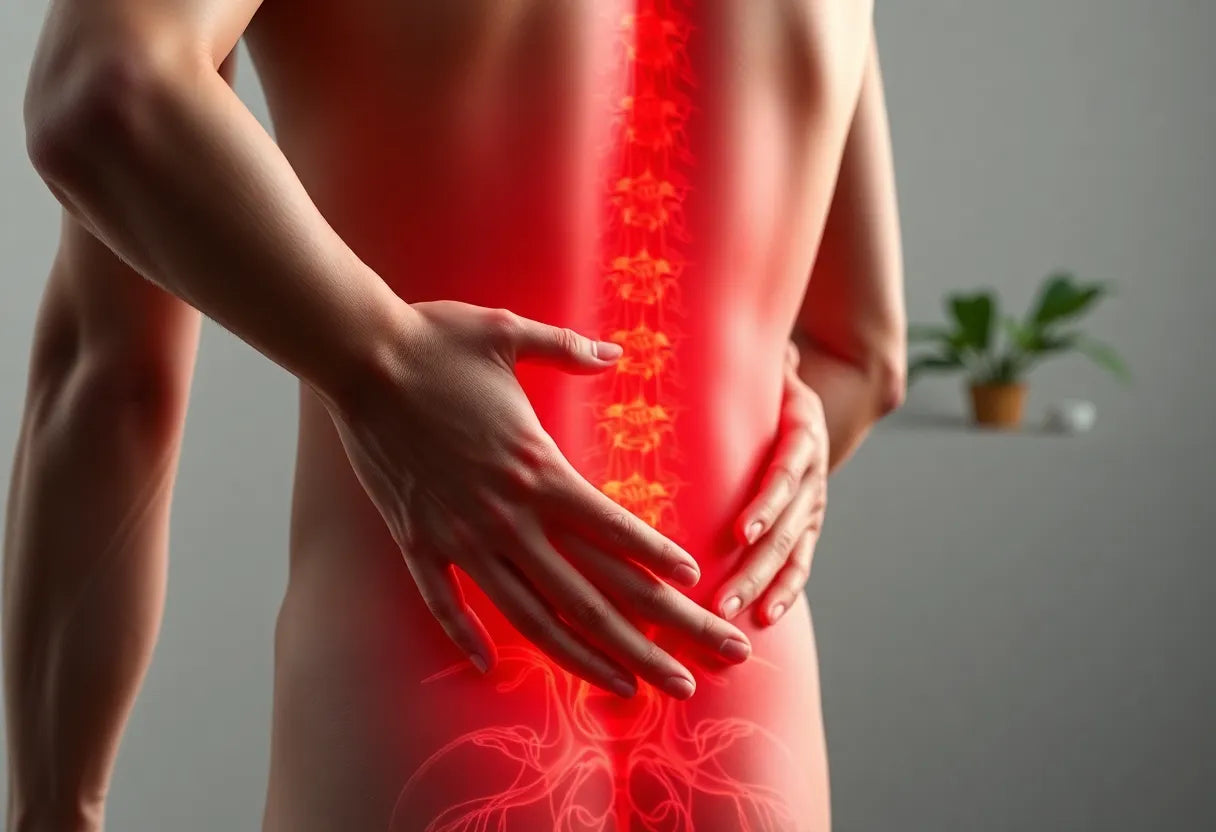
Sciatica pain is a common and often debilitating condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Characterized by pain that radiates along the sciatic nerve, it typically impacts one side of the body, causing discomfort that can range from mild to severe. Common symptoms include sharp pain, tingling, numbness, and muscle weakness in the affected leg. This pain can significantly interfere with daily activities and diminish the quality of life, making effective management crucial for those affected.
The prevalence of sciatica highlights the need for awareness and understanding of the various treatment options available. Many people experience sciatica at some point in their lives, and understanding how to manage and alleviate the pain can lead to improved outcomes and enhanced daily functioning. Whether the pain is acute or chronic, exploring the spectrum of treatment modalities is essential for effective relief.
