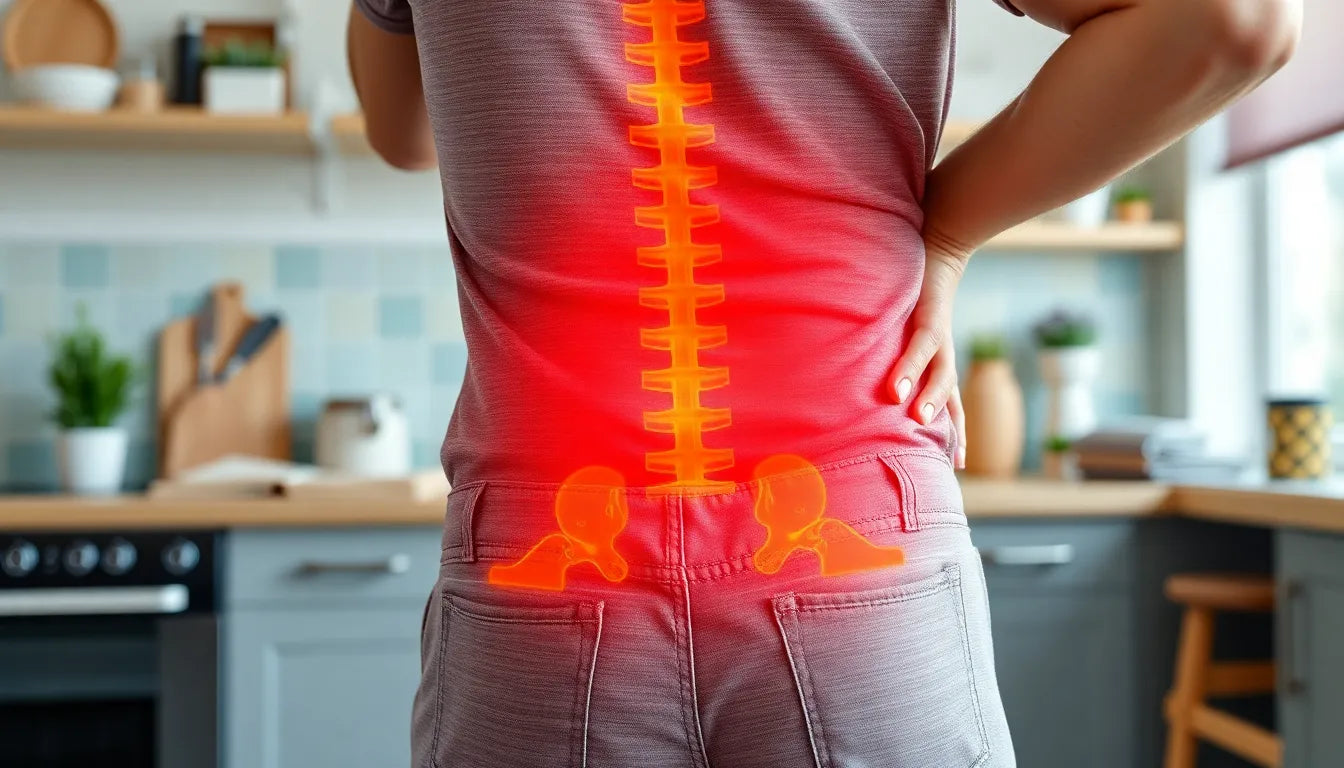
Experiencing pain in the groin and back can be both distressing and disruptive. These discomforts are not uncommon and can significantly impact daily life, making even simple movements challenging. The groin and back are critical areas of the body, and pain in these regions can often be interrelated, complicating the identification of the root cause and effective treatment. Understanding the connection between groin and back pain is essential for finding relief and preventing future occurrences.
understanding the link between groin and back pain
The relationship between groin and back pain is often overlooked, yet it is crucial to recognize that these pains can stem from interconnected causes. The body’s complex network of nerves and muscles means that an issue in one area can easily affect another. For instance, nerve compression or strain in the lower back can lead to referred pain in the groin. This is because the nerves that supply the groin also originate from the lower back, making it a common site for referred pain.
Moreover, conditions such as epididymitis, an inflammation of the epididymis, can cause pain that radiates from the groin to the back. Understanding these interconnections is vital for accurate diagnosis and treatment. Without addressing the underlying cause, relief may be temporary, and the pain could return or worsen.
exploring the causes and seeking relief
The purpose of this blog post is to delve into the common causes and symptoms of groin and back pain, as well as to provide strategies for relief. By exploring the potential reasons behind these pains, individuals can better understand their bodies and seek appropriate treatment. Whether the pain is due to conditions such as epididymitis, nerve compression, or even more serious issues like testicular cancer, identifying the cause is the first step towards effective management.
In the following sections, we will explore various causes, from infections to nerve issues, and discuss the symptoms that accompany these conditions. Additionally, we will provide practical advice on how to alleviate pain and when it is crucial to seek medical attention. By gaining a comprehensive understanding of groin and back pain, individuals can take proactive steps towards relief and improved quality of life.
common causes and interconnections of groin and back pain
Understanding the underlying causes of pain in the groin and back is crucial for effective diagnosis and treatment. One prevalent cause is epididymitis, which refers to the inflammation of the epididymis, a tube at the back of the testicles that stores and carries sperm. This condition is often accompanied by symptoms such as fever, swelling, and unilateral pain. According to insights from Anodyne and Aarhus Universitetshospital, epididymitis is a primary cause of groin pain, highlighting the importance of medical evaluation when these symptoms arise.
