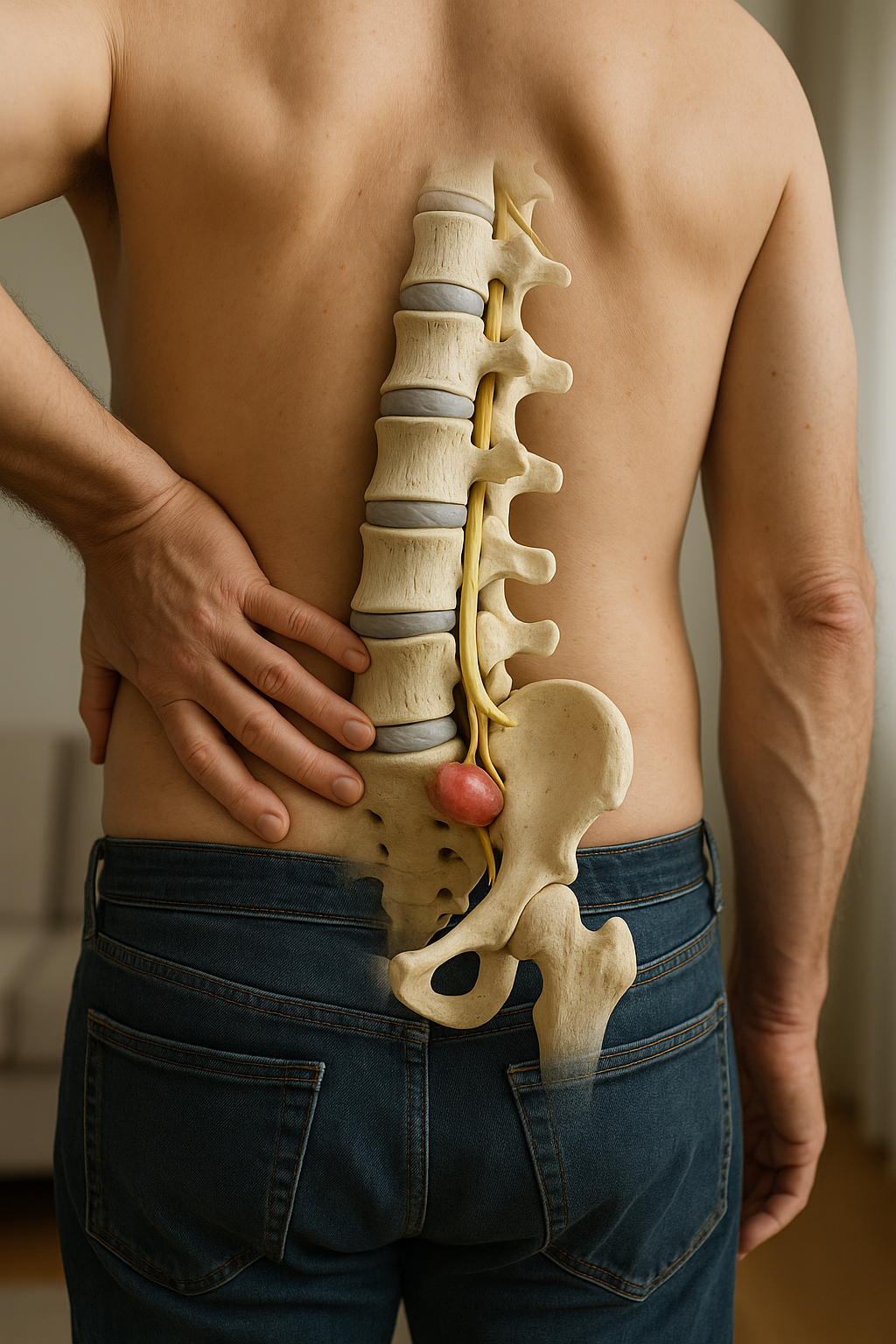
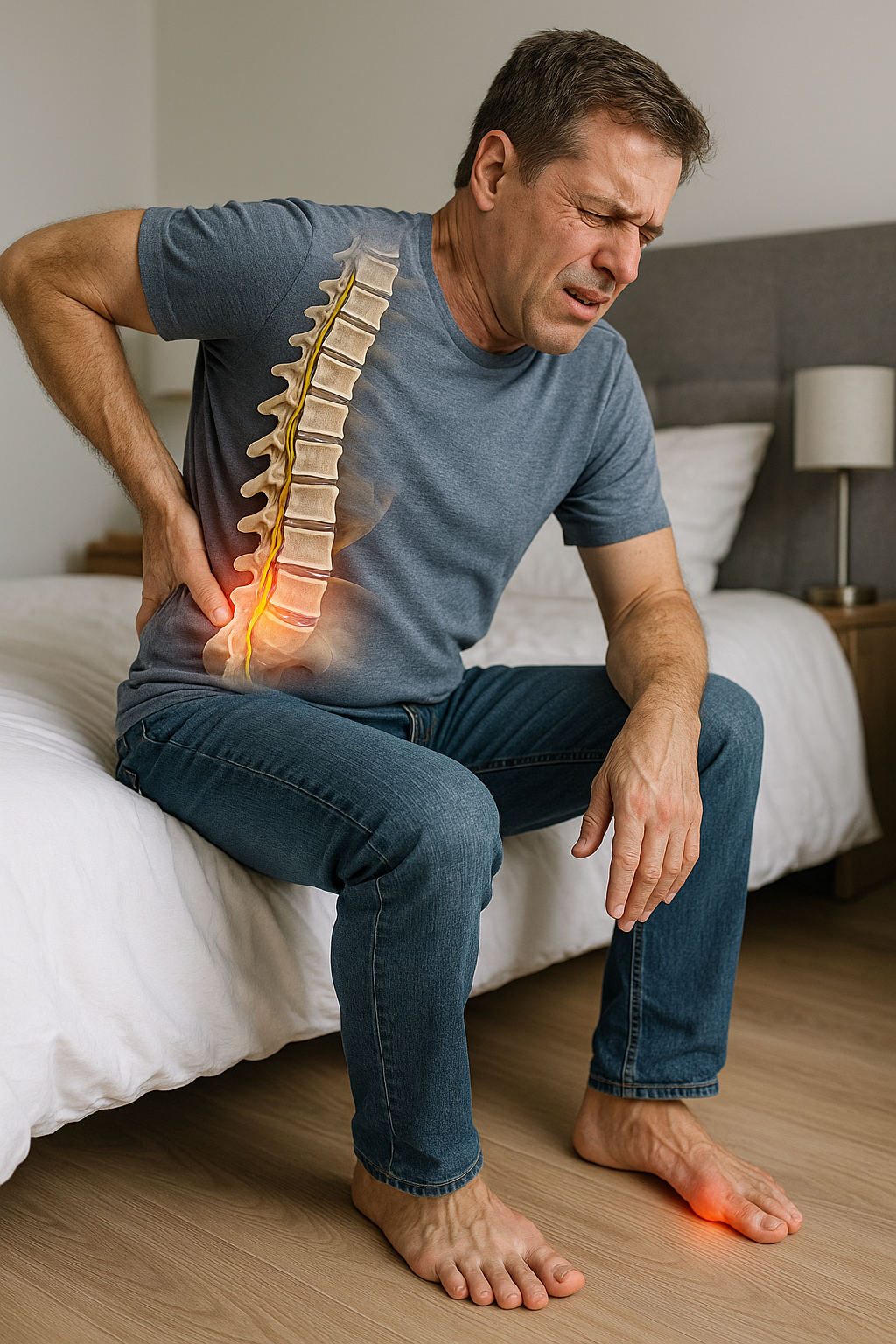
Lower back and hip pain is a pervasive issue that affects millions of individuals around the globe. This discomfort can significantly disrupt daily activities and diminish overall quality of life. Whether it's the result of long hours spent at a desk, strenuous physical activity, or simply the wear and tear of everyday life, understanding the underlying causes is crucial for effective management and relief.
