms persist despite conservative measures, interventional therapies offer more targeted relief. Facet joint injections, which involve injecting a corticosteroid directly into the affected joint, can provide significant pain relief by reducing inflammation. Medial branch blocks, another injection therapy, target the nerves that transmit pain signals from the facet joints, offering diagnostic and therapeutic benefits.
Radiofrequency ablation is an advanced technique that uses heat to disrupt nerve function, providing long-term pain relief for those with chronic facet syndrome. Combining multiple modalities, such as injections and physical therapy, can enhance treatment effectiveness and improve patient outcomes.
Physical therapy and self-management strategies
The role of physical therapy in managing facet syndrome
Physical therapy is a cornerstone of facet syndrome management, offering personalized exercise programs to strengthen the muscles supporting the spine. Specific exercises, such as trunk stabilization and flexibility routines, can reduce pain and improve mobility. Research supports the combination of trunk exercises with spinal manipulation therapy (SMT) or NSAID therapy, highlighting the benefits of a multimodal approach.

Women's Posture Shirt™ - Black
Patenteret trøje, der aktiverer muskler, afhjælper smerter og forbedrer holdningen til hverdag og træning.
At-home treatment strategies
In addition to professional interventions, practical at-home treatments can complement medical care. Heat and cold therapy, as previously mentioned, are accessible and effective methods for managing pain. Incorporating ergonomic aids, such as lumbar support cushions and adjustable chairs, can further alleviate strain on the spine during daily activities.

Lumbar support belt
Justerbart rygbælte til støtte, smertelindring og aflastning af lænden.
By understanding the comprehensive treatment landscape for facet syndrome, individuals can make informed decisions about their care, optimizing their quality of life and minimizing the condition's impact on daily activities. As we continue to explore this condition, we will delve into long-term management strategies and preventive measures that can further enhance well-being.
Long-term management and lifestyle integration
Managing facet syndrome over the long term requires a comprehensive approach that integrates medical treatments with lifestyle modifications. Chronic management strategies focus on maintaining spine health and preventing further degeneration. Regular physical activity, tailored to individual capabilities, can help maintain flexibility and strengthen the muscles supporting the spine. Incorporating ergonomic aids, such as lumbar support cushions and adjustable workstations, can significantly reduce strain during everyday activities and support long-term spine health.
Additionally, adopting a healthy diet and maintaining a healthy weight are crucial in minimizing stress on the spine. Weight management reduces the load on facet joints, slowing down the degenerative process. Consistent follow-ups with healthcare providers ensure that any changes in symptoms are promptly addressed, allowing for adjustments in treatment plans as needed.
Occupational considerations and preventive measures
Certain professions, such as those involving heavy lifting, prolonged sitting, or repetitive motions, place individuals at a higher risk for developing facet syndrome. Implementing preventive measures in the workplace is essential to mitigate these risks. Ergonomic assessments can identify areas for improvement, such as workstation adjustments or the introduction of posture-correcting devices. Encouraging regular breaks and promoting exercises that target spinal health can further reduce the likelihood of facet syndrome developing or worsening.
Employers can play a role by providing ergonomic training and resources, ensuring that employees are equipped with the knowledge and tools to protect their spine health. By prioritizing ergonomics and preventive measures, both individuals and organizations can contribute to a healthier, more productive work environment.
Conclusion
Facet syndrome, with its potential to disrupt daily life, underscores the importance of a holistic treatment approach. By understanding the condition and exploring various treatment options, individuals can manage symptoms effectively and improve their quality of life. Ergonomic solutions, integrated with medical treatments, offer a pathway to enhanced comfort and functionality. As awareness of facet syndrome grows, so does the potential for individuals to take proactive steps in managing their spine health, ensuring long-term well-being and vitality.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is facet syndrome?
Facet syndrome is a condition affecting the facet joints in the spine, often leading to pain and discomfort due to inflammation or degeneration of these joints.
What are the main symptoms of facet syndrome?
Symptoms include referred pain that can radiate to the shoulders or legs, headaches, and localized pain in the spine.
How is facet syndrome diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves physical examinations and imaging studies, such as X-rays or MRIs, to assess the condition of the facet joints and rule out other causes of back pain.
What are the treatment options for facet syndrome?
Treatment ranges from conservative approaches like medication and physical therapy to interventional therapies such as injections and radiofrequency ablation.
Can ergonomic aids help with facet syndrome?
Yes, ergonomic aids can support posture correction and reduce strain on the spine, complementing medical treatments and contributing to better outcomes.
Källor
- Atlantic Spine Center. "Facet Joint Syndrome."
- Columna. "Facet Joint Syndrome: Definition, Causes, and Treatment."
- Physio-pedia. "Facet Joint Syndrome."
- Avicenna Klinik. "Facet Syndrome (Facet Joint Arthrosis)."
- Weill Cornell Medicine. "Symptoms of Facet Syndrome."
- SingHealth. "Facet Joint Syndrome Treatment."
- UCHealth. "Facet Joint Syndrome."
- NCBI. "Facet Joint Syndrome."
- SCOS. "Telltale Signs of Facet Syndrome: Back/Neck Pain."
- Spine-health. "Symptoms and Diagnosis of Facet Joint Disorders."
- Synergy Spine. "Facet Syndrome: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment."
- New York City Spine. "Overcoming the Symptoms of Facet Joint Disorder."
- Dr. Tony Mork. "What is Facet Joint Syndrome?"
- Sciatica.com. "Facet Joint Syndrome."
- Cedars-Sinai. "Facet Joint Syndrome."