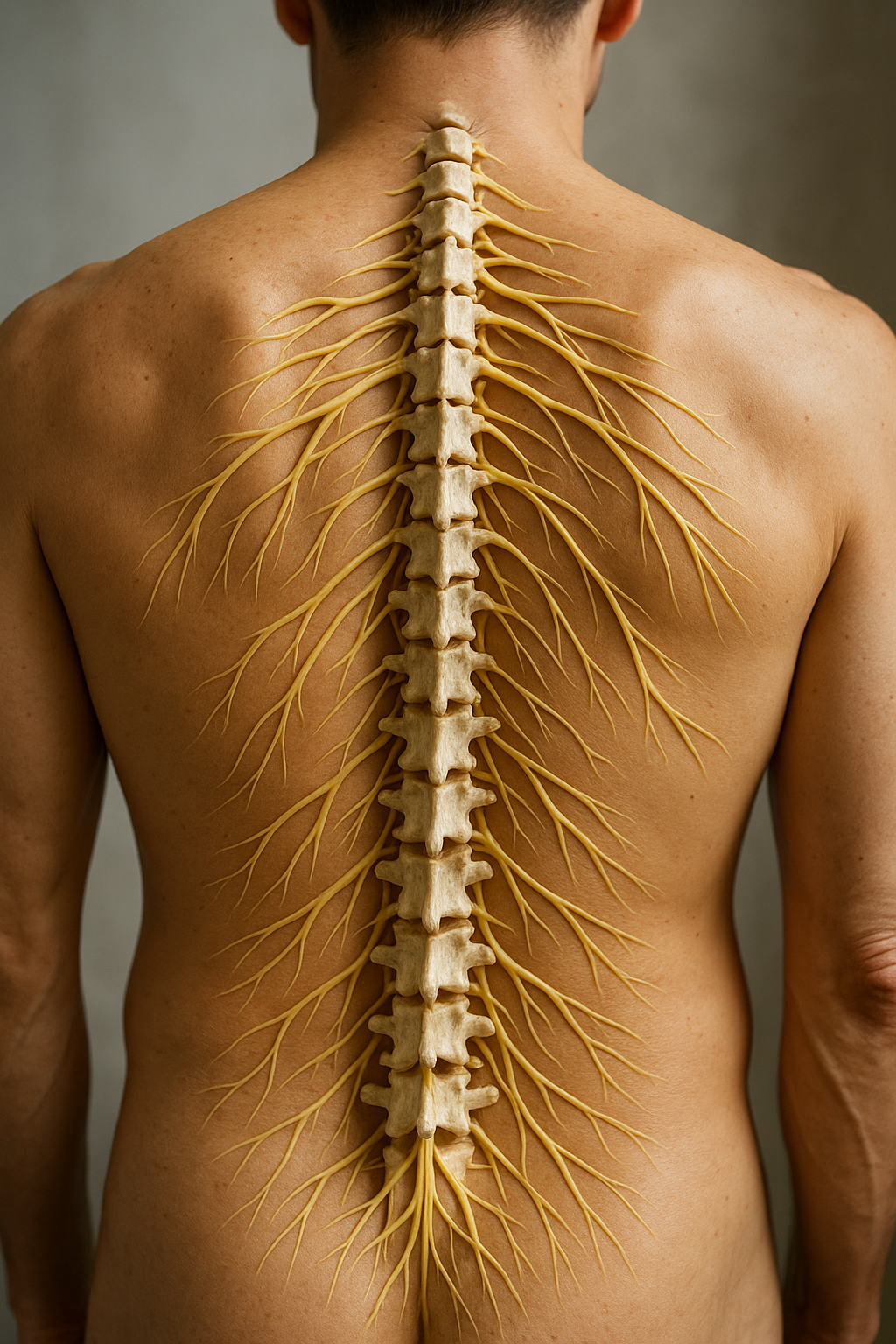
Living with a pinched nerve can be a daily struggle, especially when it manifests as left-sided back pain. This specific type of discomfort, often overlooked in broader discussions of back pain, can significantly impact one's quality of life. Understanding the nuances of left-sided back pain caused by a pinched nerve is crucial for effective treatment and lasting relief.