Understanding the prevalence and impact
The prevalence of lower back and hip pain is staggering, with studies indicating that a substantial portion of the adult population will experience some form of this pain during their lifetime. The impact is not only physical but also emotional and economic, as it can lead to decreased productivity, increased healthcare costs, and a diminished sense of well-being. Recognizing the commonality of this issue highlights the importance of addressing it with informed and proactive measures.
Common symptoms and initial concerns
Symptoms of lower back and hip pain can vary widely, ranging from a dull ache to sharp, stabbing sensations. Stiffness, reduced range of motion, and difficulty performing everyday tasks are common complaints. These symptoms can often be the body's way of signaling that something is amiss, and early recognition is key to preventing the progression to chronic pain. Addressing these symptoms promptly can prevent further complications and improve long-term outcomes.
Introduction to the approach of the post
This blog post aims to provide a comprehensive guide for those dealing with lower back and hip pain. Readers can expect an exploration of the various causes, from muscle strains to more complex conditions like arthritis and nerve impingement. We will also delve into effective treatments and management strategies, including physical therapy, medications, and lifestyle modifications. By understanding these elements, individuals can take informed steps towards alleviating pain and improving their quality of life.
Main causes of lower back and hip pain
Understanding the root causes of lower back and hip pain is essential for effective treatment. These issues often arise from a variety of factors, ranging from muscle strain to more complex joint and nerve problems. Let's explore some of the primary causes:
Muscle strain and spasms
Muscle strain is one of the most common causes of lower back and hip pain. It often results from overexertion, poor posture, or sudden injuries. Activities that frequently lead to muscle strain include:
- Heavy lifting without proper technique
- Prolonged sitting, especially with poor posture
- Sudden, awkward movements or falls
Nerve impingement and herniated discs
Conditions such as sciatica arise when nerves are compressed, often due to herniated discs. This can cause pain that radiates from the lower back to the hip and even down the leg. A helpful diagram can demonstrate how herniated discs press on nerves, leading to discomfort.
Arthritis: osteoarthritis and ankylosing spondylitis
Chronic inflammation from arthritis is another significant contributor to pain in these areas. Osteoarthritis involves the wear and tear of cartilage in joints, while ankylosing spondylitis is an inflammatory disease affecting the spine. Here’s a comparison of symptoms:
| Condition | Symptoms |
|---|---|
| Osteoarthritis | Pain with activity, joint stiffness |
| Ankylosing Spondylitis | Pain and stiffness, especially in the morning |
Sacroiliac joint dysfunction
The sacroiliac (SI) joint connects the lower spine to the pelvis. Dysfunction in this joint can lead to pain that radiates through the lower back and hips. Symptoms include:
- Localized pain in the lower back or buttocks
- Increased pain with standing or walking
- Difficulty in climbing stairs
Structural joint problems
Issues like hip labral tears and bursitis can significantly impact movement and lead to pain. A self-assessment guide might help identify potential joint problems:
- Persistent pain in the hip or groin
- Catching or clicking sensations in the hip
- Reduced range of motion
Suggested treatments and management strategies
Addressing lower back and hip pain requires a multifaceted approach. Here are some effective treatments and management strategies:
Physical therapy
Physical therapy is often the first line of treatment, focusing on strengthening muscles, improving flexibility, and correcting posture. Successful outcomes are frequently reported by individuals who adhere to tailored exercise programs.

Lumbar support belt
Stabiliserer lænden og lindrer smerter med justerbar kompression og støtte.
Medications
Medications play a crucial role in managing pain and inflammation. Common options include NSAIDs, acetaminophen, and corticosteroid injections. Here's a comparison:
| Medication | Effectiveness | Side Effects |
|---|---|---|
| NSAIDs | High for inflammation | Stomach irritation |
| Acetaminophen | Moderate for pain relief | Liver damage with high doses |
| Corticosteroids | High for short-term relief | Possible joint damage with long-term use |
Lifestyle modifications
Weight control, ergonomic adjustments, and activity modification are vital in managing pain. Practical tips include using ergonomic chairs, maintaining a healthy weight, and incorporating regular low-impact exercises.
