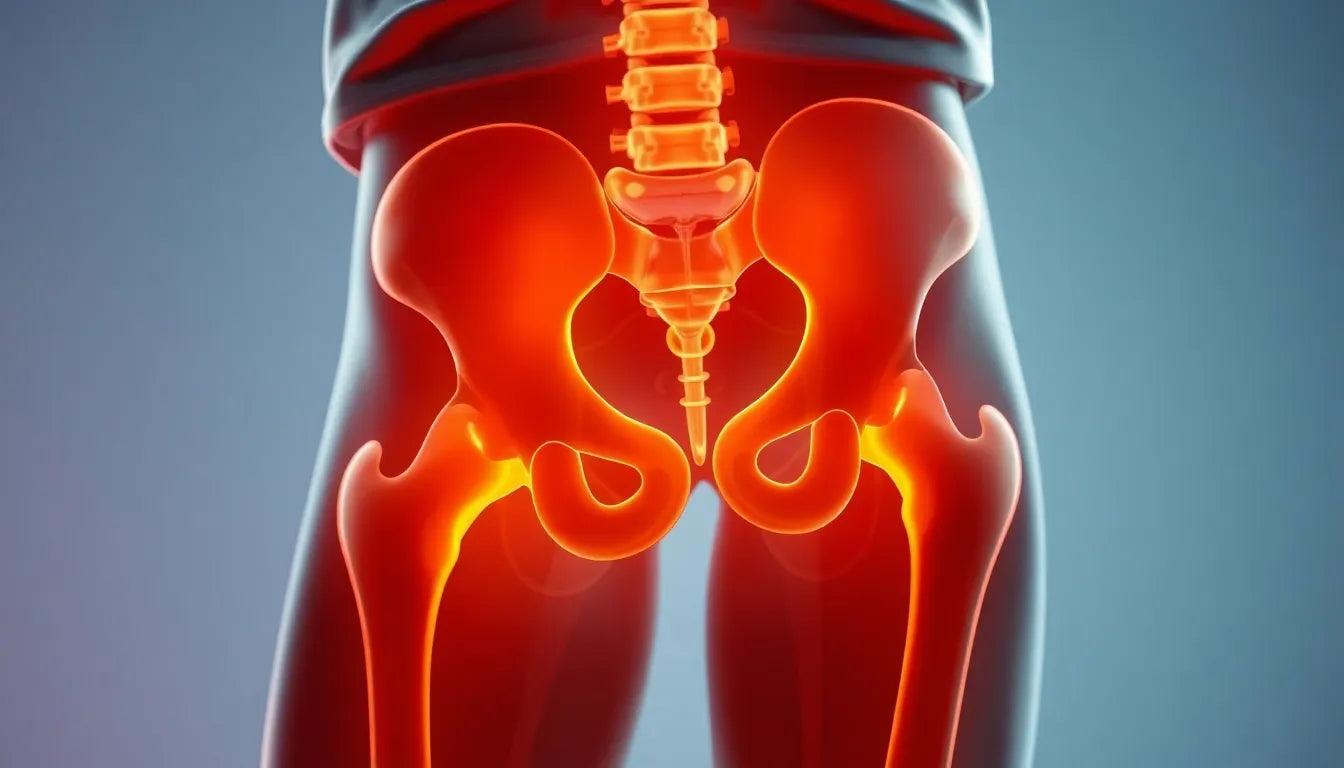
The hip plays a pivotal role in human mobility and stability, acting as the body's largest weight-bearing joint. This crucial component of our anatomy is designed to support the weight of the body while allowing for a wide range of movements. From walking and running to sitting and standing, the hip is involved in nearly every action we perform daily. Its unique ball-and-socket structure, formed by the femoral head fitting into the acetabulum of the pelvis, provides both stability and flexibility, enabling us to move with ease and balance.
Understanding common hip issues
Despite its robust design, the hip is not immune to problems. Many individuals experience hip-related issues, which can significantly impact their quality of life. Common conditions include arthritis, which can lead to pain and stiffness, making movement challenging. Osteoarthritis, the wear-and-tear form of arthritis, and rheumatoid arthritis, an autoimmune disorder, are prevalent culprits. Additionally, fractures are a serious concern, especially among older adults, as they can lead to prolonged immobility and require extensive rehabilitation.
Labral tears, another common issue, can occur from injury or repetitive motion, causing pain and limiting the range of motion. These tears affect the labrum, a ring of cartilage that follows the outside rim of the socket of the hip joint, providing cushioning and stability. Without proper care and attention, these conditions can severely restrict mobility and lead to a decline in overall health.
Maintaining hip health for a better life
Given the hip's essential role in our daily activities, maintaining its health is crucial for ensuring a high quality of life. Keeping the hip joint healthy can prevent many of the common issues associated with it. Regular exercise, a balanced diet rich in nutrients that support bone health, and maintaining a healthy weight can all contribute to the longevity and functionality of the hip joint. Additionally, being mindful of posture and ergonomics, especially in sedentary environments, can help reduce stress on the hips and prevent injury.

Lumbar support belt
Provides adjustable lower back support and relief for everyday activities.
By understanding the importance of the hip and the common challenges it faces, individuals can take proactive steps to preserve their hip health. Whether through lifestyle adjustments, exercise, or seeking professional advice, prioritizing hip health can lead to a happier, more active life.
anatomy of the hip: a closer look
The hip's intricate design is a marvel of human anatomy, characterized as a synovial, ball-and-socket joint. This configuration allows for a wide range of motion while maintaining the stability necessary to support the body's weight. The joint is formed by the femoral head, which acts as the 'ball,' fitting snugly into the acetabulum of the pelvis, the 'socket.' This union is crucial for the hip's function as a major weight-bearing joint.
