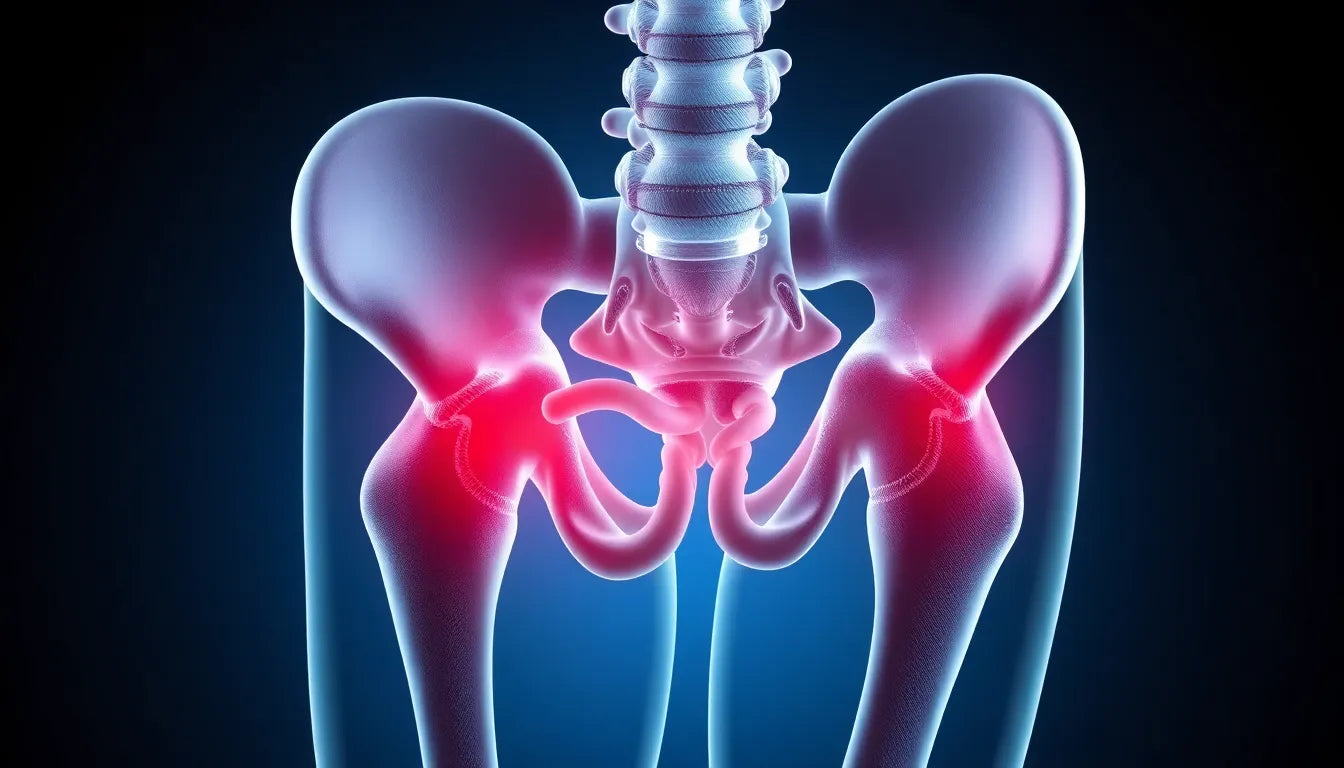
Snapping hip syndrome is a condition that often intrigues both medical professionals and those affected by its peculiar symptoms. Characterized by a noticeable snapping or popping sensation in the hip, this syndrome is classified into three types: internal, external, and intra-articular. Among these, internal snapping hip is a subtype that predominantly affects athletes, dancers, and individuals who lead active lifestyles. Understanding its nuances is essential for effective management and differentiation from other hip-related conditions.
Understanding internal snapping hip
Internal snapping hip, also known as iliopsoas snapping hip, occurs when the iliopsoas tendon slides over bony prominences in the hip, such as the iliopectineal eminence or the anterior aspect of the femoral head. This movement results in the characteristic snapping sensation, which can be both audible and palpable. Activities that involve repetitive hip flexion and extension, such as running, cycling, or dancing, often exacerbate this condition, making it a common issue among those who frequently engage in these motions.