Understanding the mystery of left-sided back pain
At its core, a pinched nerve occurs when excessive pressure is applied to a nerve by surrounding tissues such as bones, cartilage, muscles, or tendons. This pressure disrupts the nerve's function, leading to pain, tingling, numbness, or weakness in the affected area. While pinched nerves can occur in various parts of the body, they often affect the back, with symptoms sometimes localized to one side.
Left-sided back pain, in particular, deserves attention as it can indicate specific underlying issues that may not be present in right-sided or central back pain. By focusing on the side-specific nature of this pain, individuals can better tailor their treatment approaches to address the root cause effectively.
The anatomy of a pinched nerve
A pinched nerve is essentially a nerve that is compressed by surrounding tissues, which can include herniated discs, bone spurs, or even swollen muscles. This compression can lead to a variety of symptoms, such as sharp pain, tingling sensations, numbness, and muscle weakness. These symptoms can vary in intensity and duration, depending on the severity of the nerve compression.
Identifying whether the left or right side is affected is crucial, as it allows for more targeted treatment strategies. For instance, left-sided back pain may require different ergonomic adjustments or therapeutic exercises compared to right-sided pain.
Why left-sided back pain deserves attention
Back pain is a prevalent issue, affecting millions of people worldwide. However, the unique challenges presented by left-sided symptoms are often underrepresented in general discussions about back pain. Left-sided back pain can stem from various causes, including specific lifestyle factors, anatomical differences, or underlying medical conditions that preferentially affect one side.
By exploring the causes, symptoms, and solutions specific to left-sided pinched nerves, individuals can gain a deeper understanding of their condition and how to manage it effectively. This knowledge empowers them to seek appropriate treatments and make informed decisions about their health, ultimately leading to improved well-being and a reduction in pain.
Symptoms and diagnosis of a pinched nerve on the left side
Experiencing a pinched nerve on the left side of the back can manifest through a range of symptoms that vary in intensity. Common indicators include sharp or stabbing pain, tingling sensations, numbness, and muscle weakness. These symptoms often extend beyond the back, potentially radiating down the left leg or wrapping around the left ribcage, depending on the nerve affected. Such side-specific symptoms can significantly disrupt daily activities, making it essential to recognize them early.
Diagnosing a pinched nerve involves a thorough examination by a healthcare professional. This process typically includes a physical assessment to evaluate mobility and identify areas of tenderness or weakness. Imaging tests, such as MRI or CT scans, may be employed to pinpoint the exact location and cause of the nerve compression. Accurate diagnosis is crucial for developing an effective treatment plan tailored to the individual's specific needs.
Common causes of left-sided pinched nerves
Several factors can lead to the development of a pinched nerve on the left side of the back. Herniated or bulging discs are among the most prevalent causes, where the disc material protrudes and exerts pressure on nearby nerves. Spinal stenosis, a narrowing of the spinal canal, can also compress nerves, leading to pain and discomfort. Bone spurs and spondylolisthesis, where one vertebra slips over another, further contribute to nerve compression.
These conditions can specifically affect the left side due to anatomical variations or lifestyle habits. Risk factors include repetitive strain from certain activities, poor posture, a sedentary lifestyle, and age-related changes in the spine. Understanding these causes is essential for both prevention and management of the condition.
The role of lifestyle and ergonomics in managing pinched nerves
Lifestyle choices and ergonomic practices play a significant role in both the development and management of pinched nerves. Poor posture, prolonged sitting, and heavy lifting are common contributors to nerve compression. Asymmetric movements or habits, such as always carrying a bag on the same shoulder, can exacerbate left-sided issues.
Implementing ergonomic interventions can significantly alleviate symptoms and prevent further nerve damage. This includes using posture-supporting clothing, lumbar supports, and modifying activities to reduce strain on the back. Ergonomic adjustments in the workplace, such as setting up a desk to promote good posture, can also be beneficial.

