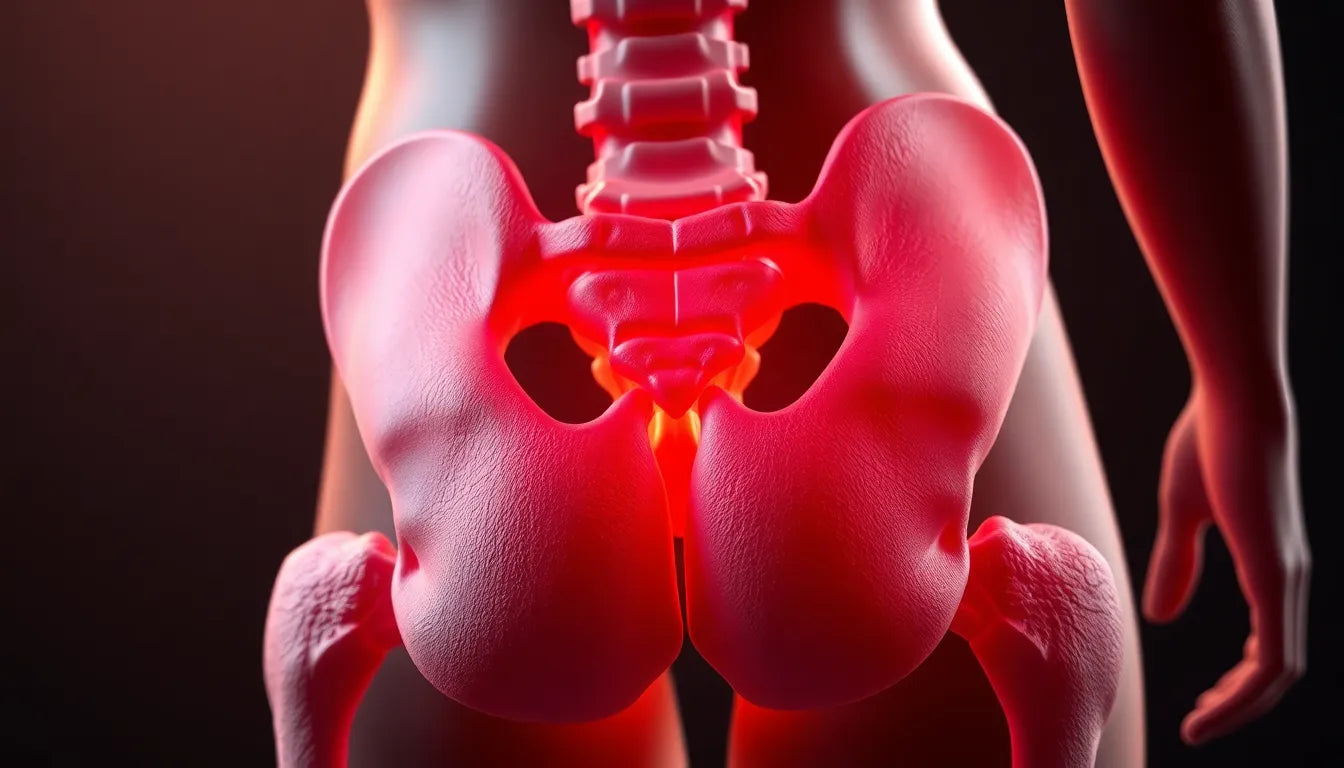
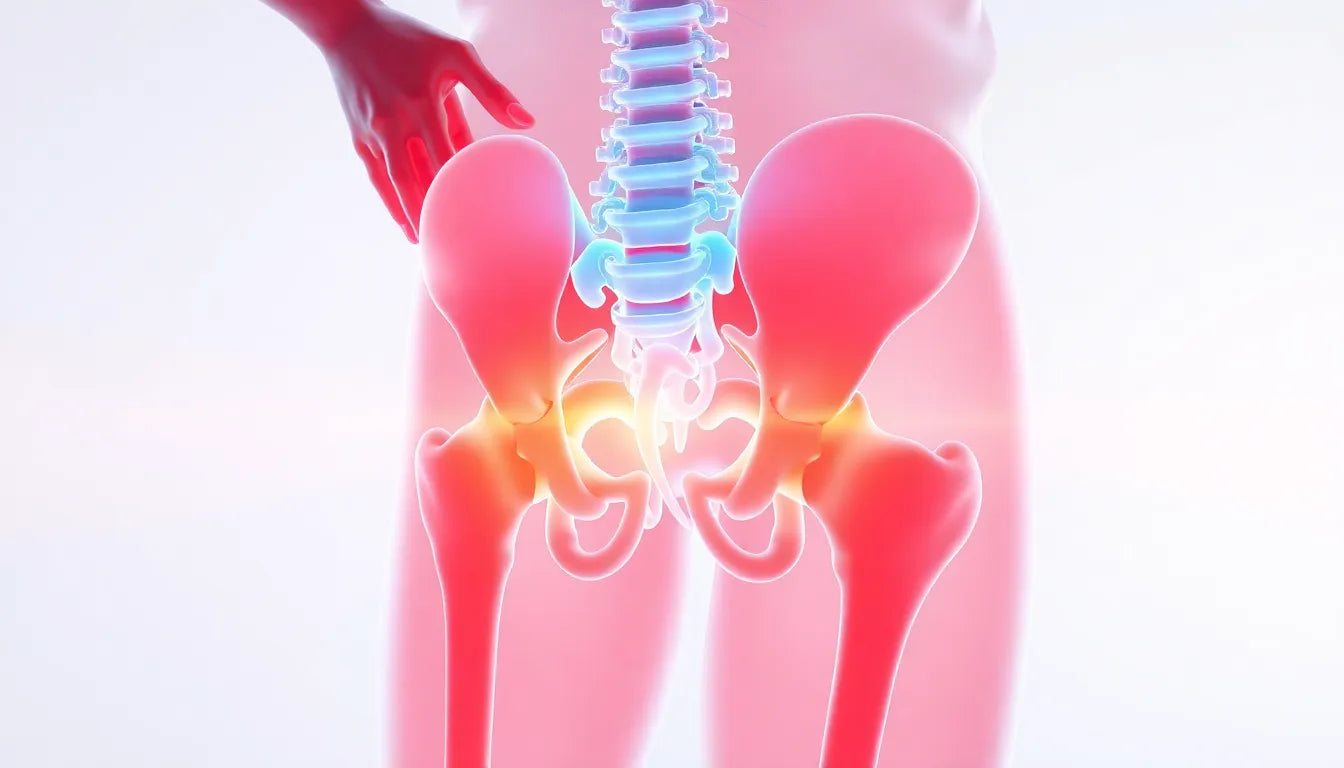
The hip socket, or acetabulum, plays a pivotal role in our daily lives, enabling us to perform essential activities such as walking, sitting, running, and jumping. As a central component of the hip joint, it is crucial for maintaining mobility and ensuring a high quality of life. Without a healthy hip socket, even the simplest movements can become challenging, impacting our ability to engage in everyday tasks and enjoy an active lifestyle.
understanding the hip socket's anatomy and function
The hip socket is part of a sophisticated ball-and-socket joint, which is one of the most flexible types of joints in the human body. This design allows for a wide range of motion, making it possible for us to move our legs in multiple directions with ease. The acetabulum is the cup-shaped cavity on the pelvis that houses the femoral head, the ball-like top of the femur, or thigh bone. Together, these structures form the hip joint, which is stabilized by a network of strong ligaments and muscles.
The hip joint's ability to support major body movements is vital for overall health. It not only facilitates movement but also bears the weight of the upper body when standing and moving. The cartilage lining the acetabulum acts as a cushion, reducing friction and preventing wear and tear on the bones. Additionally, the labrum, a ring of cartilage that surrounds the acetabulum, enhances the joint's stability and helps maintain its structural integrity.
the purpose of exploring hip socket health
This blog post aims to provide readers with a comprehensive understanding of the hip socket, covering its anatomy, common issues, and strategies for maintaining hip health. By delving into the intricacies of the hip joint, we hope to equip you with the knowledge needed to keep your hips pain-free and functional. Whether you're experiencing discomfort or simply want to prevent future problems, understanding the hip socket's role in your body is the first step towards ensuring a lifetime of mobility and activity.
