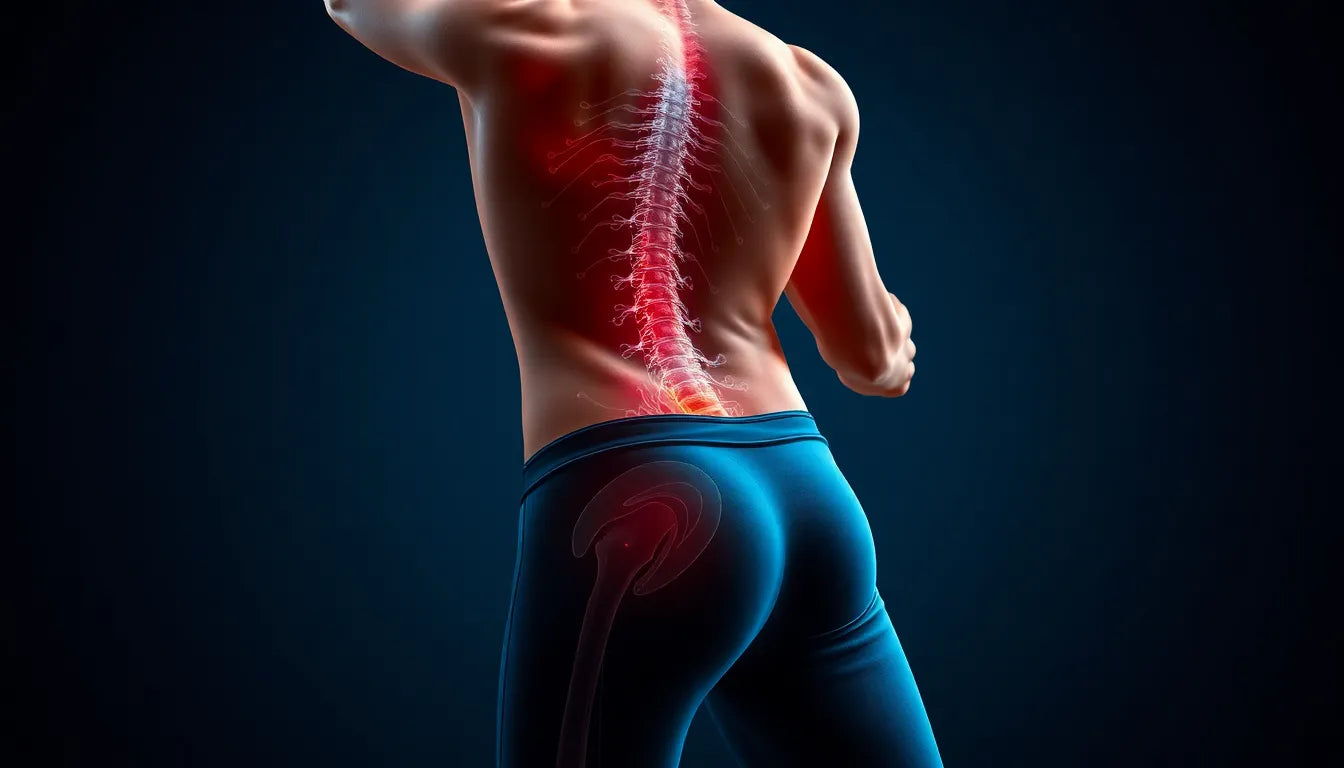
Facet joint syndrome is a condition that affects the small stabilizing joints located between and behind adjacent vertebrae in the spine. These joints, known as facet joints, can become inflamed or degenerate over time, leading to what is commonly referred to as facet joint syndrome. This condition often results in localized back pain, stiffness, and a reduced range of motion, significantly impacting a person’s mobility and quality of life.
Understanding the intricacies of facet joint syndrome is crucial for managing its symptoms effectively. The pain associated with this condition is typically due to inflammation or irritation of the facet joints, which can occur as a result of aging, injury, or repetitive stress. Common symptoms include persistent back pain that may radiate into the buttocks or thighs, morning stiffness, and a noticeable decrease in flexibility, particularly in the lower back.
the importance of exercise in managing facet joint syndrome
Exercise plays a pivotal role in managing facet joint syndrome, offering a non-invasive approach to alleviate pain and enhance spinal health. Regular, gentle exercises can help reduce pain, improve flexibility, and strengthen the muscles supporting the spine, thus enhancing overall spinal stability. By focusing on exercises that minimize stress on the spine, individuals can avoid exacerbating their symptoms and instead promote healing and comfort.

Lumbar support belt
Supports the lower back to help reduce pain and stabilize the lumbar area during daily activities.
When selecting exercises for facet joint syndrome, it is crucial to prioritize those that are evidence-based and safe. These exercises should aim to improve the range of motion, strengthen core muscles, and enhance overall spinal support. The right exercise regimen can lead to significant improvements in daily function and quality of life, making it an essential component of a comprehensive management plan for those with facet joint syndrome.
In the following sections, we will explore specific exercises recommended for individuals dealing with facet joint syndrome. These exercises are designed to promote flexibility, strength, and pain relief, all while ensuring safety and effectiveness. By incorporating these exercises into a regular routine, individuals can take proactive steps toward a pain-free life, unlocking relief through consistent practice.
recommended exercises to alleviate facet joint syndrome
For individuals grappling with facet joint syndrome, incorporating specific exercises into their routine can be a transformative step toward reducing pain and enhancing mobility. These exercises are carefully selected to promote flexibility, build strength, and provide relief, all while ensuring the safety of the spine. Let's delve deeper into some effective exercises that can be seamlessly integrated into daily life.
knee-to-chest exercise
The knee-to-chest exercise is a gentle yet effective stretch that targets the lower back, helping to alleviate tension without placing undue stress on the spine.
- Instructions: Lie on your back on a comfortable surface. Bring one knee towards your chest, holding it with both hands. Hold the position for 15-30 seconds, then switch legs. Repeat 5–10 times for each leg.
- Benefits: This exercise gently stretches the lower back, reducing tension and promoting relaxation in the affected area.
bridging exercise
The bridging exercise focuses on strengthening the muscles of the lower back and glutes, which are crucial for maintaining spinal stability.
- Instructions: Lie on your back with knees bent and feet flat on the floor. Lift your pelvis upward, engaging your glutes and lower back. Hold for a few seconds, then slowly lower back down. Perform 10–15 repetitions.
- Benefits: By strengthening the lower back and gluteal muscles, this exercise helps to stabilize the spine and reduce the risk of further injury.
cat/cow stretch
This dynamic stretch enhances spinal flexibility and relieves tension, making it a staple in any exercise routine for facet joint syndrome.
- Instructions: Start on all fours with hands under shoulders and knees under hips. Inhale, arching your back (cow position), then exhale, rounding your back (cat position). Alternate between positions for 10–15 cycles.
- Benefits: The cat/cow stretch improves spinal flexibility and helps in easing tension, promoting a wider range of motion.
child’s pose
Rooted in yoga, the child's pose is a restorative stretch that gently elongates the spine and hips, providing relief from stiffness.
- Instructions: Kneel on the floor, then sit back on your heels. Extend your arms forward, lowering your torso towards the ground. Hold the stretch for 30 seconds to 1 minute.
- Benefits: This pose helps in elongating the spine and hips, relieving stiffness and promoting relaxation.
core stabilization exercises
Core stabilization exercises, such as planks and abdominal bracing, are essential for providing additional support to the spinal joints.
- Instructions: Engage in exercises like planks or abdominal bracing to strengthen core muscles. Focus on maintaining a neutral spine position throughout.
