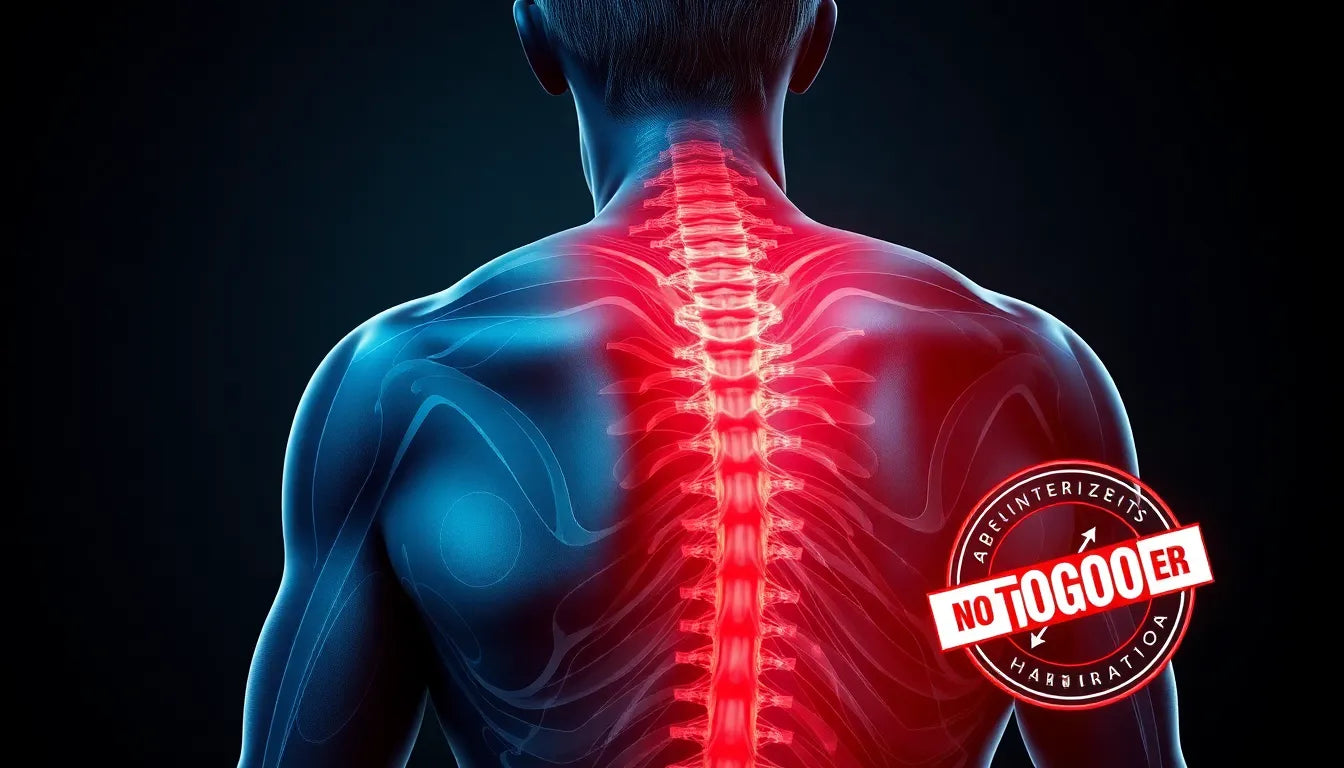
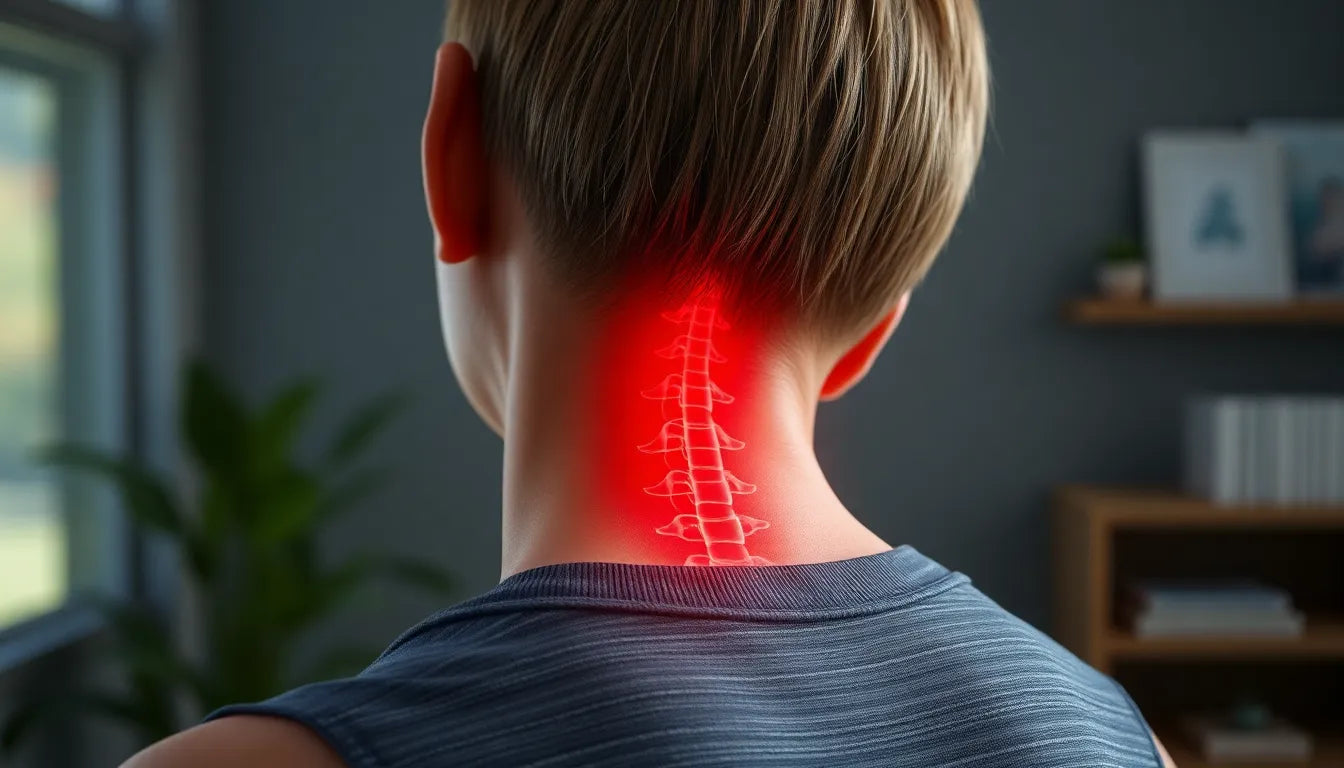
Experiencing discomfort in your neck can be more than just a minor inconvenience—it might be a sign of a pinched nerve, medically known as cervical radiculopathy. This condition occurs when one of the nerves in your neck is compressed or irritated, often resulting from common causes like herniated discs, bone spurs, or age-related degenerative changes in the spine. These issues can lead to significant pain and discomfort, affecting your daily activities and quality of life.
Understanding a pinched nerve in the neck
A pinched nerve in the neck is a prevalent condition, impacting a significant number of individuals at some point in their lives. The cervical spine, which consists of the first seven vertebrae in the neck, houses numerous nerves that extend to your shoulders, arms, and hands. When these nerves are compressed, it can lead to a range of symptoms, including pain, tingling, or numbness in these areas. The causes of such compression are varied but often include herniated discs, where the inner gel-like core of a disc protrudes outward, or bone spurs, which are bony projections that develop along the edges of bones.
As we age, our bodies undergo various degenerative changes that can affect the spine, making older adults more susceptible to developing a pinched nerve. This condition can severely impact one’s ability to perform everyday tasks, from working at a computer to lifting objects, and can even disrupt sleep due to pain.
