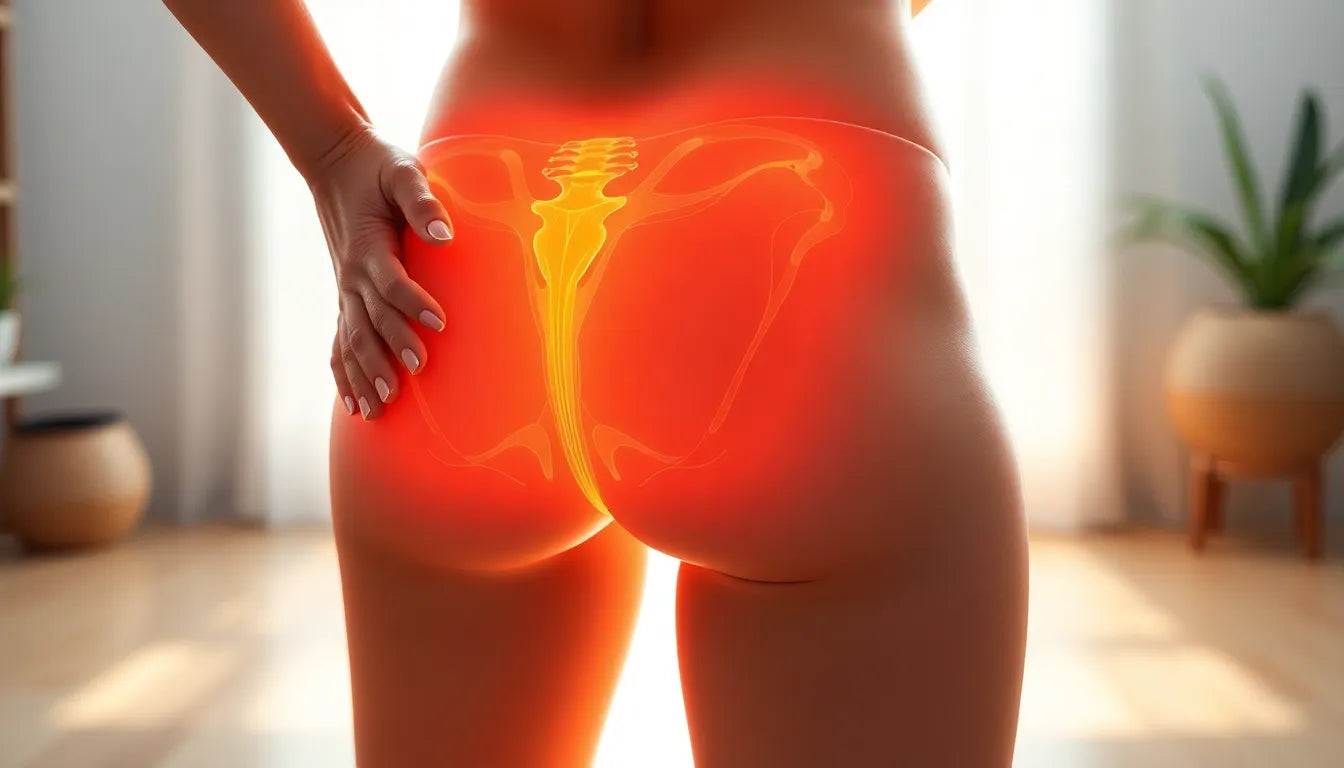
Lower back pain is a common ailment that affects a significant portion of the population, with up to 80% of Americans experiencing it at some point in their lives. This widespread issue does not discriminate; it impacts individuals across all ages and lifestyles. From the young athlete recovering from an injury to the elderly person dealing with age-related spinal changes, lower back pain is a universal concern that can arise from a variety of causes.
The origins of lower back pain are diverse. It can stem from sudden injuries, such as strains and sprains, or develop gradually due to age-related changes in the spine, like herniated discs or spinal stenosis. Additionally, underlying medical conditions, including arthritis and osteoporosis, can contribute to the discomfort. This complexity in causes makes it crucial to understand the specific nature of one's pain to manage it effectively.
