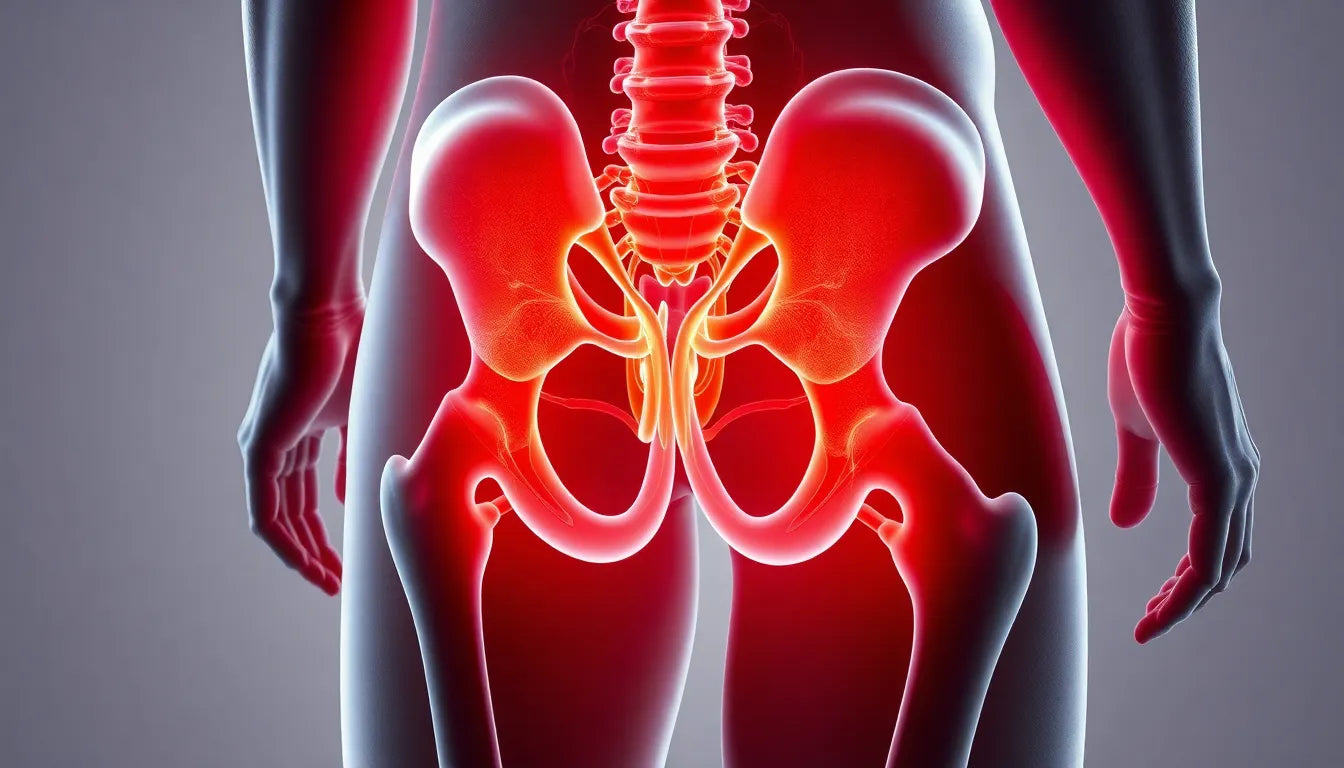
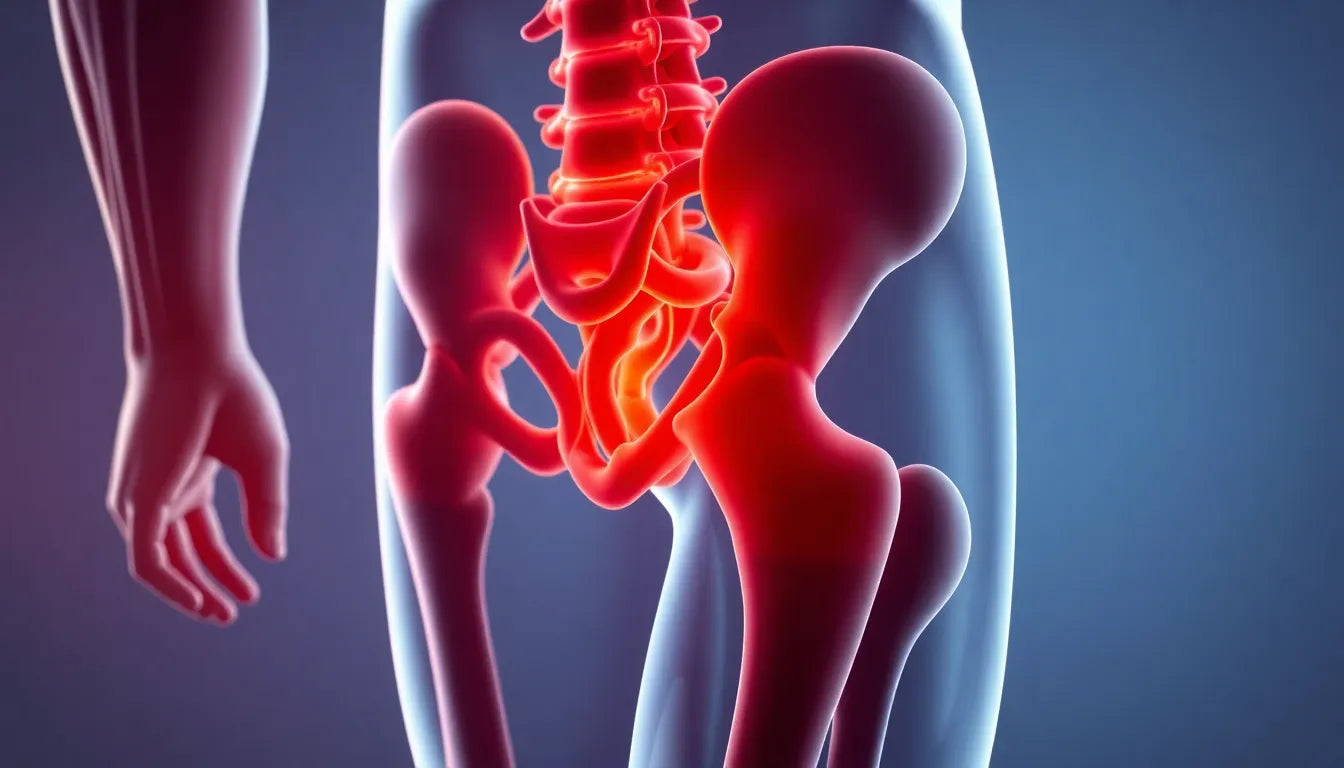
The gluteal muscles, comprising the gluteus maximus, medius, minimus, and the tensor fasciae latae, form a powerful group essential for a wide range of daily movements and maintaining proper posture. Often referred to as the "glutes," these muscles are pivotal in activities such as walking, running, and climbing stairs. Their role extends beyond mere movement; they are integral to our body's ability to maintain stability and efficiency in motion.
Understanding the importance of gluteal muscles
The gluteus maximus, the largest and most superficial of the gluteal muscles, is primarily responsible for hip extension and trunk stabilization. It comes into play during activities that require powerful lower limb actions, such as standing up from a seated position or sprinting. Beneath it lie the gluteus medius and minimus, which are crucial for thigh abduction and the stabilization of the pelvis during walking. These muscles help maintain balance and prevent the pelvis from dropping to one side when we lift a leg. The tensor fasciae latae, in collaboration with the iliotibial band, assists in hip flexion and abduction, further contributing to lower limb stability.
Common issues and their impact
Weakness in the gluteal muscles is a common issue that can lead to a host of problems, including lower back pain and poor posture. These muscles are often dubbed "antigravity muscles" because of their role in counteracting the force of gravity to keep us upright. When they are underdeveloped or not functioning optimally, the body may struggle to maintain proper alignment, leading to discomfort and increased risk of injury. In particular, weak glutes can result in an over-reliance on other muscle groups, such as the lower back and hamstrings, which may lead to muscle imbalances and strain.
