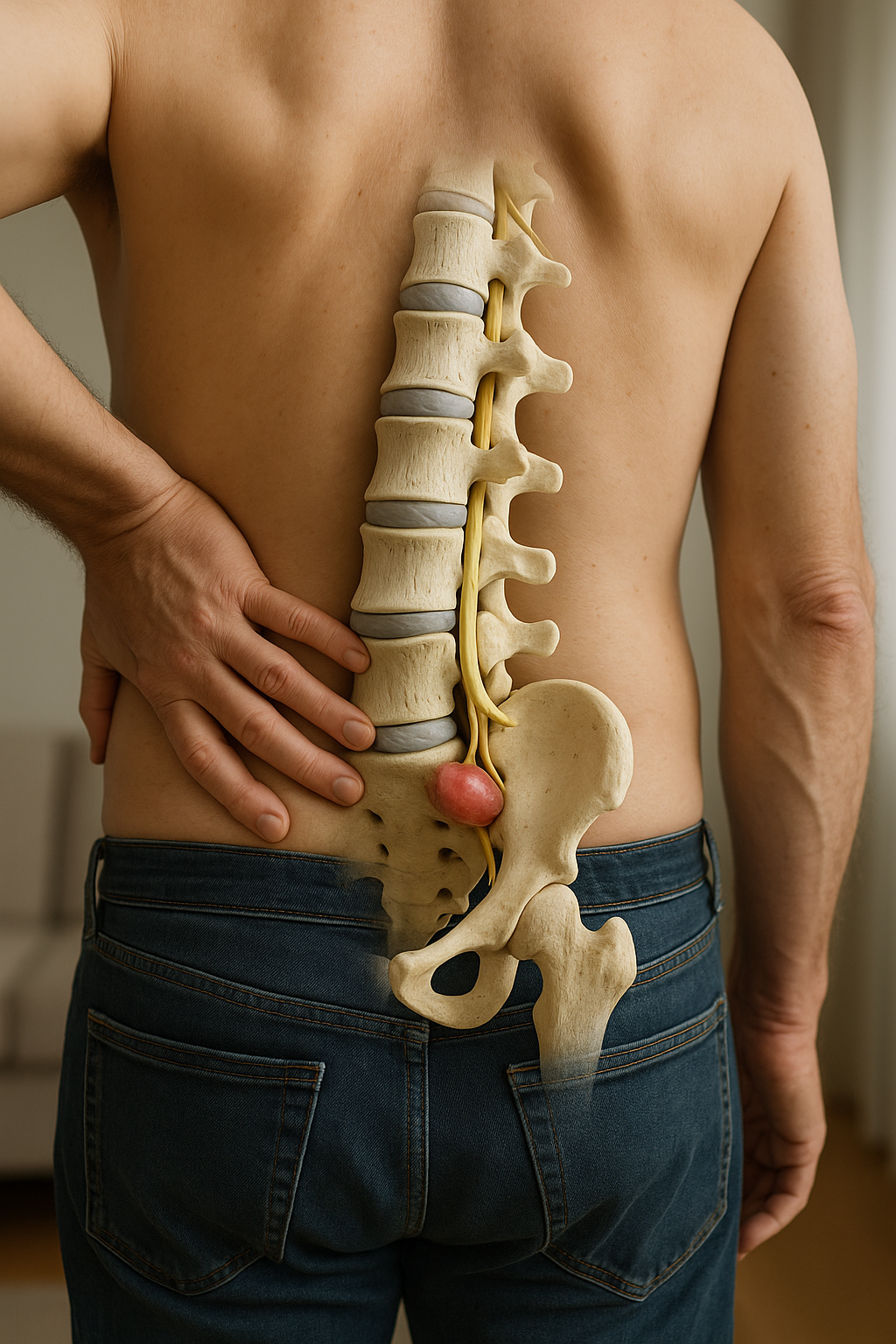
Living with lumbar disc herniation can significantly impact daily life, often presenting challenges that range from persistent back pain to discomfort radiating down the legs, and even limited mobility. Understanding this condition is crucial for anyone seeking relief and a return to their normal activities. A lumbar disc herniation occurs when a disc in the lower spine becomes damaged and protrudes, potentially pressing on nearby nerves. This can lead to the symptoms mentioned, making it difficult to perform even simple tasks without experiencing pain.