Advanced interventions
For cases where conservative strategies fail, advanced interventions such as surgical procedures or minimally invasive techniques may be necessary. A flowchart can guide decisions on when to consider these options based on symptom severity and response to other treatments.
Complementary therapies for pain management
In addition to traditional treatments, complementary therapies can play a crucial role in managing lower back and hip pain. Techniques such as acupuncture, transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS), and yoga have shown promise in providing relief and improving mobility. These therapies can be integrated into a comprehensive pain management plan, offering holistic benefits that address both physical and mental well-being.
- Acupuncture: This ancient practice involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body to alleviate pain and promote healing.
- TENS: A non-invasive method that uses electrical impulses to reduce pain perception and improve circulation.
- Yoga: Incorporating gentle stretches and mindfulness, yoga can enhance flexibility, reduce stress, and support overall health.
Ergonomic solutions for prevention and relief
Ergonomic solutions are essential for both preventing and managing lower back and hip pain. By focusing on posture and body mechanics, ergonomic aids can reduce strain and discomfort during daily activities. Consider these examples of ergonomic products and their benefits:
- Ergonomic chairs: Designed to support the natural curve of the spine, these chairs help maintain proper posture during prolonged sitting.
- Standing desks: Alternating between sitting and standing can relieve pressure on the lower back and hips.
- Footrests and lumbar supports: These accessories provide additional support and alignment, reducing strain on the back and hips.

ActivePosture® Shirt for men
Forbedrer holdning og komfort i hverdagen – hjælper dig med at sidde og stå rigtigt.
Conclusion
Managing lower back and hip pain requires a comprehensive approach that combines traditional treatments, complementary therapies, and ergonomic solutions. By understanding the underlying causes and implementing these strategies, individuals can significantly improve their quality of life and reduce the impact of pain on their daily activities. It's essential to tailor a pain management plan to individual needs, ensuring a balanced and effective approach to relief.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the early signs of lower back and hip pain?
Early signs include stiffness, a dull ache, or sharp pain in the lower back or hip area. These symptoms may worsen with activity or prolonged sitting. If these signs persist, it's advisable to seek medical advice to prevent further complications.
How can I differentiate between hip pain and lower back pain?
Hip pain typically presents in the groin or front of the hip, while lower back pain is felt in the lumbar region. Pain that radiates down the leg may indicate nerve involvement. Diagnostic imaging and a physical examination can help distinguish between the two.
Are there specific exercises I should avoid if I have lower back or hip pain?
High-impact activities, heavy lifting, and exercises that require twisting motions can exacerbate pain. Instead, focus on low-impact exercises such as swimming, walking, or cycling. Consult a physical therapist for personalized exercise recommendations.
When should I consider seeing a specialist for my pain?
If your pain persists for more than a few weeks, worsens over time, or is accompanied by other symptoms like numbness or weakness, it's important to consult a specialist. Early intervention can prevent chronic issues and improve outcomes.
Can lifestyle changes really make a difference in managing pain?
Yes, lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy weight, improving posture, and incorporating regular exercise can significantly reduce pain and improve overall health. These modifications help alleviate stress on the lower back and hips, promoting long-term relief.
Källor
- Hinge Health. "Lower Back & Hip Pain: Causes and Treatments." Hinge Health Resources.
- Healthline Editorial Team. "Lower Back and Hip Pain: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment Options." Healthline.
- Park, K. "What Hip Pain Radiating to Your Lower Back Means." Kevin Park MD Blog.
- Mayo Clinic Staff. "Back Pain: Diagnosis and Treatment." Mayo Clinic.
- Hospital for Special Surgery. "Move Better: Lower Back and Hip Pain." HSS Health Library.
- DMOS Orthopaedic Centers. "Hip vs. Back Pain: Tips for Accurate Diagnosis and Treatment." DMOS News & Articles.
- Cleveland Clinic. "Hip Pain: Symptoms & Causes." Cleveland Clinic Health Library.