In the following sections, we will explore the detailed anatomy of the hip socket, discuss its range of motion, and address common issues that can arise. We'll also offer practical advice on how to maintain hip health, including preventive measures and lifestyle changes that can help you avoid pain and injury. By the end of this post, you'll have the tools you need to support your hip joint and enjoy a pain-free life.
anatomy and basic function of the hip socket
The hip socket, known scientifically as the acetabulum, is a crucial component of the pelvic bone structure. This cup-shaped cavity is designed to accommodate the femoral head, which is the rounded top portion of the femur or thigh bone. Together, they form the hip joint, a marvel of engineering that allows for a remarkable range of motion. This joint's design is akin to a ball-and-socket, providing the flexibility needed for various activities ranging from walking to intricate athletic movements.
Stability within this joint is achieved through a combination of ligaments and cartilage. The iliofemoral, pubofemoral, and ischiofemoral ligaments are key players in this stabilization, ensuring that the femoral head remains securely within the acetabulum during movement. Additionally, the joint is cushioned by articular cartilage, which lines the acetabulum, acting as a shock absorber to minimize friction and wear. Surrounding the acetabulum is the labrum, a ring of cartilage that not only enhances the joint's stability but also provides a seal to maintain joint fluid pressure.
mobility and range of motion in the hip socket
The hip socket's unique structure allows for a wide range of movements, essential for both everyday activities and athletic performance. Key movements facilitated by this joint include:
- Flexion: This involves lifting the thigh forward and can reach up to 140 degrees, enabling actions like walking and running.
- Extension: Stretching the thigh backward, typically up to 15 degrees, is crucial for activities such as standing upright and climbing stairs.
- Abduction/Adduction: Abduction involves moving the leg outwards up to 45 degrees, while adduction brings it inwards up to 30 degrees. These movements are vital for maintaining balance and agility.
- Rotation: The hip allows for both inward and outward rotation, facilitating complex leg movements necessary for sports and dance.