How lower back pain affects daily life
The impact of lower back pain on daily life can range from mild discomfort to severe, debilitating pain. For some, it manifests as a constant, dull ache that makes it difficult to sit or stand for extended periods. For others, it can be a sharp, intense pain that limits mobility and interferes with routine activities such as walking, lifting, or even sleeping. The severity and persistence of the pain can significantly hinder one's quality of life, making even simple tasks seem daunting.
Understanding the types and causes of lower back pain is the first step toward effective management and relief. By identifying whether the pain is acute or chronic, individuals can tailor their approach to treatment accordingly. Acute pain, which lasts a few days to weeks, often responds well to rest and conservative treatments. In contrast, chronic pain, persisting for more than 12 weeks, may require a more comprehensive management plan.
Recognizing the symptoms and seeking an accurate diagnosis is essential in addressing lower back pain. Common symptoms include stiffness, sharp or dull pain, and sometimes numbness or tingling sensations that may radiate to the legs. These symptoms can indicate different underlying issues, necessitating a thorough examination and, in some cases, diagnostic imaging to pinpoint the exact cause.
By gaining a deeper understanding of lower back pain and its effects, individuals can take proactive steps toward relief and prevention. Embracing ergonomic solutions, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and seeking appropriate medical advice are all part of a holistic approach to managing this prevalent condition. As we delve further into the complexities of lower back pain, we aim to equip you with the knowledge and tools necessary to unlock relief and regain control over your daily life.

Lumbar support belt
Stabilize and relieve lower back pain with this adjustable lumbar belt, ideal for daily activity and support.
Understanding the intricacies of lower back pain
Lower back pain can be broadly categorized into two types: acute and chronic. Acute lower back pain is short-term, typically lasting from a few days to a few weeks. It often results from a sudden injury or strain, and with appropriate care, it usually resolves on its own. Chronic lower back pain, on the other hand, persists for 12 weeks or longer. This type of pain can be more complex, often requiring a comprehensive management strategy to address underlying issues and provide relief.
Several factors contribute to the onset of lower back pain. Injuries such as strains and sprains are common culprits, often resulting from overexertion or improper lifting techniques. Age-related changes, including herniated discs and spinal stenosis, also play a significant role. As people age, the spine undergoes natural degeneration, which can lead to these conditions. Additionally, medical conditions like arthritis and osteoporosis can exacerbate lower back pain, making it crucial to address these underlying health issues as part of a holistic treatment approach.
Recognizing symptoms and seeking diagnosis
The symptoms of lower back pain can vary widely, ranging from stiffness and a dull ache to sharp, shooting pain. Some individuals may experience numbness or tingling, particularly if the pain radiates down the legs, which could indicate nerve involvement. Recognizing these symptoms is vital, as they can provide clues about the underlying cause of the pain. For instance, pain that worsens with movement or improves with rest might suggest a mechanical issue, while persistent pain that doesn't respond to changes in activity could indicate a more serious condition.
Diagnosis of lower back pain typically involves a combination of physical examination and imaging tests. During a physical exam, a healthcare provider will assess the range of motion, check for areas of tenderness, and evaluate neurological function. Imaging tests, such as X-rays or MRIs, can provide detailed insights into the spine's structure, helping to identify issues like herniated discs or spinal stenosis. These diagnostic tools are crucial for developing an effective treatment plan tailored to the individual's specific needs.
The role of inflammation in lower back pain
Inflammation is a key factor in many cases of lower back pain, particularly in acute situations. Local inflammation occurs when tissues are injured, leading to swelling, redness, and pain. This type of inflammation is often seen in cases of muscle strains or disc herniation, where the body's natural response is to protect the injured area. While this can cause discomfort, it also plays a role in the healing process.