Recognizing the impact of lumbar disc herniation
The symptoms of lumbar disc herniation can vary, but commonly include sharp or shooting pain in the lower back, pain that extends to the legs, and a noticeable decrease in mobility. This condition not only affects physical health but can also take a toll on mental well-being, as the persistent discomfort often leads to frustration and a decrease in quality of life. Addressing these symptoms effectively is essential for improving one's overall functionality and comfort.
The importance of exercise in managing lumbar disc herniation
Exercise plays a pivotal role in managing lumbar disc herniation pain. While it might seem counterintuitive to move when in pain, gentle, low-impact exercises are proven to support healing and alleviate discomfort. These exercises help by increasing blood flow to the affected area, promoting healing, and strengthening the muscles that support the spine. This approach not only aids in pain relief but also enhances overall function and mobility.

Lumbar support belt
Provides adjustable lumbar support to relieve lower back pain and tension.
Core stabilization and flexibility are key components of an effective exercise routine for those suffering from lumbar disc herniation. Strengthening the core muscles, including the abdominals, back, and pelvis, provides better support for the spine, reducing the strain on the lumbar discs. Furthermore, incorporating flexibility exercises can help to relieve tension and improve range of motion, making daily activities more manageable.
Embracing a proactive approach
By incorporating specific exercises into your routine, you can take proactive steps toward managing lumbar disc herniation. These exercises are designed to be gentle yet effective, ensuring that they do not exacerbate symptoms while providing the necessary support for recovery. The journey to relief and improved function begins with understanding the condition and embracing a tailored exercise regimen that suits your individual needs and capabilities. As you progress, you'll likely notice improvements in both your physical and mental well-being, paving the way for a more active and fulfilling life.

Men's Posture Shirt™ - Black
CE-registered medical device shirt that improves posture and can relieve back, neck, and shoulder pain.
low-impact aerobic exercises for lumbar disc herniation
Engaging in low-impact aerobic exercises is a cornerstone for managing lumbar disc herniation. These exercises are designed to enhance cardiovascular fitness, increase blood flow to the spine, and minimize additional strain on the lumbar region. Among the most recommended activities are walking, swimming, and stationary cycling, each offering unique benefits that can be tailored to individual needs.
Walking is one of the simplest yet most effective exercises for those with lumbar disc herniation. It promotes overall health without placing undue stress on the spine. To maximize benefits, maintain a proper posture by keeping your back straight and shoulders relaxed. Start with a comfortable pace and gradually increase your distance as your endurance improves.
Swimming provides an excellent full-body workout due to the buoyancy of water, which reduces pressure on the spine. It allows for a greater range of motion without the risk of injury. Focus on gentle strokes such as the backstroke or freestyle, which are less likely to strain the back while still offering cardiovascular benefits.
Stationary cycling is another viable option, offering cardiovascular benefits while minimizing impact on the back. Adjust the seat height to ensure your knees are slightly bent at the bottom of the pedal stroke, which can help prevent additional strain on the lumbar region. Start with low resistance and gradually increase intensity as your comfort level allows.
core strengthening exercises for lumbar support
Core strengthening is crucial for providing support to the lumbar spine and alleviating symptoms associated with disc herniation. Focusing on exercises that target the core muscles can help stabilize the spine and reduce pain.
Pelvic tilts are a gentle way to engage the core. Begin by lying on your back with your knees bent and feet flat on the floor. Tighten your abdominal muscles and flatten your lower back against the floor, holding for a few seconds before releasing. Repeat this motion to strengthen the lower abdominal muscles.
Bridges are effective for activating the glutes and core. Lie on your back with knees bent and feet hip-width apart. Lift your hips towards the ceiling while squeezing your glutes and engaging your core. Hold briefly at the top before lowering back down. This exercise helps in building strength in the lower back and gluteal muscles.
Plank variations offer a dynamic way to strengthen the core. Start with a basic plank by positioning yourself on your forearms and toes, ensuring your body forms a straight line from head to heels. For beginners, knee planks can be a great modification. As strength improves, consider side planks to further challenge the core muscles.
flexibility and mobility exercises
Improving flexibility and mobility is essential for reducing tension and enhancing the range of motion in those with lumbar disc herniation. Incorporating specific stretches can alleviate stress on the lower back and improve overall function.
Hamstring stretches are vital as tight hamstrings can exacerbate lower back pain. Sit on the edge of a chair with one leg extended straight. Lean forward gently, keeping your back straight until you feel a stretch in the back of your thigh. Hold for 20-30 seconds and switch legs.