Why addressing it matters
Early recognition and management of a pinched nerve in the neck are crucial to prevent the symptoms from worsening. Ignoring the pain or delaying treatment can lead to more severe complications, such as chronic pain or permanent nerve damage. Therefore, understanding the importance of addressing this issue promptly is vital for maintaining your overall health and well-being.
This blog post aims to explore both conservative and advanced treatment options available for those suffering from a pinched nerve in the neck. By identifying and implementing the right strategies, you can find relief and regain control over your daily life. Whether you're dealing with mild discomfort or more severe symptoms, understanding your condition and knowing the available options can empower you to make informed decisions about your health.
Symptoms and diagnosis of a pinched nerve in the neck
Recognizing the symptoms of a pinched nerve in the neck is the first step toward effective management and relief. Commonly, individuals experience neck pain that may radiate down into the shoulders, arms, and hands. Other symptoms include numbness or tingling sensations in these areas, weakness in the muscles of the shoulders, arms, or hands, and a noticeable reduction in sensation. These symptoms can intensify with certain neck movements, making daily tasks even more challenging.
Diagnosing a pinched nerve typically begins with a thorough physical examination and a detailed medical history review. During the examination, a healthcare professional may assess your neck's range of motion and check for any muscle weakness or sensory changes. If necessary, imaging tests such as an MRI or X-ray may be recommended to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other serious conditions. These diagnostic tools help visualize the cervical spine's structure, identifying any nerve compression due to herniated discs or bone spurs.
Conservative treatment options for neck pain relief
Addressing a pinched nerve in the neck often begins with conservative treatment options that aim to alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life without invasive procedures.
Rest and activity modification
Initially, rest is crucial to prevent further irritation of the affected nerve. Avoiding activities that exacerbate symptoms, such as heavy lifting or repetitive neck motions, can significantly reduce pain and discomfort. Adjusting your daily routine to minimize strain on the neck can aid in recovery.
Medications to alleviate pain
Over-the-counter medications, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen or naproxen, can help reduce inflammation and relieve pain. Acetaminophen is another option for pain management. In some cases, doctors may prescribe corticosteroids, anti-seizure medications like gabapentin, or certain antidepressants to manage nerve pain effectively.
Physical therapy for strengthening and flexibility
Physical therapy plays a vital role in the conservative management of a pinched nerve. A physical therapist can guide you through exercises and stretches designed to relieve pressure on the nerve, restore motion, and build strength in the neck and surrounding muscles. This approach not only helps alleviate symptoms but also prevents future occurrences.

Men's Posture Shirt™ - White
Patented shirt activates muscles & relieves neck, back and shoulder pain.

Women's Posture Shirt™ - Black
Neuroband™ technology shirt for better posture and documented relief of pain.
Immobilization with cervical collars
Using a soft cervical collar or brace to limit neck movement can provide temporary relief by reducing nerve irritation. However, these devices should only be used for short periods, as prolonged use can weaken neck muscles and hinder recovery.
Heat and cold therapy
Applying ice packs during the initial stages can help reduce swelling and numb acute pain. As the condition improves, heat therapy using warm compresses or heating pads can relax tense muscles and promote healing by increasing blood flow to the affected area.
Massage and home care strategies
Therapeutic massage can alleviate muscle tension and improve circulation, providing relief from pain. However, it's essential to avoid aggressive manipulation that might worsen symptoms. Incorporating self-management strategies, such as maintaining good posture, being aware of body positioning, and performing gentle stretching exercises, can significantly contribute to long-term relief and prevention.
By understanding and implementing these conservative treatment options, individuals can manage their symptoms effectively and reduce the impact of a pinched nerve in the neck on their daily lives. In cases where symptoms persist despite these measures, further evaluation and advanced treatment options may be necessary.