The complexity of sciatica pain treatment
Treating sciatica is not a one-size-fits-all approach; it involves a broad spectrum of strategies that range from conservative self-care measures to more invasive surgical interventions. The complexity of sciatica pain treatment lies in the need for a personalized approach tailored to the individual's specific symptoms and overall health status. Factors such as the severity of the pain, its impact on daily activities, and the patient's medical history play a crucial role in determining the most appropriate course of action.
Conservative treatments often serve as the first line of defense against sciatica pain. These include self-care practices, physical therapy, and medication, all aimed at reducing pain and improving mobility. For some, these measures may be sufficient to manage symptoms effectively. However, in cases where conservative treatments fail to provide adequate relief, more advanced interventions such as epidural steroid injections or surgical options like microdiscectomy may be considered.
Ultimately, the goal of sciatica pain treatment is to alleviate discomfort, restore function, and improve the quality of life. By understanding the available options and working with healthcare professionals to develop a personalized treatment plan, individuals with sciatica can find the relief they need to lead more comfortable and active lives.
Conservative treatments for sciatica pain
When it comes to managing sciatica pain, conservative treatments are often the first line of defense. These non-invasive methods focus on reducing pain and enhancing mobility, allowing individuals to maintain their daily activities with minimal discomfort.
Self-care and physical activity
Staying active is a crucial aspect of sciatica pain treatment. Contrary to the outdated advice of prolonged bed rest, modern guidelines emphasize the importance of movement. Engaging in gentle exercises and stretches can help alleviate pain and improve flexibility. Activities such as walking, swimming, and yoga are particularly beneficial. Physical therapy plays a vital role here, as therapists can develop personalized exercise programs designed to strengthen the muscles supporting the spine, thereby reducing pressure on the sciatic nerve.

Men's Posture Shirt™ - Black
Boost posture and relieve tension with patented NeuroBand™ tech for work, exercise, and leisure.
Medication options
For many individuals, medication provides a necessary complement to physical activity. Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen and acetaminophen are often recommended for initial relief. In cases of moderate symptoms, healthcare providers might prescribe muscle relaxants, anti-inflammatories, or short courses of oral steroids to manage pain and inflammation more effectively.
Behavioral and patient education
Understanding the nature of sciatica and setting realistic expectations are critical components of effective treatment. Patient education helps individuals manage their condition by providing insights into the prognosis and empowering them to take an active role in their recovery. This approach not only aids in pain management but also fosters a sense of control over the condition.
Interventional procedures for advanced relief
When conservative treatments do not provide sufficient relief, interventional procedures may be considered. These options are typically less invasive than surgery and can offer significant benefits for individuals with persistent sciatica pain.
Epidural steroid injections
Epidural steroid injections are a common choice for those seeking temporary relief from severe sciatica pain. The procedure involves injecting a corticosteroid into the epidural space around the spinal cord, which can reduce inflammation and alleviate pain. While these injections can provide short-term relief, typically lasting several weeks to a few months, they are not a long-term solution and may need to be repeated if symptoms persist.
Advanced techniques
For chronic or refractory cases of sciatica, advanced techniques such as radiofrequency ablation and spinal cord stimulation may be recommended. Radiofrequency ablation targets specific nerves to interrupt pain signals, while spinal cord stimulation involves implanting a device that modifies pain signals before they reach the brain. These minimally invasive options can significantly reduce the need for ongoing medication and offer an alternative for those who are not candidates for surgery.
When to consider surgical treatment
Surgery is generally considered a last resort for sciatica pain treatment, reserved for cases where conservative and interventional methods have failed, or when there is a risk of permanent neurological damage. Common surgical procedures include microdiscectomy and laminectomy, both of which aim to relieve pressure on the sciatic nerve by removing part of the herniated disc or bone spurs.
While surgery can provide faster symptom relief, it is essential to weigh the benefits against potential risks and consider long-term outcomes. Studies have shown that, over time, the results of surgery may not differ significantly from those achieved with conservative management. Therefore, a thorough evaluation by a healthcare professional is crucial to determine the most appropriate course of action for each individual.
