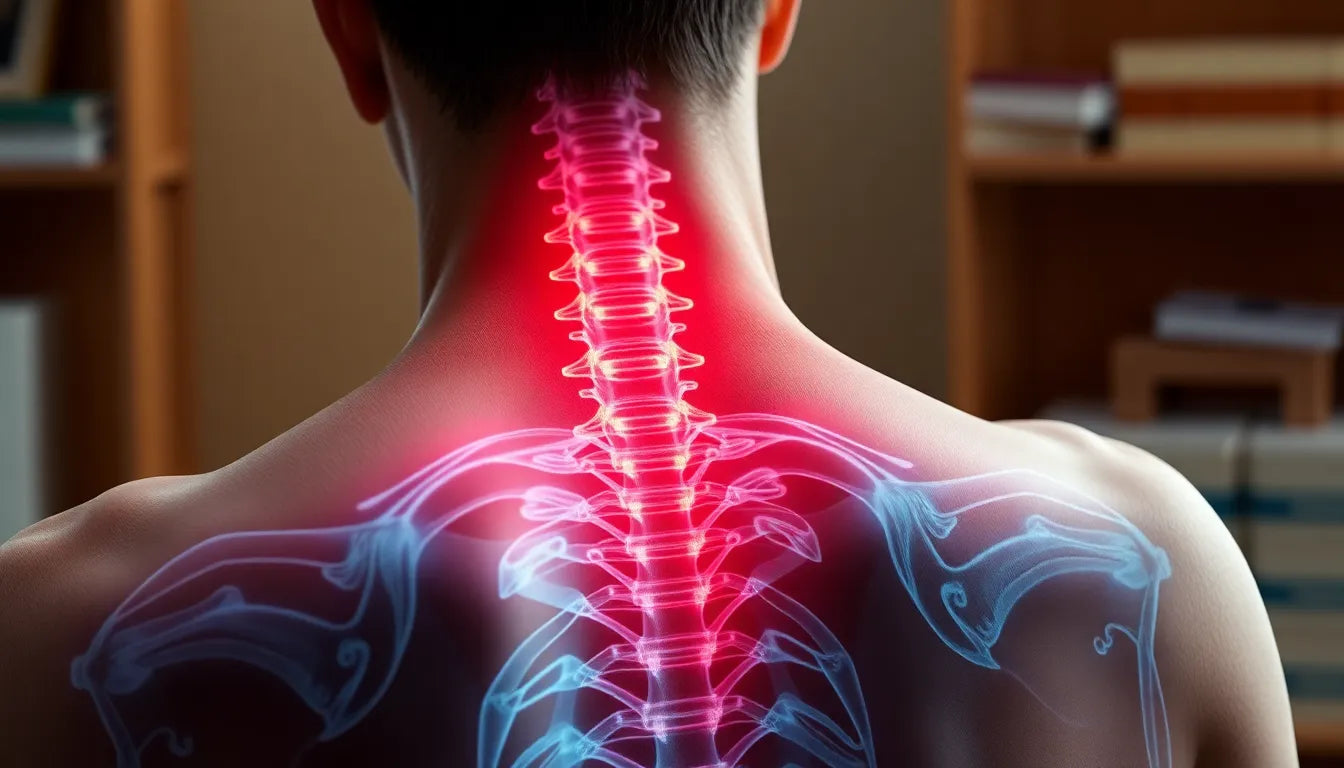
Dealing with pain from a herniated disc can be a daunting experience, impacting both physical well-being and daily life activities. A herniated disc, often referred to as a slipped or ruptured disc, occurs when the soft center of a spinal disc pushes through a crack in the tougher exterior casing. This condition can result in discomfort ranging from mild to severe, manifesting as pain, numbness, or weakness in the arms or legs, depending on the location of the herniation. Understanding the nature of herniated disc pain is the first step toward effective management and relief.
The presence of herniated disc pain can severely disrupt daily routines, making even simple tasks seem challenging. This type of pain can affect your ability to sit, stand, or move comfortably, often leading to significant lifestyle adjustments. The importance of effective pain management cannot be overstated, as it plays a crucial role in enhancing quality of life and enabling individuals to regain control over their daily activities. By exploring various pain management strategies, individuals can transform their lives, moving from a state of discomfort to one of improved functionality and well-being.
Embarking on the journey to relief
The path from experiencing pain to finding relief is often described as a journey, one that involves exploring various treatment options and management strategies. The journey to relief from herniated disc pain is unique for each individual, as the severity and impact of the condition can vary widely. This journey emphasizes the importance of adopting a personalized approach to pain management, recognizing that what works for one person may not be suitable for another.
Understanding the available options and the need for a tailored treatment plan is essential in navigating this journey. From conservative treatments like physical therapy and pain medications to more advanced interventions, the goal is to find the most effective approach for each individual's specific situation. By focusing on personalized care, individuals can better manage their symptoms and work towards a more comfortable and pain-free life.
In the following sections, we will delve deeper into the comprehensive treatment options available for managing herniated disc pain, exploring both non-surgical and surgical interventions. This exploration will provide valuable insights into how individuals can effectively address their pain, ultimately leading to an improved quality of life.
Comprehensive treatment options for herniated disc pain
When it comes to managing pain from a herniated disc, a variety of treatment options are available, ranging from conservative approaches to surgical interventions. Understanding these options can empower individuals to make informed decisions about their care and improve their quality of life.
Conservative/non-surgical treatments
Conservative treatments are often the first line of defense against herniated disc pain. These methods focus on relieving symptoms and improving function without the need for invasive procedures.
Rest: While it might seem counterintuitive, limited rest is crucial for recovery. Taking a break from strenuous activities for one to three days can help reduce inflammation and give the body time to heal. However, prolonged bed rest should be avoided as it can lead to muscle stiffness and exacerbate symptoms.