The mechanism behind the snap
The iliopsoas tendon plays a crucial role in hip flexion, and its movement over the hip's bony structures is the primary cause of the snapping sensation. This phenomenon is particularly prevalent during transitions from a flexed to an extended hip position, where the tendon moves abruptly, creating the snap. While this can occur without pain, inflammation or tendinitis may accompany the snapping if the condition is aggravated, leading to discomfort and requiring medical attention.
Why understanding internal snapping hip matters
Recognizing and diagnosing internal snapping hip is crucial for several reasons. First, it allows for effective management of symptoms and prevents potential complications that may arise from untreated cases. Second, it helps distinguish this condition from other hip pathologies, such as labral tears, which may present with similar symptoms but require different treatment approaches. Understanding the specific characteristics of internal snapping hip can guide individuals toward appropriate interventions and improve overall outcomes.
As we delve deeper into the complexities of internal snapping hip, we aim to answer pertinent questions surrounding its symptoms, causes, and treatment options. This exploration not only aids those experiencing the condition but also provides valuable insights for healthcare professionals seeking to enhance their diagnostic and therapeutic strategies.
delving into the causes of internal snapping hip
The etiology of internal snapping hip primarily revolves around the anatomical and physiological behavior of the iliopsoas tendon. This tendon, a crucial component of the hip flexor group, is responsible for lifting the thigh towards the body. The snapping sensation arises when this tendon moves over bony structures, like the iliopectineal eminence or the anterior femoral head. While this is the most common cause, other factors can contribute to the condition. These include abnormalities in the tendon itself, such as thickening or partial bifurcation, which can increase the likelihood of snapping. Additionally, paralabral cysts, which are fluid-filled sacs that develop near the hip joint, may also play a role in exacerbating this snapping phenomenon.
symptoms and clinical presentation
The hallmark symptom of internal snapping hip is the distinct snapping or clicking sensation felt in the anterior hip or groin area. This sensation is particularly noticeable during activities that involve hip flexion and extension, such as walking, running, or rising from a seated position. In many cases, the snapping occurs without pain. However, if inflammation or tendinitis develops, individuals may experience discomfort or pain accompanying the snapping. This pain can sometimes be mistaken for intra-articular pathologies, like labral tears, making accurate diagnosis essential. Understanding the specific symptoms of internal snapping hip can aid in distinguishing it from other hip conditions.
diagnostic techniques for internal snapping hip
Diagnosing internal snapping hip involves a comprehensive approach that combines clinical history, physical examination, and imaging techniques. A detailed clinical history can reveal patterns of activity that exacerbate the snapping sensation, while a physical examination can help pinpoint the exact location and nature of the snapping. Provocative maneuvers, such as the Stinchfield test or active hip flexion/extension, are often employed to reproduce the snapping and confirm the diagnosis. Imaging techniques, particularly dynamic ultrasound, play a crucial role in visualizing the iliopsoas tendon's movement over the bony structures. This real-time imaging can confirm the diagnosis and rule out other potential causes. In some cases, MRI or CT scans may be utilized to exclude intra-articular disorders or underlying abnormalities in the hip joint.
treatment options for internal snapping hip
Management of internal snapping hip typically begins with conservative treatment strategies. Rest and activity modification are often recommended to reduce repetitive stress on the hip, allowing inflammation and irritation to subside. Physical therapy is a cornerstone of treatment, focusing on stretching and strengthening exercises for the hip flexors and surrounding muscles. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may be prescribed to alleviate pain and inflammation. For cases that do not respond to conservative measures, more advanced treatments may be considered. Corticosteroid injections can provide temporary relief by reducing inflammation around the tendon. In rare instances, surgical intervention, such as iliopsoas tendon release, may be necessary, particularly for individuals with persistent pain or functional limitations despite exhaustive conservative management.