Understanding the function and importance of the gluteal muscles is the first step towards harnessing their power for a pain-free lifestyle. By focusing on strengthening these muscles, individuals can improve their overall movement efficiency and reduce the risk of common musculoskeletal issues. This understanding is crucial not only for athletes but for anyone looking to enhance their physical health and well-being.
In the following sections, we will delve deeper into the anatomy and function of each gluteal muscle, explore their clinical relevance, and provide practical tips for strengthening these vital muscles. By doing so, we aim to equip you with the knowledge and tools needed to optimize your gluteal health and enjoy a life free from pain.
anatomical and functional breakdown of gluteal muscles
The gluteal muscle group plays a pivotal role in movement and stability, with each muscle contributing uniquely to hip and lower limb function. Understanding the specific anatomical and functional aspects of these muscles can help you appreciate their importance in daily activities and athletic performance.
gluteus maximus: the powerhouse
The gluteus maximus is the largest and most superficial muscle of the gluteal group. It is primarily responsible for hip extension, a crucial movement when rising from a sitting position, climbing stairs, or running. This muscle also plays a vital role in trunk stabilization, particularly during activities that require significant power output. The gluteus maximus is less active during walking but becomes highly engaged during running, where it helps stabilize the trunk and maintain balance. Its activation is essential for efficient and powerful lower limb movements, making it a key muscle for athletes and active individuals.
gluteus medius and minimus: stabilizers of the pelvis
Situated beneath the gluteus maximus, the gluteus medius and minimus are crucial for thigh abduction and the stabilization of the pelvis during walking. These muscles prevent the pelvis from dropping to one side when lifting a leg, ensuring balance and smooth gait. They also assist in internal and external rotation of the thigh, contributing to the dynamic stability of the hip joint. Strong gluteus medius and minimus muscles are vital for maintaining proper alignment and preventing injuries, especially in activities that require lateral movements, such as side-stepping or playing sports.
tensor fasciae latae: the multi-tasker
The tensor fasciae latae works closely with the iliotibial band to assist in hip flexion and abduction. This muscle is involved in stabilizing the knee, particularly during activities that involve weight-bearing on one leg, such as standing or walking. It also plays a role in maintaining balance and posture, making it an important muscle for overall lower limb stability. The tensor fasciae latae's contribution to hip and knee stability underscores its importance in preventing injuries and enhancing movement efficiency.
clinical relevance and health implications
The strength and proper functioning of the gluteal muscles are crucial for core stability and injury prevention. Weak glutes can lead to a host of musculoskeletal issues, particularly in individuals with sedentary lifestyles. When the gluteal muscles are underdeveloped, there is an increased reliance on other muscle groups, such as the lower back and hamstrings, leading to muscle imbalances and potential strain. This can result in lower back pain, knee pain, and poor posture, all of which can significantly impact quality of life.

Lumbar support belt
Provides stabilisation and relief for lower back pain, ideal for daily use.
Strengthening the gluteal muscles can help address these issues by improving posture, enhancing movement efficiency, and reducing the risk of injuries. For desk workers and those with sedentary jobs, incorporating exercises that target the glutes can be particularly beneficial in preventing lower back pain and promoting overall musculoskeletal health.
the evolutionary context of gluteal muscles
From an evolutionary perspective, the development of the gluteus maximus has been instrumental in human locomotion. Unlike our primate relatives, humans have evolved to run efficiently, and the gluteus maximus plays a unique role in this capability. Its ability to stabilize the trunk during running has been a significant factor in human evolution, allowing for greater endurance and speed. This evolutionary advantage highlights the importance of maintaining strong and functional gluteal muscles for both everyday activities and athletic pursuits.
By understanding the anatomy and function of the gluteal muscles, you can take proactive steps to strengthen these vital muscles and enjoy a pain-free, active lifestyle. In the next section, we will explore practical exercises and stretches to help you unlock the full potential of your glutes.
practical tips for strengthening gluteal muscles
Strengthening the gluteal muscles is essential not only for athletes but for anyone looking to improve their posture and reduce the risk of injury. Incorporating specific exercises and stretches into your routine can significantly enhance the strength and flexibility of these muscles.
effective exercises for gluteal strength
To target the gluteal muscles effectively, consider integrating exercises like squats, lunges, and bridges into your workout regimen. Squats and lunges engage the gluteus maximus and help in building overall lower body strength. Bridges are particularly useful for isolating the glutes, providing a focused workout that enhances muscle activation.