Another significant factor is referred pain from the back to the groin. This occurs when nerve compression or issues in the lower back, such as disc herniation or muscle tension, lead to pain that radiates to the groin area. The nerves that supply the groin originate from the lower back, making it susceptible to referred pain when these nerves are affected. Recognizing this connection is essential for targeting the root cause rather than just treating the symptoms.
While less common, testicular cancer is a critical condition to rule out, especially if symptoms persist. Testicular cancer can present with symptoms like swelling, lumps, or changes in testicular consistency. It is imperative to seek medical attention for persistent symptoms to exclude this serious condition. Additionally, back pain can occur if the cancer spreads to lymph nodes in the abdomen, further emphasizing the interconnected nature of these pains.
Other causes of pain in the groin and back include conditions such as hernia, hydrocele, chronic pain syndromes, and rare nerve disorders like pudendal neuralgia. These conditions can vary in severity and require different approaches for management and relief.
recognizing symptoms and warning signs
Identifying the symptoms associated with groin and back pain can aid in early diagnosis and treatment. For instance, infection indicators such as unilateral testicular pain, swelling, fever, and urinary issues are commonly linked to epididymitis. These symptoms necessitate prompt medical evaluation to prevent complications.
In terms of cancer warning signs, unexplained swelling or lumps in the testicular area should not be ignored. These symptoms warrant immediate medical evaluation to rule out testicular cancer and ensure timely intervention.
Additionally, nerve compression symptoms can manifest as combined back and groin pain, suggesting nerve involvement. This can be due to conditions like herniated discs or muscle tension, requiring targeted treatment strategies like physiotherapy or ergonomic adjustments.
Urgent symptoms, such as acute and severe pain, demand immediate medical attention. These could indicate conditions like testicular torsion, which is a medical emergency. Rapid evaluation and treatment are crucial to prevent long-term damage.
treatment and relief strategies
Addressing pain in the groin and back involves a combination of medical intervention and lifestyle adjustments. For infections like epididymitis, treatment typically includes antibiotics, rest, pain relief, supportive underwear, and adequate hydration. These measures help alleviate symptoms and promote recovery.
For functional or nerve-related issues, physiotherapy, ergonomic adjustments, and pelvic floor exercises can be beneficial. Stress management and holistic approaches are often emphasized in lifestyle and commercial blogs, highlighting the importance of a comprehensive treatment plan that addresses both the physical and mental aspects of pain management.

Lumbar support belt
Provides stabilisation, strong compression, and relief for lower back pain and tension.
Consulting a specialist is recommended for chronic or concerning symptoms to ensure accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. A healthcare professional can provide personalized advice and interventions based on the specific cause of the pain.
By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for groin and back pain, individuals can take proactive steps towards relief and improved quality of life. Early recognition and intervention are key to preventing complications and achieving long-term pain management.
effective strategies for managing groin and back pain
Finding relief from pain in the groin and back often requires a multifaceted approach that combines medical treatment with lifestyle modifications. Proper management can significantly improve quality of life and prevent the recurrence of symptoms. For individuals experiencing these pains, understanding the available treatment options is crucial.
For infections such as epididymitis, the primary treatment involves antibiotics to address the underlying bacterial cause. Complementary measures include rest, pain relief medication, wearing supportive underwear, and ensuring adequate hydration. These steps are essential for reducing inflammation and promoting healing.
When pain is linked to functional or nerve issues, physiotherapy can play a pivotal role. Techniques such as targeted exercises and ergonomic adjustments aim to relieve pressure on affected nerves and improve muscle function. Pelvic floor exercises are particularly beneficial for strengthening the muscles that support the groin and lower back, providing additional stability and reducing pain.

Men's Posture Shirt™ - Black
Patented Neuroband™ shirt activates muscles, improves posture, and eases back pain.
Stress management is another vital component of a comprehensive pain relief strategy. Chronic pain can be exacerbated by stress, making relaxation techniques, mindfulness, and holistic approaches valuable tools in managing symptoms. Lifestyle and commercial blogs often emphasize these methods, highlighting their importance in a well-rounded treatment plan.
For persistent or severe symptoms, consulting a specialist is recommended. A healthcare professional can conduct a thorough evaluation to identify the specific cause of pain and recommend tailored interventions. This might include imaging studies, specialized therapies, or even surgical options if necessary.
By combining medical treatments with lifestyle changes, individuals can effectively manage groin and back pain, leading to improved overall well-being. Early intervention and a proactive approach are key to achieving long-term relief and preventing complications.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the most common causes of pain in the groin and back?
Pain in the groin and back can be caused by various conditions, including epididymitis, nerve compression, and hernias. These conditions often involve inflammation or pressure on nerves, leading to discomfort in both areas.
When should I see a doctor for groin and back pain?
It is essential to seek medical evaluation if you experience persistent pain, noticeable lumps, or any symptoms that do not improve with home care. Early diagnosis can prevent complications and ensure appropriate treatment.
Can lifestyle changes help alleviate these pains?
Yes, lifestyle changes such as ergonomic adjustments, regular exercise, and stress reduction can significantly help in managing groin and back pain. These modifications aim to reduce strain on affected areas and improve overall health.
Is testicular cancer a common cause of these pains?
While testicular cancer is not a common cause, it is critical to rule it out in cases of persistent symptoms. Early detection is crucial for effective treatment, so any unexplained changes should prompt medical evaluation.
What are the immediate steps to take when experiencing severe groin pain?
If you experience severe groin pain, seek urgent medical attention. In the meantime, rest and avoid activities that exacerbate the pain. Applying a cold compress can help reduce swelling and provide temporary relief.