Understanding the intricacies of internal snapping hip is essential for effective management and treatment. By exploring the detailed causes, symptoms, and diagnostic techniques, individuals and healthcare professionals can work together to develop tailored treatment plans that address the unique needs of each patient. As we continue to explore this condition, the focus remains on improving outcomes and quality of life for those affected by internal snapping hip.
comparison with other types of snapping hip
Understanding the distinctions between internal, external, and intra-articular snapping hip is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment. Internal snapping hip involves the iliopsoas tendon moving over bony prominences, primarily affecting athletes and dancers. In contrast, external snapping hip is caused by the iliotibial band or gluteus maximus tendon snapping over the greater trochanter. This often occurs in runners or individuals who engage in repetitive lateral movements. Intra-articular snapping hip, the least common type, is linked to loose bodies within the hip joint or labral tears, requiring different diagnostic and therapeutic approaches.
Here's a simplified comparison:
| Type | Cause | Common Activities |
|---|---|---|
| Internal Snapping Hip | Iliopsoas tendon over bony prominences | Running, cycling, dancing |
| External Snapping Hip | Iliotibial band over greater trochanter | Running, lateral movements |
| Intra-articular Snapping Hip | Loose bodies, labral tears | Various hip motions |
the role of ergonomic solutions
Ergonomic solutions can significantly impact the management of internal snapping hip by reducing repetitive stress on the hip joint. Adjusting workspaces to promote better posture and incorporating ergonomic furniture can alleviate strain during daily activities. For instance, using chairs with proper lumbar support or adjustable desks can help maintain optimal hip alignment, reducing the frequency and intensity of snapping episodes.

Lumbar support belt
Provides adjustable support and relief to the lower back and lumbar region during daily activities.
Additionally, ergonomic aids such as cushioned shoe inserts can decrease impact during physical activities, providing relief to those experiencing symptoms of internal snapping hip. These interventions, combined with targeted physical therapy, can enhance recovery and prevent recurrence.

Women's Posture Shirt™ - Nude
Patented shirt stimulating muscles to improve posture and relieve tension in work or activity.
real-world applications and case studies
Consider the case of a professional dancer who experiences internal snapping hip due to the repetitive hip flexion and extension required in her routines. Through a combination of physical therapy focusing on strengthening and stretching, ergonomic adjustments in her training environment, and activity modification, she successfully manages her symptoms. This approach not only reduces pain but also allows her to continue performing at a high level.
Similarly, a desk worker suffering from internal snapping hip might benefit from ergonomic office solutions. By adjusting his chair height and using a standing desk, he can minimize hip strain, reducing the frequency of snapping sensations and improving comfort during long work hours.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main cause of internal snapping hip?
The primary cause of internal snapping hip is the iliopsoas tendon snapping over bony structures in the hip, often due to repetitive movements.
Can internal snapping hip lead to long-term damage?
While internal snapping hip is often benign, untreated cases with persistent pain may lead to complications and require further intervention.
How is internal snapping hip diagnosed?
Diagnosis involves clinical history, physical examination, and imaging techniques like dynamic ultrasound or MRI to confirm the condition and rule out other issues.
What are the best exercises for managing internal snapping hip?
Exercises focusing on stretching and strengthening the hip flexors and surrounding muscles are beneficial for managing internal snapping hip.
When should I consider seeing a specialist?
If conservative treatments fail to alleviate symptoms or if pain is severe and persistent, it is advisable to consult a specialist for further evaluation and treatment options.
Kilder
- Ilizaliturri, V. M. (2019). "Snapping Hip Syndrome." NCBI Bookshelf.
- "Snapping Hip Syndrome." Physio-pedia.
- "Snapping Hip Syndrome: A Comprehensive Update." Orthopedic Reviews.
- "Snapping Hip." OrthoInfo - AAOS.
- "Snapping Hip Syndrome." Aurora Health Care.
- "Snapping Hip Syndrome." Cleveland Clinic.
- "Internal Snapping Hip." Cincinnati Sports Surgeon.
- "Snapping Hip Syndrome." Stanford Health Care.
- "Snapping Hip Syndrome in Children and Teens." Children's Hospital of Philadelphia.