Exploring other modalities for sciatica pain relief
While traditional methods for treating sciatica pain are widely practiced, exploring complementary and alternative therapies can offer additional avenues for relief. These modalities are often used in conjunction with conventional treatments to enhance overall outcomes.
Complementary therapies
Acupuncture, an ancient practice originating from traditional Chinese medicine, has gained attention for its potential benefits in relieving sciatica symptoms. While results can vary, some individuals report significant pain reduction following acupuncture sessions. Similarly, massage therapy is frequently utilized to provide short-term relief and improve functional outcomes. By targeting muscle tension and promoting relaxation, massage can be a valuable component of a comprehensive pain management strategy.
Pharmacological treatments
In addition to conventional medications, certain nerve pain medications, such as pregabalin, are sometimes prescribed for sciatica. However, evidence supporting their effectiveness is limited, and they may not be suitable for all patients. It is crucial to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate pharmacological approach based on individual needs and response to treatment.
Recovery and long-term management
Recovery from sciatica can vary significantly among individuals, with many experiencing improvement through conservative therapy. Statistics indicate that approximately 70% of sciatica cases resolve within a few weeks to a few months with non-invasive treatment. However, ongoing management is essential to prevent recurrence and maintain a pain-free lifestyle.
Engaging in regular physical activity is paramount for long-term relief. Incorporating exercises that strengthen the core and back muscles can help support the spine and reduce pressure on the sciatic nerve. Additionally, making ergonomic improvements in daily activities, such as adjusting workstation setups and practicing proper lifting techniques, can further contribute to sustainable relief.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the first step in treating sciatica pain?
The initial step in treating sciatica pain typically involves self-care measures. This includes staying active, engaging in gentle exercises, and applying heat or cold packs to the affected area. If pain persists or worsens, it is advisable to seek medical advice to explore further treatment options.
How long does it take for sciatica to heal with conservative treatment?
Recovery timelines for sciatica vary, with many individuals experiencing relief within a few weeks to a few months. Factors influencing healing include the severity of the condition, adherence to treatment plans, and individual health status. Consistent follow-up with healthcare providers can help monitor progress and adjust treatment as needed.
Are there any lifestyle changes that can help prevent sciatica recurrence?
Yes, adopting certain lifestyle changes can help prevent sciatica recurrence. Maintaining a healthy weight, practicing proper posture, and engaging in regular exercise are crucial steps. Additionally, incorporating ergonomic aids and avoiding prolonged periods of sitting or standing can reduce the risk of future episodes.
When should I consider surgery for sciatica?
Surgery is typically considered when conservative and interventional treatments fail to provide relief, or when there is a risk of permanent neurological damage. A thorough evaluation by a healthcare professional is essential to determine the necessity and potential benefits of surgical intervention.
Can ergonomic aids help with sciatica pain?
Yes, ergonomic supports can play a significant role in managing sciatica pain. By reducing nerve pressure and promoting proper posture, ergonomic aids such as lumbar cushions and adjustable chairs can help alleviate discomfort and prevent further strain on the sciatic nerve.

Lumbar support belt
Adjustable belt stabilizes and relieves the lower back—great for sciatica and leg pain relief.
Källor
- American Academy of Family Physicians. (2015). "Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute Low Back Pain." American Family Physician.
- ClinicalTrials.gov. "Study to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of a New Treatment for Sciatica."
- Stafford, M.A., Peng, P., & Hill, D.A. (2007). "Sciatica: A Review of History, Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, and the Role of Epidural Steroid Injection in Management." British Journal of Anaesthesia.
- Genevay, S. & Atlas, S.J. (2018). "Lumbar Spinal Stenosis." StatPearls.
- Mayo Clinic. "Sciatica: Diagnosis & Treatment."
- Cleveland Clinic. "Sciatica: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments."
- CenterWatch. "Sciatica Clinical Trials."
- Harvard Health Publishing. "Sciatica: What You Need to Know."