Quadriceps and hip flexor stretches can also relieve tension. Stand with one hand on a wall for balance, grab your ankle, and pull your heel towards your buttocks. Ensure your knees are aligned and hold the stretch for 20-30 seconds. This stretch helps in opening up the hips and reducing strain on the lower back.
benefits of aquatic therapy
For individuals with severe symptoms, aquatic therapy offers a unique and effective way to exercise without exacerbating pain. The buoyancy of water supports the body, reducing the load on the spine and making movement easier.
Water walking is a simple yet effective exercise. Walk in waist-deep water, focusing on maintaining an upright posture and using your arms to aid balance. The resistance of the water provides a gentle workout that enhances cardiovascular fitness and muscle strength.
Water aerobics can be tailored to individual comfort levels. These exercises involve a variety of movements that improve flexibility, strength, and endurance, all while minimizing impact on the spine. Adjust the intensity according to your comfort, ensuring a safe and effective workout.
Incorporating these exercises into your routine can significantly aid in managing lumbar disc herniation. By focusing on low-impact aerobic activities, core strengthening, and flexibility, you can take proactive steps towards alleviating pain and improving your quality of life. Remember to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new exercise regimen, especially if you have underlying health concerns.
McKenzie exercises and lumbar extensions for pain management
One effective method for managing lumbar disc herniation pain is through McKenzie exercises, which focus on promoting pain centralization. This technique aims to move pain away from the extremities and back towards the center of the spine, reducing discomfort in the legs and improving overall mobility.
Standing lumbar extensions are a simple yet effective exercise. Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart and place your hands on your lower back for support. Gently lean backward, extending your spine, and hold for a few seconds before returning to the starting position. This exercise helps in reducing pressure on the discs and alleviating pain.
Gentle “press-up” back extensions can be performed by lying face down on a mat. Place your hands under your shoulders and slowly press your upper body off the ground, keeping your hips in contact with the floor. Hold the position briefly before lowering back down. This movement helps to relieve pressure on the lumbar discs and can be a beneficial addition to your routine.
Clinical evidence supporting exercise therapy
Numerous studies have demonstrated the benefits of exercise therapy for individuals with lumbar disc herniation. Research indicates that structured exercise routines can significantly improve pain levels, enhance functionality, and increase quality of life. While the optimal frequency and intensity of these exercises may vary, engaging in a consistent routine for more than two weeks has been associated with notable improvements.
Clinical trials and meta-analyses have confirmed that exercises focusing on core stabilization and flexibility are particularly effective. By strengthening the core muscles and improving flexibility, individuals can better support their spine and reduce the strain on lumbar discs. These findings underscore the importance of incorporating these exercises into a comprehensive pain management plan.
Frequently asked questions
What exercises should be avoided with lumbar disc herniation?
Individuals with lumbar disc herniation should avoid high-impact activities, twisting motions, and heavy lifting, as these can exacerbate symptoms and increase the risk of further injury. Instead, focus on low-impact exercises that promote healing and stability.
How often should I perform these exercises?
It is generally recommended to perform these exercises several times a week, based on clinical guidelines. Consistency is key, so aim for a routine that allows for gradual progression without causing discomfort. Consulting with a healthcare professional can provide personalized recommendations based on your specific condition.
When should I consult a healthcare professional?
If you experience severe pain, numbness, or weakness in your legs, or if your symptoms do not improve with exercise, it is important to seek medical advice. A healthcare professional can assess your condition and recommend appropriate interventions.
Can ergonomic aids help in recovery?
Yes, ergonomic aids can be beneficial in supporting recovery. Products such as supportive seats, back braces, and ergonomic chairs can help reduce strain on the lumbar spine and complement your exercise routine. These aids can enhance comfort and facilitate a more effective recovery process.
Incorporating these exercises and understanding the role of clinical evidence can greatly aid in managing lumbar disc herniation pain. By addressing common concerns through this FAQ section, individuals can make informed decisions about their exercise routines and seek professional guidance when necessary.
Källor
- Spine.md. (n.d.). "Workouts for Herniated Disc."
- Mainstay Medical. (n.d.). "Exercises for Herniated Disc in Lower Back."
- Orthopedic NJ. (n.d.). "Herniated Disc Exercises and Stretches."
- PTCOA. (n.d.). "Exercises and Stretches for Herniated Disc Relief."
- YouTube. (n.d.). "Exercise for Herniated Disc L4-L5 and L5-S1."
- Petersen Physical Therapy. (n.d.). "Herniated Disc Exercises to Heal Quickly."
- Medical News Today. (2019). "Herniated Disk: 6 Safe Exercises and What to Avoid."
- YouTube. (n.d.). "Best Exercises for a Herniated Disc."