Supporting the hip's structure is a robust bony architecture comprising the femur, ilium, ischium, and pubis. These bones form the framework that supports the joint. The hip's stability is further reinforced by a network of strong ligaments, including the iliofemoral, pubofemoral, and ischiofemoral ligaments, which limit excessive movement and protect the joint from injury.
Muscles play a vital role in hip function, with key groups such as the gluteals, adductors, iliopsoas, quadriceps, and hamstrings working in concert to facilitate movement and maintain stability. The soft tissues, including articular cartilage, the labrum, and the synovial membrane, provide cushioning and lubrication, reducing friction and wear within the joint.
biomechanics and functionality: the hip in motion
The hip's primary functions center around providing stability and facilitating a diverse range of movements. It supports the body's weight during standing and dynamic activities like walking, running, and jumping. The hip allows for movements such as flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, internal and external rotation, and circumduction, making it one of the most versatile joints in the body.
Balancing stability with a wide range of motion is critical for optimal hip function. This balance is achieved through the interplay of the joint's structural components and the surrounding muscles and ligaments. While the hip must be stable enough to bear weight and resist dislocation, it also needs the flexibility to perform complex movements. This dynamic equilibrium is essential for maintaining joint health and preventing injuries.
common conditions affecting the hip
Despite its robust design, the hip is susceptible to various conditions that can impact its function and an individual's quality of life. Arthritis is a common ailment, with osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis being the most prevalent types. Osteoarthritis results from wear and tear, leading to pain and stiffness, while rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder that causes joint inflammation.
Injuries such as fractures and labral tears are also significant concerns. Fractures, particularly in older adults, can lead to prolonged immobility and require extensive rehabilitation. Labral tears, which affect the cartilage around the hip socket, can result from trauma or repetitive motion, causing pain and limiting mobility.
The clinical significance of these conditions cannot be overstated, as they often lead to pain, weakness, and restricted movement, severely affecting daily life. Understanding these issues is crucial for early intervention and management, which can help preserve hip function and improve overall well-being.
clinical and rehabilitation perspectives for hip health
Maintaining optimal hip health is crucial not only for daily activities but also for recovery after injuries. Clinical interventions, particularly physiotherapy, play a vital role in rehabilitation. Physiotherapists design personalized exercise programs to strengthen the muscles around the hip, improve flexibility, and restore movement patterns. These programs are essential for individuals recovering from surgeries or injuries, such as fractures or labral tears, as they help regain strength and functionality.

Women's Posture Shirt™ - Nude
Patented shirt to help improve posture and reduce pain for women.
Ergonomic interventions also contribute significantly to hip health. By incorporating ergonomic solutions into daily life, individuals can prevent injuries and manage existing conditions more effectively. For instance, using ergonomic chairs that support proper posture can alleviate hip pain associated with prolonged sitting. Similarly, standing desks and cushioned mats can reduce strain on the hips during work hours, promoting better joint health.
ergonomic considerations for hip health
Integrating ergonomic practices into daily routines is a proactive approach to maintaining hip health. Lifestyle changes, such as incorporating regular breaks to stretch and move, can prevent stiffness and discomfort. Ergonomic aids, like supportive footwear and cushions, provide additional comfort and reduce the risk of hip-related issues.
Incorporating exercises that focus on strengthening the hip muscles is equally important. Activities like swimming, cycling, and yoga can enhance flexibility and support joint health. These exercises not only improve muscle tone but also promote better blood circulation, which is vital for maintaining healthy hip joints.
frequently asked questions
What are the main causes of hip pain?
Hip pain can result from various factors, including arthritis, injuries, and overuse. Arthritis, such as osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis, leads to joint inflammation and pain. Injuries like fractures or labral tears can also cause significant discomfort. Overuse from repetitive movements or poor posture can strain the hip, leading to pain over time.
How can I prevent hip injuries?
Preventing hip injuries involves a combination of regular exercise, ergonomic aids, and lifestyle adjustments. Strengthening exercises for the hip muscles, maintaining a healthy weight, and using supportive footwear can reduce the risk of injuries. Additionally, incorporating ergonomic solutions, such as adjustable workstations, can help maintain proper posture and prevent strain on the hips.
When should I see a doctor for hip pain?
It is advisable to consult a doctor if hip pain persists despite home remedies, affects daily activities, or is accompanied by swelling, redness, or warmth around the joint. Sudden, severe hip pain or an inability to bear weight on the affected leg also warrants immediate medical attention.
What are the treatment options for hip arthritis?
Treatment options for hip arthritis range from non-surgical to surgical interventions. Non-surgical treatments include physical therapy, medications for pain relief and inflammation, and lifestyle modifications. In severe cases, surgical options such as hip replacement may be considered to restore mobility and alleviate pain.
How can ergonomic aids help with hip health?
Ergonomic aids support hip health by promoting proper posture and reducing strain on the joints. Products like ergonomic chairs, standing desks, and supportive cushions help maintain alignment and distribute weight evenly, minimizing the risk of pain and injury. These aids are particularly beneficial for individuals with sedentary lifestyles or those recovering from hip conditions.
Kilder
- iHip. (2023). "BL-33 True Wireless Lightup LU Soundpods Manual."
- iFi. (2023). "Hip-DAC2: Our Portable USB Amplifier Manual."
- ActivePosture. (2023). "Practice Reader Finds Relief from Spændingshovedpine with These Exercises."
- ClinicalTrials.gov. (2023). "NCT06977529."
- Aarhus University Health. (2023). "Research Publications."