The gluteal muscles, often referred to simply as the glutes, are a powerhouse of movement and stability in the human body. These muscles are not only crucial for everyday activities but also play a significant role in maintaining a pain-free lifestyle. Unfortunately, many people overlook their functional importance, focusing instead on aesthetics. While having well-defined glutes might be a common fitness goal, it's essential to understand that strong glutes contribute far more than just an appealing appearance. They are vital for movement efficiency, injury prevention, and overall health.
Understanding the gluteal muscles
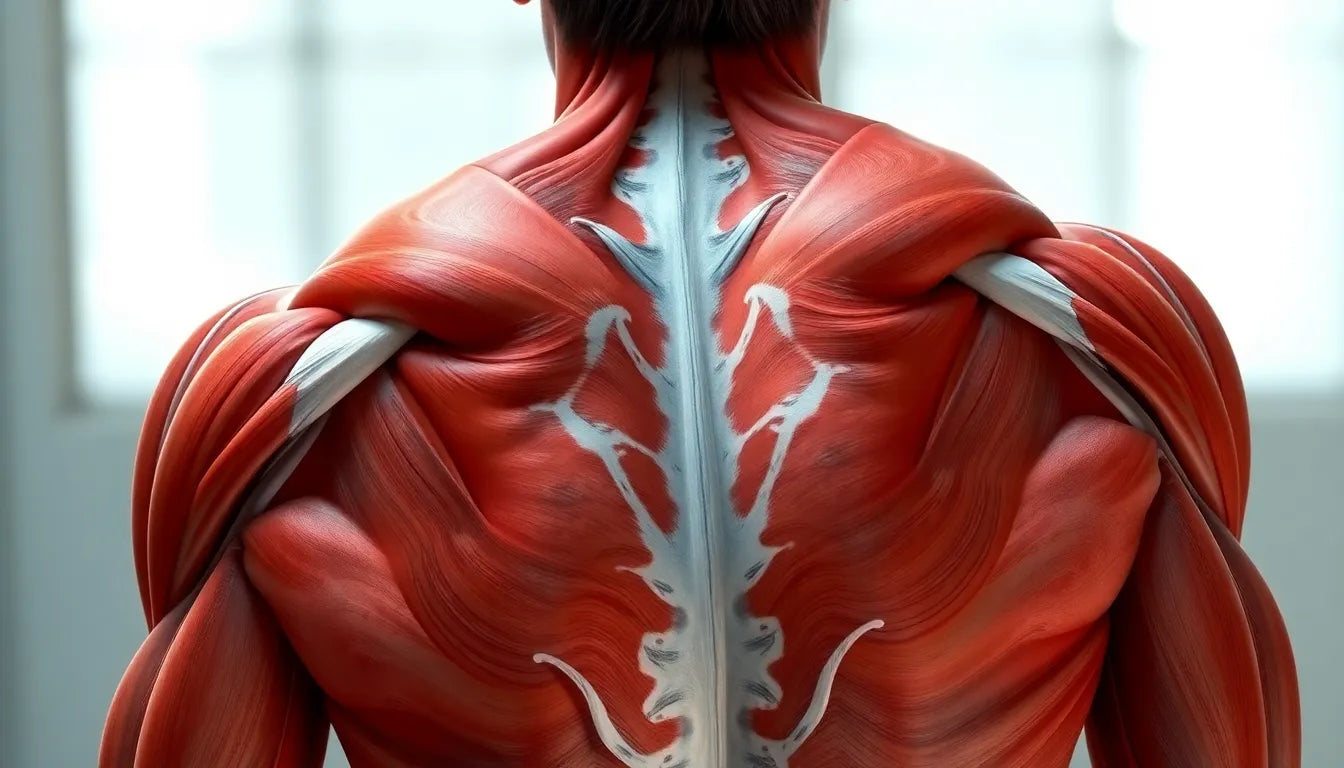
The gluteal region comprises three main muscles: the gluteus maximus, gluteus medius, and gluteus minimus. Each of these muscles has distinct roles that contribute to our ability to move and stabilize effectively. The gluteus maximus is the largest and most superficial of the three, primarily responsible for hip extension and contributing to our ability to stand upright, walk, and run. It is this muscle that gives the buttocks their characteristic shape and is crucial for power movements.
The gluteus medius and minimus, while smaller and located deeper, are equally important. These muscles are key players in pelvic stabilization and are essential for activities that require balance, such as walking and climbing stairs. They also assist in hip abduction and rotation, which are necessary for maintaining proper posture and preventing injuries. The evolutionary significance of the gluteal muscles in humans cannot be understated; they have developed to support bipedal locomotion, setting us apart from our primate relatives.
By focusing on strengthening the glutes, individuals can enhance their overall quality of life. Strong glutes support the lower back, reducing the risk of pain and discomfort. They also improve posture and balance, which are critical components in preventing falls and injuries. As we delve deeper into the anatomy and function of these muscles, it becomes clear that investing time and effort into glute health is a worthwhile endeavor for anyone seeking a pain-free lifestyle.
In-depth look at the anatomy and function of the glutes
The gluteus maximus, often referred to as the powerhouse of the gluteal muscles, plays a pivotal role in our daily movements. This muscle is primarily responsible for hip extension, which is crucial for activities like climbing stairs, running, and jumping. Its significant size and location make it a key player in maintaining posture and movement efficiency. By engaging this muscle, you enhance your ability to perform power movements with greater force and stability, thereby supporting a range of physical activities from athletic endeavors to routine tasks.