Women's Posture Shirt™ - Black
Forbedrer holdning og kan lindre smerter og spændinger i ryggen.
By addressing lifestyle factors and incorporating ergonomic solutions, individuals can reduce the risk of developing a pinched nerve and manage existing symptoms more effectively. These strategies not only aid in pain relief but also enhance overall spinal health, contributing to a better quality of life.
Treatment and management options for left-sided back pain
Addressing left-sided back pain caused by a pinched nerve requires a comprehensive approach that balances conservative and, if necessary, more invasive treatments. Initially, conservative methods are recommended, which include rest, the use of anti-inflammatory medications, and engaging in physical therapy. These strategies aim to reduce inflammation and alleviate pressure on the affected nerve.
Ergonomic adjustments play a crucial role in managing symptoms. Implementing ergonomic solutions, such as using lumbar supports or posture-correcting clothing, can significantly reduce strain on the back. These interventions, when combined with activity modifications, help in maintaining proper spinal alignment and preventing further nerve compression.

Lumbar support belt
Justerbart bælte til støtte og aflastning af lænden ved rygsmerter.
For those who do not find relief through conservative methods, more invasive options may be considered. Injections, such as corticosteroids, can provide temporary relief by reducing inflammation. In severe cases, surgical interventions might be necessary to relieve pressure on the nerve. However, these are typically reserved for situations where other treatments have failed.
Non-pharmaceutical management strategies, including ergonomic solutions, offer additional support. These solutions focus on enhancing posture and reducing muscle tension, contributing to long-term relief and prevention of future issues.
Self-care and prevention tips
Engaging in self-care is essential for managing and preventing left-sided pinched nerves. Gentle mobility exercises, such as stretching and yoga, can improve flexibility and reduce tension in the affected area. Regularly correcting posture, especially during prolonged sitting or standing, is vital in minimizing strain on the back.
Setting up an ergonomic workspace is another crucial step. Ensure that your desk and chair promote good posture, with the computer screen at eye level and feet flat on the ground. Investing in ergonomic aids, like supportive seating or standing desks, can further prevent nerve compression.
Early intervention and regular monitoring of symptoms are key to preventing complications. By addressing minor discomforts promptly, individuals can avoid the progression of symptoms and maintain a healthier spine.
Frequently asked questions
Can a pinched nerve cause pain only on one side of my back?
Yes, a pinched nerve can cause pain localized to one side of the back, depending on which nerve root is affected. This side-specific pain is often due to the anatomical path of the nerve.
How do I know if my left-sided back pain is serious?
Serious symptoms include severe pain that does not improve with rest, progressive muscle weakness, or loss of bladder or bowel control. These require immediate medical attention.
What can I do at home to relieve left-sided back pain?
At-home remedies include resting, applying heat or cold packs, maintaining good posture, and using ergonomic supports to reduce strain on the back.
When should I see a doctor for left-sided back pain?
If your pain persists despite self-care measures or if you experience symptoms such as numbness or weakness, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional.
Can ergonomic aids really help with pinched nerves?
Yes, ergonomic aids can significantly help by supporting proper posture, reducing muscle tension, and preventing further compression of the nerves, contributing to pain relief and improved function.
Kilder
- University of Utah Health. (2023). "What to Do for a Pinched Nerve in Your Back."
- Sciatica.com. "9 Treatment Options for Pinched Nerves in the Back and Neck."
- Texas Pain and Spine. "How to Soothe a Pinched Nerve in the Lower Back."
- Medical News Today. "Pinched Nerve in Lower Back: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments."
- Wiles, D. "What Are the Treatments for a Pinched Nerve?"
- Mayo Clinic. "Pinched Nerve: Diagnosis and Treatment."
- Cleveland Clinic. "Pinched Nerves."
- Cedars-Sinai. "Radiculopathies."
- Tenet Health. "Pinched Nerve Pain: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatments."