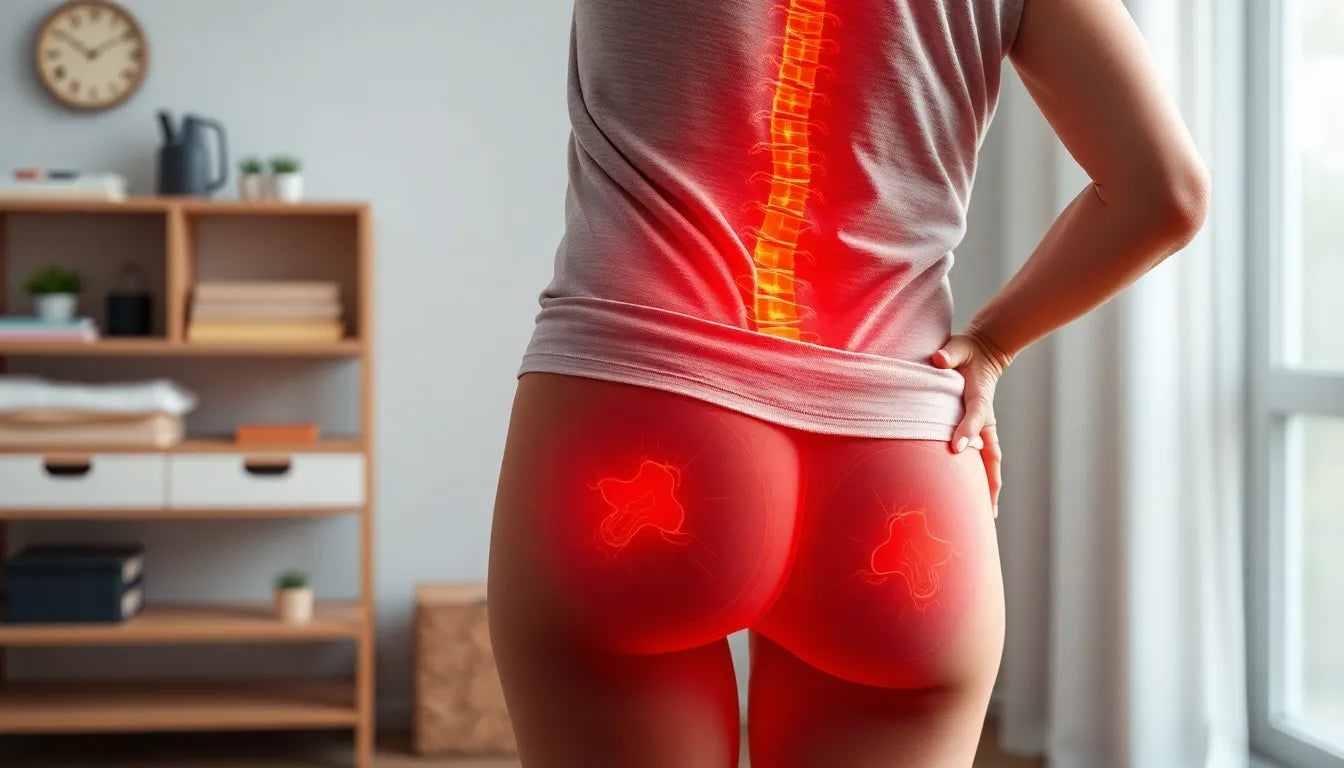
Stabbing lower back pain is a sudden and often debilitating experience that can catch anyone off guard. Unlike the persistent, dull ache that many associate with typical lower back pain, this sharp, acute sensation can strike without warning, leaving individuals searching for relief and answers. Understanding the nature of this intense discomfort is crucial, as it can significantly impact daily life and overall well-being.
importance of understanding causes of stabbing lower back pain
Identifying the underlying causes of stabbing lower back pain is essential for effective treatment and management. This type of pain can arise from a variety of sources, each requiring a different approach to care. While musculoskeletal injuries like muscle strains, ligament tears, or herniated discs are common culprits, more serious conditions such as kidney stones, infections, or issues with internal organs can also manifest as sharp back pain. Recognizing these potential causes helps in taking timely and appropriate action, preventing further complications.
setting the stage for understanding and action
The purpose of this blog is to delve into the complexities of stabbing lower back pain, providing readers with a comprehensive understanding of its causes, symptoms, and the necessary steps to take when faced with such discomfort. By exploring the various factors that contribute to this type of pain, we aim to equip you with the knowledge needed to make informed decisions about your health. Whether it's distinguishing between mechanical and non-mechanical pain or recognizing when to seek medical evaluation, this guide is designed to support you on your journey to relief and recovery.
common causes of stabbing lower back pain
Stabbing lower back pain can be triggered by a range of factors, each presenting distinct symptoms and requiring tailored interventions. Understanding these causes is pivotal for effective management and relief. Let's explore the primary culprits behind this intense discomfort:
musculoskeletal causes
Muscle strains and spasms are frequent offenders when it comes to sudden, sharp lower back pain. Overexertion, awkward movements, or lifting heavy objects can lead to muscle fibers stretching or tearing, resulting in acute pain. Similarly, spasms occur when muscles involuntarily contract, often as a protective response to injury, causing intense discomfort.
Herniated discs represent another common cause. This condition occurs when the soft inner gel of a spinal disc protrudes through its outer layer, irritating nearby nerves. This can lead to stabbing pain, often accompanied by numbness or weakness in the legs.
Facet joint syndrome, a less-discussed condition, involves inflammation or degeneration of the joints that connect the vertebrae. This can cause sharp pain, particularly when bending or twisting.
structural and mechanical causes
Lumbar spinal stenosis, characterized by the narrowing of the spinal canal, can exert pressure on the spinal cord and nerves, leading to stabbing pain. This condition often manifests as increased discomfort during activities like walking or standing.
Compression fractures, typically resulting from osteoporosis, occur when the vertebrae become fragile and collapse. This can cause sudden, severe pain, especially in older adults or those with weakened bones.
non-mechanical and organ-related causes
Beyond the musculoskeletal system, internal organ issues can also manifest as stabbing lower back pain. Kidney stones, for instance, are notorious for causing sharp pain that radiates to the lower back and abdomen. Accompanying symptoms may include urine discoloration and fever, necessitating prompt medical attention.
Infections, such as kidney infections, can similarly present with stabbing pain, often alongside systemic symptoms like fever and malaise. Additionally, conditions affecting the bladder, colon, or reproductive organs can refer pain to the lower back, making it crucial to consider these possibilities in diagnosis.
distinguishing mechanical vs. non-mechanical pain
Understanding whether your pain is mechanical or non-mechanical is essential in guiding appropriate treatment. Mechanical pain typically arises from physical stressors or structural abnormalities, while non-mechanical pain may stem from internal organ issues or systemic conditions. Here's a simple checklist to help differentiate:
- Mechanical pain: Often worsens with movement or specific activities, may improve with rest, and is typically localized.
- Non-mechanical pain: May be constant, not relieved by rest, and often accompanied by systemic symptoms like fever or changes in urination.
importance of professional diagnosis
Given the complexity of potential causes, seeking a professional diagnosis is crucial, especially for persistent, severe, or radiating pain. Medical evaluation often involves imaging studies, such as X-rays or MRIs, to identify the underlying issue accurately. Consulting with healthcare professionals ensures that you receive a tailored treatment plan, addressing both the symptoms and root causes of your pain.
In conclusion, while stabbing lower back pain can be distressing, understanding its various causes and seeking timely medical advice can pave the way for effective relief and recovery. By distinguishing between mechanical and non-mechanical origins, you can take informed steps towards managing your condition and improving your quality of life.

Lumbar support belt
Provides adjustable lumbar support to relieve and prevent lower back pain.
effective treatment and management strategies for stabbing lower back pain
Experiencing stabbing lower back pain can be distressing, but understanding how to manage it effectively can make a significant difference in recovery. Here, we explore both conservative management techniques and advanced care options to provide a comprehensive approach to treatment.
conservative management
For many, initial treatment of stabbing lower back pain involves conservative management strategies. Rest is crucial, but it should be balanced with gentle activity to prevent stiffness and promote healing. Modifying daily activities to avoid exacerbating the pain is also essential. Over-the-counter non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and analgesics can help reduce inflammation and alleviate pain. However, it is important to use these medications as directed to avoid potential side effects.
Physical therapy plays a vital role in managing lower back pain. Early intervention with tailored exercises can strengthen the back muscles, improve flexibility, and prevent future episodes. A physical therapist can design a personalized program that addresses specific needs and promotes long-term recovery.

Men's Posture Shirt™ - White
Patented shirt that supports posture and relieves back, neck, and shoulder pain.
when to seek advanced care
While many cases of stabbing lower back pain improve with conservative treatment, some situations require advanced care. Surgical options might be necessary if the pain is due to structural issues like herniated discs or spinal stenosis, and conservative measures have failed. A multidisciplinary approach, involving pain management specialists, neurosurgeons, and other healthcare professionals, ensures comprehensive care for complex cases.
preventive measures and ergonomic tips
Preventing future episodes of stabbing lower back pain involves adopting ergonomic practices both at home and in the workplace. Here are some practical tips to consider:
- Ensure your workstation is ergonomically sound by adjusting chair height, desk level, and monitor position to maintain a neutral spine posture.
- Incorporate regular breaks to stand, stretch, and move around to reduce strain on your back.
- Practice safe lifting techniques by bending at the knees and keeping heavy objects close to your body.
- Engage in regular physical activity to maintain a healthy weight and strengthen the core muscles that support the spine.
frequently asked questions
What are the red-flag symptoms that warrant immediate medical attention?
Red-flag symptoms include persistent pain, radiating pain to the legs, sensory changes such as numbness or tingling, fever, urinary symptoms, and loss of bladder or bowel control. These signs require urgent medical evaluation.
Can lifestyle changes help prevent stabbing lower back pain?
Yes, lifestyle changes such as regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, and practicing ergonomic habits can significantly reduce the risk of developing stabbing lower back pain.
How long should I try conservative treatment before seeing a doctor?
If the pain persists beyond 1-2 weeks or worsens, it is advisable to seek medical evaluation to rule out serious underlying conditions and receive appropriate treatment.
Is stabbing lower back pain always a sign of a serious condition?
Not necessarily. While stabbing lower back pain can be alarming, it is not always indicative of a serious condition. However, it is important to have it assessed by a healthcare professional to rule out any serious causes.
What role do ergonomic aids play in managing back pain?
Ergonomic aids, such as supportive chairs, adjustable desks, and lumbar supports, can help maintain proper posture and reduce strain on the back, potentially alleviating pain and preventing future episodes.
Kilder
- Redefine Healthcare. "Sharp Stabbing Pain in the Lower Left Side of the Back."
- Mainstay Medical. "Sudden Sharp Pain in Lower Back."
- ASAP Pain Docs. "What Causes Sudden Sharp Pain in Lower Back."
- Medical News Today. "Lower Back Pain: Causes, Treatment, and When to See a Doctor."
- UT Southwestern Medical Center. "5 Signs Your Back Pain Might Be an Emergency."
- Cleveland Clinic. "Lower Back Pain."
- Mayo Clinic. "Back Pain - Symptoms and Causes."
- University of Maryland Medical System. "Spine Conditions: Signs and Symptoms."
- Cleveland Clinic. "Lower Right Back Pain."