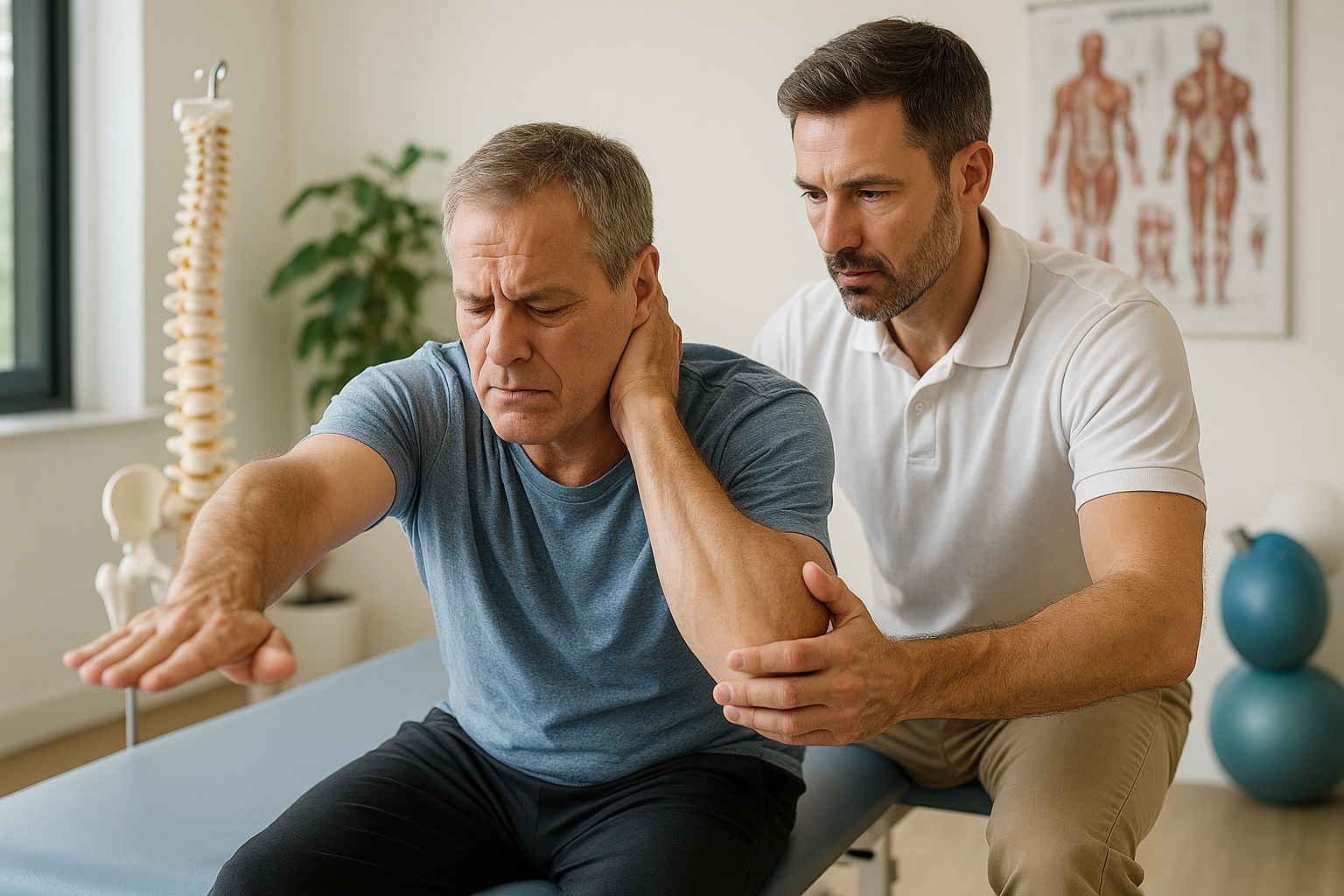
Neuropathic pain in spinal stenosis is a condition that affects millions, particularly within the aging population. As we age, the risk of developing spinal stenosis increases, a condition characterized by the narrowing of the spinal canal. This narrowing can lead to compression of the spinal nerves, causing a host of symptoms, the most debilitating of which is neuropathic pain. This type of pain is a direct result of nerve damage and is often described by sufferers as a tingling, burning, or sharp sensation that can severely impact daily life.
understanding spinal stenosis and neuropathic pain
Spinal stenosis occurs when spaces within the spine become narrowed, putting pressure on the nerves that travel through the spine. This condition is most commonly seen in the lower back and the neck. As the spinal canal narrows, it can lead to a range of symptoms, including pain, numbness, muscle weakness, and problems with bladder or bowel function in severe cases. The pain associated with spinal stenosis is often neuropathic, meaning it stems from nerve damage rather than tissue damage, presenting unique challenges in pain management.