Advanced treatment options for a pinched nerve in the neck
When conservative treatments do not provide sufficient relief, advanced options may be considered to address persistent symptoms of a pinched nerve in the neck. These methods aim to reduce inflammation and relieve pressure on the affected nerves.
Epidural injections
Epidural steroid injections can be a viable option for those experiencing persistent pain that does not respond to initial treatments. These injections deliver corticosteroids directly into the epidural space around the spinal cord, reducing inflammation and alleviating pain. This procedure is typically performed under imaging guidance to ensure accuracy and is often used in conjunction with physical therapy for optimal results.
Surgical interventions
Surgery is generally considered a last resort for severe cases of cervical radiculopathy, particularly when symptoms are unresponsive to conservative treatments or when neurological deficits are present. Common surgical procedures include:
- Anterior cervical discectomy and fusion (ACDF): This procedure involves removing the herniated or damaged disc and fusing the adjacent vertebrae to stabilize the spine.
- Artificial disc replacement: In this surgery, the damaged disc is replaced with an artificial one, preserving more natural movement compared to fusion.
- Posterior spinal decompression: This involves relieving pressure on the spinal cord and nerves from the back of the spine, often used when multiple levels are affected.
Surgical options are tailored to the individual's specific condition and overall health, with the goal of relieving symptoms and improving quality of life.
Recovery and prognosis
The prognosis for a pinched nerve in the neck is generally favorable, with many individuals experiencing significant improvement through non-surgical treatments. Conservative management, including physical therapy and lifestyle adjustments, can effectively alleviate symptoms and prevent recurrence. Surgery, though rare, tends to have positive outcomes for those requiring it, with most patients experiencing relief from pain and a return to normal activities.
Frequently asked questions
What is a pinched nerve in the neck?
A pinched nerve in the neck, medically known as cervical radiculopathy, occurs when one of the nerves in the cervical spine is compressed, leading to pain and other symptoms in the neck, shoulders, and arms.
What are the symptoms of a pinched nerve in the neck?
Symptoms often include neck pain, numbness or tingling in the arms and hands, weakness in the shoulders, arms, or hands, and reduced sensation. These symptoms may worsen with certain neck movements.
How is a pinched nerve diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination, review of symptoms, and may include imaging tests such as MRI or X-ray to confirm nerve compression and rule out other conditions.
What are the best home remedies for a pinched nerve in the neck?
Effective home remedies include rest, ice and heat therapy, gentle stretching exercises, and maintaining proper posture to alleviate symptoms and promote healing.
When should I see a doctor for a pinched nerve?
It is advisable to seek medical attention if symptoms persist, worsen, or are accompanied by significant neurological deficits, such as severe weakness or loss of sensation.
Is surgery necessary for a pinched nerve in the neck?
Surgery is rarely necessary and is typically reserved for severe cases that do not respond to conservative treatments or when there are serious neurological symptoms present.
Källor
- Cleveland Clinic. (n.d.). "Cervical Radiculopathy (Pinched Nerve)."
- Mayo Clinic. (n.d.). "Pinched Nerve: Diagnosis & Treatment."
- Cleveland Clinic. (n.d.). "Pinched Nerves."
- Dignity Health. (n.d.). "Pinched Nerve: Diagnosis and Treatment."
- Medical News Today. (n.d.). "Pinched Nerve in Neck."
- Mayo Clinic. (n.d.). "Pinched Nerve: Symptoms & Causes."
- OrthoVirginia. (n.d.). "How to Manage Pinched Nerves in the Neck."
- Harvard Health Publishing. (n.d.). "Treating a Pinched Nerve."
- American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. (n.d.). "Cervical Radiculopathy (Pinched Nerve)."
- UCHealth. (n.d.). "Pinched Nerve."
- Sciatica.com. (n.d.). "9 Treatment Options for Pinched Nerves in the Back and Neck."
- MyHealth.Alberta.ca. (n.d.). "Pinched Nerve."