In contrast, systemic inflammation is generally less significant in chronic lower back pain. However, it can still influence pain perception and management strategies. Understanding the role of inflammation is essential for developing effective treatment plans. Anti-inflammatory medications, such as NSAIDs, are commonly used to manage pain and reduce inflammation, but it's important to balance these with other approaches, such as physical therapy and lifestyle modifications, to achieve long-term relief.
By delving deeper into the types, causes, and symptoms of lower back pain, individuals can better understand their condition and take proactive steps toward effective management. Recognizing the role of inflammation and the importance of accurate diagnosis can guide treatment choices, helping to alleviate pain and improve quality of life. As we continue to explore solutions for lower back pain, the focus remains on empowering individuals with the knowledge and tools needed to regain control over their well-being.
Treatment and management strategies for lower back pain
Effectively managing lower back pain often involves a multifaceted approach that combines conventional medical treatments with lifestyle modifications. Conventional treatments typically include rest, physical therapy, and medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and muscle relaxants. In cases where conservative measures fail to provide relief, surgical interventions might be considered, particularly for conditions like herniated discs or spinal stenosis.
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in rehabilitation, focusing on strengthening the back muscles, improving flexibility, and promoting proper posture. A tailored exercise program can help alleviate pain and prevent future episodes by enhancing core stability and reducing strain on the lower back.

Women's Posture Shirt™ - Black
Designed to stimulate muscles and relieve pain, this shirt promotes better posture for daily comfort.
Lifestyle factors are equally important in managing lower back pain. Maintaining a healthy weight reduces stress on the spine, while regular exercise keeps the muscles strong and flexible. Additionally, stress management and mental health support can influence pain perception and improve overall well-being. Techniques such as mindfulness, yoga, and cognitive-behavioral therapy have been shown to be beneficial in managing chronic pain conditions.
Ergonomic solutions and prevention
Preventing lower back pain often involves making ergonomic adjustments in daily life. Ergonomic products, such as supportive chairs, standing desks, and lumbar cushions, can significantly reduce strain during work and leisure activities. These tools help maintain proper posture, distribute weight evenly, and minimize pressure on the spine.
Incorporating ergonomic principles into everyday activities, such as lifting techniques and workstation setups, can prevent the onset of lower back pain. Simple changes, like adjusting the height of a chair or using a footrest, can make a significant difference in comfort and spinal health.
By combining ergonomic solutions with a proactive lifestyle approach, individuals can effectively manage and prevent lower back pain, enhancing their quality of life and promoting long-term spinal health.
Frequently Asked Questions
What causes lower back pain to become chronic?
Lower back pain can become chronic due to several factors, including inadequate treatment of acute pain, ongoing physical strain, and underlying medical conditions such as arthritis or degenerative disc disease. Psychological factors, such as stress and depression, can also contribute to the persistence of pain.
Can lower back pain be prevented?
Yes, lower back pain can often be prevented through regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, and practicing good posture. Ergonomic adjustments at work and home, such as using supportive furniture and proper lifting techniques, can also reduce the risk of developing lower back pain.
When should I see a doctor for lower back pain?
It is advisable to see a doctor if lower back pain is severe, persists for more than a few weeks, or is accompanied by symptoms such as numbness, tingling, or weakness in the legs. Immediate medical attention is necessary if the pain is due to an injury or if there is a loss of bladder or bowel control.
Källor
- Brown Health. (n.d.). Lower Back Pain: Causes and Treatments.
- Hospital for Special Surgery. (n.d.). Lower Back Pain In-Depth.
- American Society of Anesthesiologists. (n.d.). Back Pain.
- UPMC. (n.d.). Lower Back Pain.
- Cleveland Clinic. (n.d.). Lower Back Pain.
- Mayo Clinic. (n.d.). Back Pain: Symptoms and Causes.
- University of Maryland Medical System. (n.d.). Spine Signs and Symptoms.
- Yale New Haven Health. (n.d.). Lower Back Pain.