When performing these exercises, proper form is crucial to maximize benefits and prevent injury. Start with a manageable number of repetitions and gradually increase as your strength improves. Ensure that your knees do not extend beyond your toes during squats and lunges, and keep your core engaged to maintain balance and stability.
importance of stretching for flexibility
In addition to strengthening exercises, incorporating stretches into your routine is vital for maintaining the flexibility of the gluteal muscles. Regular stretching can prevent tightness, which often leads to discomfort and reduced range of motion. Simple stretches like the pigeon pose or seated forward bend can effectively target the glutes, promoting flexibility and relaxation.
Hold each stretch for at least 20-30 seconds, breathing deeply to allow your muscles to relax and elongate. Consistent stretching not only aids in recovery but also enhances overall muscle function, supporting pain-free movement.
ergonomic and lifestyle considerations
Beyond exercise, lifestyle adjustments can also play a significant role in promoting gluteal health. Incorporating ergonomic aids, such as supportive seating, can encourage proper posture and glute engagement, particularly for those who spend long hours sitting. Ergonomic chairs that support the natural curvature of the spine can alleviate pressure on the lower back and promote a more active sitting posture.

Men's Posture Shirt™ - Black
Activates and stimulates muscles to help improve posture and relieve tension.
For desk workers, taking regular active breaks to stand, stretch, or walk can help prevent muscle stiffness and encourage circulation. Being mindful of posture throughout the day, whether sitting or standing, can significantly impact gluteal muscle health and overall well-being.
case studies and testimonials
Many individuals have experienced significant improvements in their quality of life through targeted gluteal strengthening and ergonomic adjustments. For example, a study involving office workers found that those who incorporated glute-focused exercises and ergonomic seating reported reduced lower back pain and improved posture over time. Testimonials from individuals who have strengthened their glutes often highlight increased confidence in movement and a reduction in discomfort during daily activities.
frequently asked questions
what are the gluteal muscles, and what do they do?
The gluteal muscles consist of the gluteus maximus, medius, minimus, and tensor fasciae latae. They are responsible for movements such as hip extension, thigh abduction, and stabilization of the pelvis, playing a crucial role in maintaining balance and efficient movement.
why is it important to strengthen the gluteal muscles?
Strengthening the gluteal muscles is important for improving posture, reducing the risk of injuries, and enhancing movement efficiency. Strong glutes support the lower back and knees, contributing to overall musculoskeletal health.
how can I tell if my gluteal muscles are weak?
Signs of weak glutes include lower back pain, knee pain, and difficulty with movements such as climbing stairs or standing from a seated position. Poor posture and a tendency to rely on other muscle groups for support may also indicate gluteal weakness.
what exercises are best for strengthening the glutes?
Effective exercises for strengthening the glutes include squats, lunges, and bridges. These exercises target the gluteal muscles directly and should be performed with proper form to prevent injury and maximize benefits.
can ergonomic products help with gluteal muscle issues?
Yes, ergonomic products such as supportive chairs can help with gluteal muscle issues by promoting proper posture and reducing strain on the lower back. These products encourage active sitting, which engages the glutes and supports overall musculoskeletal health.
Kilder
- Kenhub. "Gluteal Muscles Anatomy."
- Wikipedia. "Gluteal Muscles."
- NCBI. "Anatomy, Bony Pelvis and Lower Limb, Gluteus Maximus Muscle."
- Cleveland Clinic. "Gluteal Muscles (Glutes)."
- TeachMeAnatomy. "The Gluteal Region."
- Mayo Clinic. "Got Glutes? Part 1: The Role of the Gluteus Maximus."
- NCBI. "Anatomy, Bony Pelvis and Lower Limb, Gluteus Medius Muscle."