Neuropathic pain is notoriously difficult to treat because it doesn't respond well to conventional pain relief methods that are effective for other types of pain. This type of pain can be persistent and debilitating, affecting the quality of life and posing significant challenges for those who suffer from it. Understanding the nature of neuropathic pain is crucial for developing effective management strategies.
the challenge of pain management
Treating neuropathic pain in spinal stenosis is complex due to its non-physiological nature, which means it doesn't always respond to traditional pain management techniques. This complexity necessitates a multi-modal treatment approach, which combines medical interventions with lifestyle changes to effectively manage symptoms. While medications and procedures are often the first line of treatment, incorporating ergonomic solutions can play a critical role in managing pain.
Ergonomic solutions are an essential, yet frequently overlooked, component of pain management strategies for spinal stenosis. These solutions focus on optimizing the environment and daily activities to reduce nerve compression and improve posture, thereby alleviating pain. Ergonomic aids such as lumbar supports, ergonomic chairs, and specially designed pillows can significantly enhance comfort and reduce strain on the spine, providing much-needed relief from neuropathic pain.

Lumbar support belt
Provides strong adjustable support and decompression for lower back pain relief.
By integrating ergonomic solutions into a comprehensive treatment plan, individuals suffering from neuropathic pain due to spinal stenosis can find a balance between medical treatments and lifestyle adjustments. This holistic approach not only addresses the symptoms but also empowers individuals to take control of their pain management journey, offering a path to improved quality of life.
medical and procedural interventions for neuropathic pain in spinal stenosis
When it comes to managing neuropathic pain associated with spinal stenosis, medical and procedural interventions play a crucial role. Medications are often the first line of defense, providing symptom relief and improving the quality of life for many patients. Commonly prescribed medications include non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), which help reduce inflammation and pain. Antidepressants such as amitriptyline and anti-seizure medications like gabapentin are also frequently used to target neuropathic pain by altering the way the brain perceives pain signals.
While these medications can be effective in managing symptoms, it is important to note that they do not address the root cause of the pain. For more persistent or severe cases, procedural interventions may be considered. Minimally invasive procedures such as epidural steroid injections and nerve blocks can provide temporary relief by reducing inflammation around the affected nerves. These procedures are often used when medications alone are insufficient in controlling pain.
In cases where conservative treatments fail to provide adequate relief, surgical interventions may be considered as a last resort. Surgical options, such as decompression surgery, aim to relieve pressure on the spinal nerves by removing the structures causing the narrowing of the spinal canal. However, surgery is typically reserved for severe cases due to the risks and recovery time involved.
lifestyle and physical therapy approaches
In addition to medical and procedural interventions, lifestyle modifications and physical therapy are essential components of a comprehensive treatment plan for neuropathic pain in spinal stenosis. Activity modification is crucial, as certain exercises can exacerbate symptoms, while others can help alleviate them. Low-impact exercises like swimming and walking are particularly beneficial as they promote cardiovascular health without placing undue strain on the spine. Additionally, maintaining a healthy weight can reduce pressure on the spine, further alleviating pain.
Physical therapy is another vital aspect of managing spinal stenosis. A tailored physical therapy program can focus on strengthening and flexibility exercises that support spinal health and improve overall function. By enhancing the muscles that support the spine, physical therapy can help reduce nerve compression and alleviate pain. Moreover, incorporating ergonomic aids into physical therapy sessions can enhance outcomes by ensuring proper posture and reducing strain on the spine during exercises.
ergonomic solutions: filling the gap in pain management
Ergonomic solutions offer a unique and often underutilized approach to managing neuropathic pain in spinal stenosis. Proper ergonomics can significantly reduce nerve compression by promoting correct posture and spinal alignment in daily activities. Ergonomic aids such as lumbar supports, ergonomic chairs, and specially designed pillows can be seamlessly integrated into daily routines, providing continuous support and comfort.
The importance of ergonomics lies in its ability to complement other treatment modalities. By supporting proper posture, ergonomic products can reduce the frequency and severity of pain episodes, making other treatments more effective. For instance, adjustable workstations and proper seating arrangements can help maintain spinal alignment during prolonged sitting, a common trigger for pain in individuals with spinal stenosis.
By addressing the often-overlooked aspect of ergonomics, individuals can fill a critical gap in their pain management strategy. Ergonomic solutions not only provide immediate relief but also contribute to long-term spinal health, making them an indispensable component of a holistic approach to managing neuropathic pain in spinal stenosis.