To better understand these movements, a visual representation can be immensely helpful. Imagine a table summarizing the range of motion for each type of movement, providing a clear picture of the hip socket's capabilities.
common issues and prevention strategies
Despite its robust design, the hip socket is not immune to problems. Common issues include arthritis, which results from cartilage damage and leads to pain and reduced mobility. Labral tears are another concern, often causing joint instability and discomfort. Additionally, the synovial membrane, which produces lubricating fluid for the joint, plays a vital role in maintaining joint health. Damage or inflammation here can lead to pain and stiffness.
Preventing these issues involves maintaining mobility and engaging in regular exercise. Strengthening the muscles around the hip can provide additional support and reduce the risk of injuries. Ergonomic aids, such as supportive footwear and cushions, can also help in minimizing stress on the hip joint. Incorporating lifestyle changes, like maintaining a healthy weight and avoiding repetitive strain, can further protect the hip socket.

Lumbar support belt
Provides lower back support and relief for pain and tension, fully adjustable for daily use.
For those looking for more interactive learning, animated tutorials and videos can offer valuable insights into the hip joint's function and common injury mechanisms. By understanding the intricacies of the hip socket, individuals can take proactive steps to ensure a lifetime of pain-free mobility.
common hip socket issues and prevention strategies
The hip socket, despite its robust and well-engineered design, can encounter several common issues that may affect mobility and cause discomfort. One prevalent issue is arthritis, which occurs when the cartilage cushioning the acetabulum deteriorates, leading to pain and stiffness. This condition can significantly impede daily activities and reduce the quality of life.
Another common problem is labral tears, which involve the ring of cartilage surrounding the acetabulum. These tears can lead to joint instability and pain, often resulting from repetitive movements or acute injuries. The synovial membrane, responsible for producing the lubricating fluid in the joint, can also become inflamed, causing pain and reduced mobility.
Preventing these issues involves a proactive approach to maintaining hip health. Regular exercise, particularly activities that strengthen the muscles around the hip joint, can provide additional support and reduce the risk of injuries. Flexibility exercises can also help maintain a healthy range of motion, ensuring that the joint remains functional and pain-free.
Ergonomic aids, such as supportive footwear and cushions, can play a crucial role in minimizing stress on the hip joint. These aids help distribute weight evenly and reduce the impact on the hip socket during daily activities. Additionally, maintaining a healthy weight is essential, as excess weight can increase the strain on the hip joints, accelerating wear and tear.

Women's Posture Shirt™ - Black
Improves posture, relieves pain and tension, and activates muscles for daily support.
Incorporating lifestyle changes, such as avoiding repetitive strain and ensuring proper posture, can further protect the hip socket. For those who prefer interactive learning, animated tutorials and videos can offer valuable insights into the hip joint's function and common injury mechanisms. By understanding the intricacies of the hip socket, individuals can take proactive steps to ensure a lifetime of pain-free mobility.
frequently asked questions
What causes hip socket pain?
Hip socket pain can be caused by various factors, including arthritis, labral tears, and overuse injuries. Arthritis results from the deterioration of cartilage, leading to pain and stiffness. Labral tears can cause joint instability and discomfort, often due to repetitive movements or acute trauma. Overuse injuries, common in athletes, can also contribute to hip socket pain.
How can I prevent hip socket injuries?
Preventing hip socket injuries involves maintaining a regular exercise routine that focuses on strengthening the muscles around the hip joint. Flexibility exercises can help preserve a healthy range of motion. Ergonomic aids, such as supportive footwear and cushions, can minimize stress on the joint. Additionally, maintaining a healthy weight and avoiding repetitive strain can further protect the hip socket.
What are the treatment options for hip socket issues?
Treatment options for hip socket issues vary depending on the specific condition. Physical therapy is often recommended to strengthen the surrounding muscles and improve flexibility. Ergonomic aids, such as braces or orthotics, can provide additional support. In some cases, medical interventions like corticosteroid injections or surgery may be necessary to address severe conditions.
When should I see a doctor for hip pain?
It is advisable to see a doctor if hip pain persists despite home remedies or if it significantly affects your daily activities. Other signs that warrant medical evaluation include sudden, severe pain, swelling, or inability to bear weight on the affected leg. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent further complications and ensure a better outcome.
Kilder
- Grossman, E. (n.d.). "Hip Anatomy." Eric Grossman MD.
- Same Day Hip and Knee Surgery. (n.d.). "Anatomy and Function of the Hip."
- Kelly, B. (n.d.). "Normal Anatomy of the Hip Joint." Bryan Kelly MD.
- Kelley, T. (n.d.). "Hip Orthopaedic Surgeon." Todd Kelley MD.
- Arthritis Foundation. (n.d.). "Anatomy of the Hip."
- MedlinePlus. (n.d.). "Hip Joint Anatomy."
- NCBI. (n.d.). "Hip Joint Anatomy."
- TeachMeAnatomy. (n.d.). "Hip Joint."
- Cleveland Clinic. (n.d.). "Hip Joint."
- TeachMeAnatomy. (n.d.). "Hip Bone."