- Benefits: Strengthening the core muscles provides crucial support to the spinal joints, reducing stress on the facet joints and enhancing overall stability.
exercises and activities to avoid
While exercise is beneficial, it is equally important to avoid activities that may exacerbate symptoms of facet joint syndrome. High-impact sports, heavy lifting, and excessive twisting or bending can place undue stress on the spine and should be approached with caution. Always consult a healthcare professional before embarking on new exercise regimens to ensure they are safe and suitable for your specific condition.
By incorporating these recommended exercises and being mindful of activities to avoid, individuals with facet joint syndrome can take proactive steps toward a pain-free life. Consistent practice of these exercises can unlock relief, enhancing mobility and improving quality of life.
adjunct therapies and broader management strategies
In addition to targeted exercises, various adjunct therapies can play a significant role in managing facet joint syndrome. Physical therapy is often recommended as a primary non-invasive treatment, focusing on personalized exercise regimens and manual therapy techniques to alleviate pain and improve function. Techniques such as muscle energy therapy and lumbar stabilization exercises have shown short-term benefits in reducing pain and enhancing mobility.
Pain Neuroscience Education (PNE) is another promising approach that, when combined with exercise, can lead to significant improvements in pain management. PNE helps patients understand the mechanisms of pain, which can reduce fear and improve engagement with treatment plans. Recent studies highlight the effectiveness of telerehabilitation, where PNE and exercise are delivered remotely, offering convenient access to therapy and potentially enhancing adherence to exercise programs.
For individuals with more severe symptoms, additional interventions such as medication, weight management, and injections may be necessary. These treatments can provide temporary relief and support the effectiveness of exercise and therapy. However, they should be considered in consultation with healthcare professionals to ensure a comprehensive and tailored treatment plan.
enhancing user engagement through multimedia and resources
In today's digital age, incorporating multimedia content such as videos and images can significantly enhance user engagement and understanding. Demonstrating exercises through visual aids can help individuals perform movements correctly and safely, reducing the risk of injury and maximizing the benefits of their exercise routine. Offering downloadable resources, such as printable exercise guides, can also provide users with convenient access to exercise instructions, encouraging consistent practice.

Women's Posture Shirt™ - Black
Patented Posture Shirt™ that helps relieve back pain and improve postural awareness throughout daily activity.
With the growing trend of telerehabilitation, there is an increasing demand for virtual exercise programs and resources that individuals can access from the comfort of their homes. By providing comprehensive, evidence-based content and utilizing multimedia tools, individuals with facet joint syndrome can be better equipped to manage their condition effectively.
frequently asked questions
what is facet joint syndrome?
Facet joint syndrome involves inflammation and pain in the joints connecting the vertebrae, often leading to back pain and stiffness.
can exercise cure facet joint syndrome?
While exercise cannot cure the condition, it can significantly reduce symptoms and improve mobility.
how often should I do these exercises?
Aim for consistency, performing these exercises several times a week, but adjust based on comfort and professional guidance.
are these exercises safe for everyone?
Generally safe, but individuals should consult with healthcare providers to tailor exercises to their specific needs.
By integrating these strategies and recommendations, individuals dealing with facet joint syndrome can take proactive steps towards a pain-free life. With a combination of targeted exercises, adjunct therapies, and the use of engaging multimedia content, managing this condition becomes more accessible and effective.
Källor
- Best Health System. ”Three Exercises for Facet Syndrome Patients.”
- Sciatica.com. ”Exercises for Facet Syndrome.”
- Medical News Today. ”Facet Joint Pain: Exercises to Avoid.”
- YouTube. ”Facet Joint Syndrome Exercises.”
- YouTube. ”Exercises for Facet Joint Pain.”
- Bodi Empowerment. ”4 Exercises for Lumbar Facet Irritation and Lumbar Facet Syndrome.”
- Sperling Medical Group. ”Gentle Exercise Can Help Reduce Facet Joint Pain.”