Integrating ergonomic solutions with traditional treatments
In managing neuropathic pain from spinal stenosis, a multi-modal treatment strategy is essential. Ergonomic solutions play a vital role in this approach, complementing medications and physical therapy. While medications aim to alleviate symptoms and physical therapy focuses on strengthening and flexibility, ergonomic solutions provide foundational care. They ensure proper posture and reduce nerve compression, which can enhance the effectiveness of other treatments.
Ergonomics should be considered the first line of defense in managing spinal stenosis. By incorporating ergonomic aids such as lumbar supports and ergonomic chairs into daily routines, individuals can reduce the frequency and intensity of pain episodes. These aids help maintain spinal alignment, thereby minimizing the triggers that exacerbate neuropathic pain.

Men's Posture Shirt™ - Black
Posture Shirt™ supports muscle activation and posture—CE approved for pain relief.
Case studies and testimonials
Consider the case of Sarah, a 65-year-old woman who struggled with neuropathic pain due to spinal stenosis. After incorporating ergonomic solutions into her daily life, she experienced significant relief. By using an ergonomic chair and lumbar support at her workstation, Sarah noticed a reduction in her pain levels and an improvement in her overall comfort. Her story illustrates how ergonomic solutions can be an integral part of a comprehensive pain management plan.
Testimonials from individuals like Sarah highlight the transformative impact of ergonomic aids. Many report that these solutions not only provide immediate relief but also contribute to long-term spinal health. By promoting proper posture and reducing nerve compression, ergonomic solutions empower individuals to take control of their pain management journey.
Conclusion
In conclusion, managing neuropathic pain in spinal stenosis requires a comprehensive approach that combines medical treatments, lifestyle modifications, and ergonomic solutions. By integrating ergonomic aids into a multi-modal treatment plan, individuals can find relief from pain and improve their quality of life. Ergonomic solutions offer a practical and effective way to manage pain, making them an essential component of any pain management strategy.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is neuropathic pain in spinal stenosis?
Neuropathic pain in spinal stenosis is a type of pain resulting from nerve damage due to the narrowing of the spinal canal. This narrowing compresses the spinal nerves, leading to symptoms such as tingling, burning, and sharp pain.
How do ergonomic aids help with spinal stenosis?
Ergonomic aids support proper posture and spinal alignment, reducing nerve compression and alleviating pain. By using aids such as lumbar supports and ergonomic chairs, individuals can minimize the strain on their spine and manage their symptoms more effectively.
Can ergonomic solutions replace medical treatments?
No, ergonomic solutions are complementary to medical treatments. They are part of a multi-modal approach that includes medications, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications to manage neuropathic pain effectively.
What are some simple ergonomic changes I can make at home?
Simple ergonomic changes include using lumbar supports while sitting, optimizing desk setups to maintain proper posture, and choosing ergonomic chairs that support spinal alignment. These adjustments can significantly reduce pain and improve comfort.
When should I consider surgery for spinal stenosis?
Surgery is typically considered when conservative treatments fail to provide adequate relief. It is important to consult with healthcare professionals to evaluate the severity of your condition and determine if surgical options are necessary.
Kilder
- Hospital for Special Surgery. "Spinal Stenosis."
- Physiotutors. "Lumbar Spinal Stenosis Cluster."
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. "Understanding Spinal Stenosis."
- Kiropraktor Vejle. "Folder om Lumbal Spinalstenose."
- NY Spine. "Connection Between Spinal Stenosis and Neuropathy."
- Aalborg Rygklinik. "Vejledning til Spinalstenose."
- Weill Cornell Medicine. "Pain Management for Spinal Stenosis."
- Helsebiblioteket. "Lumbal Nerverotsaffeksjon og Lumbal Spinal Stenose."
- NewYork-Presbyterian. "Spinal Stenosis Treatment."
- Kiropraktoren. "Kiropraktoren Forklarer: Lumbal Spinalstenose."
- Cleveland Clinic. "Spinal Stenosis."
- A Family Today. "Hvad er Spinal Stenose og Hvordan Behandles Det?"
- American College of Rheumatology. "Spinal Stenosis."
- Tidens Kiropraktor. "Lumbal Spinal Stenose: Når Nerverne Klemmes i Rygsøjlen."
- California Sports & Spine. "Understanding Spinal Stenosis: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options."
- Kiroball. "Spinal Stenose."
- Privathospitalet Mølholm. "Spinalstenose."
- Sundhedsstyrelsen. "NKR: Behandling af Lumbal Spinalstenose."