In contrast, the gluteus medius and minimus serve as the stabilizers within the gluteal group. Nestled deeper than the gluteus maximus, these muscles are essential for pelvic stability and injury prevention. They play a critical role in hip abduction and internal rotation, which are necessary for maintaining balance and alignment during movement. These functions are particularly important for preventing injuries, as they help to stabilize the pelvis and lower body, reducing strain on other muscle groups and joints.
Training and strengthening your glutes
To effectively activate and strengthen the glutes, incorporating specific exercises into your routine is essential. Squats, lunges, and deadlifts are foundational movements that significantly impact glute development. These exercises engage the gluteus maximus extensively, promoting muscle growth and strength. Additionally, single-leg movements, such as single-leg squats and step-ups, are critical for enhancing balance and stability. These exercises challenge the gluteus medius and minimus, ensuring a comprehensive workout that targets all areas of the gluteal muscles.
When training the glutes, proper form and technique are paramount to prevent injury and maximize results. It is vital to focus on activation patterns and ensure muscle engagement throughout each movement. This means consciously engaging the glutes during exercises to optimize their effectiveness. Incorporating a variety of exercises and progressively increasing resistance can help achieve optimal results, promoting both strength and endurance in the gluteal region.
Visual and aesthetic considerations for the buttocks
Understanding the visual and aesthetic aspects of the buttocks involves recognizing the different shapes and how they relate to muscle development and fat distribution. Common buttock shapes include heart, round, and square, each with its anatomical basis. The shape of the buttocks is influenced by the size and strength of the gluteal muscles, as well as the distribution of fat in the area. Muscle building and fat loss can significantly alter the appearance of the buttocks, highlighting the importance of targeted exercises and overall fitness.
For those aiming to achieve specific glute shapes, targeted exercises can be particularly beneficial. For instance, focusing on exercises that enhance the gluteus maximus can help achieve a fuller, more rounded appearance. Meanwhile, exercises that target the gluteus medius and minimus can enhance the overall symmetry and balance of the buttocks. Additionally, nutrition and lifestyle choices play a crucial role in shaping the buttocks, as a balanced diet and active lifestyle contribute to muscle development and fat management.
By understanding the anatomy and function of the gluteal muscles, and implementing effective training strategies, individuals can unlock the full potential of their glutes. This not only enhances physical appearance but also supports a pain-free and active lifestyle. Whether the goal is to improve performance, prevent injuries, or achieve a desired aesthetic, focusing on glute health is a vital component of overall well-being.
the role of glutes in pain management and ergonomics
The gluteal muscles are not just about aesthetics; they are integral to maintaining a pain-free lifestyle. Weak glutes can often lead to chronic pain, particularly in the lower back. This is because the glutes play a crucial role in supporting the pelvis and spine, helping to maintain proper posture and alignment. When the glutes are weak, other muscles and structures may have to compensate, leading to strain and discomfort.

Lumbar support belt
Helps support and stabilize the lower back to reduce pain and tension during daily activities.
Strengthening the glutes can significantly alleviate such issues. By enhancing the strength and functionality of these muscles, individuals can improve their posture, reduce the risk of lower back pain, and enhance overall movement efficiency. This is particularly important for those who spend long hours sitting, as prolonged sitting can lead to gluteal amnesia, where the glutes stop firing effectively. Regular glute exercises can counteract this issue, promoting better posture and reducing the strain on the back and hips.
ergonomics and everyday life
Incorporating glute exercises into daily routines is a practical approach to maintaining glute health and preventing pain. Simple exercises like glute bridges or bodyweight squats can be performed at home or even during breaks at work. These exercises require minimal equipment and can be easily integrated into a daily schedule, ensuring that the glutes remain active and engaged.
Additionally, ergonomic interventions can further support glute health. Using supportive seating that encourages proper posture can help maintain glute activation even while sitting. Ergonomic chairs or cushions that provide adequate support to the lower back can prevent slouching and encourage the engagement of the core and glutes, reducing the risk of pain and discomfort.

Men's Posture Shirt™ - Black
Posture shirt with NeuroBand™ tech to help reduce back pain, activate muscles, and encourage upright posture.
frequently asked questions
Why are glutes important for overall health?
Glutes are essential for movement, stability, and injury prevention. They support the pelvis and spine, enhance posture, and improve movement efficiency, reducing the risk of pain and injuries.
How often should I train my glutes?
For optimal results, aim to train your glutes 2-3 times a week, incorporating a mix of exercises that target all areas of the gluteal muscles. Ensure proper rest and recovery between sessions to prevent overtraining.
Can strengthening my glutes help with back pain?
Yes, strengthening the glutes can help alleviate back pain by improving posture and reducing strain on the lower back. Strong glutes support the pelvis and spine, enhancing overall stability and reducing discomfort.
What are the best exercises for beginners to target glutes?
Beginner-friendly exercises include glute bridges, bodyweight squats, and lunges. Focus on proper form and gradually increase intensity as you become more comfortable with these movements.
How can I maintain glute health as I age?
Maintaining glute health as you age involves regular exercise, focusing on strength and mobility. Incorporate a variety of glute exercises, maintain an active lifestyle, and ensure a balanced diet to support muscle health.