Pain medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen and naproxen are commonly used to alleviate pain and reduce inflammation. These medications can be effective in managing mild to moderate pain, making daily activities more manageable.
Physical therapy: A tailored physical therapy program can play a significant role in recovery. Specific exercises designed to strengthen the muscles supporting the spine and improve flexibility can help alleviate pressure on the affected disc. This approach not only aids in pain reduction but also enhances overall mobility.
Heat and cold therapy: Alternating between heat and cold can be beneficial in managing herniated disc pain. Cold therapy can help reduce inflammation and numb the area, while heat therapy promotes blood flow and relaxes tense muscles.
Spinal decompression therapy: This non-surgical treatment involves gently stretching the spine to relieve pressure on the herniated disc. It can be an effective method for reducing pain and promoting healing by enhancing nutrient-rich fluid circulation around the discs.
Epidural steroid injections: For individuals experiencing significant pain, epidural steroid injections can provide relief by reducing inflammation around the affected nerve. This treatment can be particularly beneficial for those who have not responded well to other conservative measures.
Surgical interventions
In cases where conservative treatments fail to provide adequate relief, surgical options may be considered. Surgery is typically reserved for individuals with persistent symptoms that significantly impact their quality of life.
When surgery becomes necessary: Surgery is usually considered when symptoms persist for more than four to six weeks despite conservative treatments, or if there is significant nerve damage or loss of function.
Types of surgery:
- Diskectomy: This procedure involves removing the damaged portion of the herniated disc to relieve pressure on the nerves. Patients can expect a reduction in pain and improvement in mobility following the surgery.
- Artificial disc replacement: This surgical option involves replacing the damaged disc with an artificial one, allowing for continued movement between the vertebrae. It can offer benefits such as maintaining spinal flexibility and reducing the risk of further degeneration.
Recovery timeline and expectations
Recovery from herniated disc pain varies depending on the treatment approach. For those undergoing conservative treatments, significant improvement is often seen within four to six weeks. However, it may take three to four months to become symptom-free. Factors such as age, overall health, and adherence to treatment plans can influence recovery speed and outcomes.
By understanding and exploring these comprehensive treatment options, individuals can effectively manage their herniated disc pain, paving the way for a more comfortable and active lifestyle. In the next section, we will discuss pain management strategies and lifestyle adjustments that can further support recovery and long-term well-being.
Pain management and lifestyle adjustments for herniated disc relief
Effectively managing pain from a herniated disc requires a combination of medication, physical therapy, and lifestyle adjustments. Understanding the differences between over-the-counter and prescription medications can help tailor pain relief strategies. Over-the-counter options like NSAIDs are suitable for mild to moderate pain, while prescription medications may be necessary for more severe symptoms. It is essential to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate medication plan.
Physical therapy remains a cornerstone in the recovery process, with specific exercises designed to strengthen core muscles and improve flexibility. Techniques such as McKenzie exercises and lumbar stabilization can significantly aid in reducing pain and preventing future issues. Engaging in regular sessions with a licensed physical therapist can provide personalized guidance and ensure exercises are performed correctly.
Activity modification is another crucial aspect of managing herniated disc pain. Simple changes, such as avoiding heavy lifting and maintaining proper posture, can alleviate stress on the spine. Incorporating ergonomic aids, like lumbar support cushions and adjustable desks, can further support recovery by promoting correct alignment and reducing strain during daily activities.
Long-term management and prevention strategies
Preventing the recurrence of herniated disc pain involves maintaining an active lifestyle and incorporating regular exercise into daily routines. Activities like swimming, walking, and yoga can enhance flexibility and strengthen the muscles supporting the spine. Additionally, weight management plays a vital role in reducing stress on the spine, making a balanced diet and regular physical activity essential components of long-term management.
For those with chronic conditions, ongoing collaboration with healthcare providers is crucial. Regular check-ups and adjustments to treatment plans can help manage symptoms and prevent further complications. By adopting a proactive approach to spinal health, individuals can minimize the risk of future herniated disc issues and enjoy a more active and pain-free life.
Frequently asked questions
What are the first steps to take when experiencing herniated disc pain?
Initial steps include resting for one to three days and using over-the-counter pain medications like NSAIDs to manage discomfort. If pain persists or worsens, seeking medical advice is crucial to explore further treatment options.
How can ergonomic aids assist in managing herniated disc pain?
Ergonomic aids, such as lumbar support cushions, standing desks, and ergonomic chairs, can help maintain proper posture and reduce strain on the spine during daily activities. These aids promote spinal alignment and can significantly alleviate pain.
When should I consider surgery for a herniated disc?
Surgery is generally considered when symptoms persist for more than four to six weeks despite conservative treatments, or if there is significant nerve damage or loss of function. Consultation with a healthcare provider is essential to evaluate the need for surgical intervention.
How long does it typically take to recover from a herniated disc?
Recovery timelines vary, but most individuals see improvement within four to six weeks with conservative treatment. Complete recovery can take three to four months, depending on factors such as age, overall health, and adherence to treatment plans.
What lifestyle changes can help prevent future herniated disc issues?
Maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular exercise, and practicing good posture are key strategies for preventing future issues. Regular physical activity, such as swimming or yoga, strengthens the muscles supporting the spine, reducing the risk of recurrence.
Sources
- Mayo Clinic. "Herniated disk - Diagnosis and treatment."
- Cleveland Clinic. "Herniated Disk (Slipped or Bulging Disk)."
- WebMD. "Herniated Disk Treatment, Remedies, and Medications."
- OrthoInfo (AAOS). "Herniated Disk in the Lower Back."
- American Association of Neurological Surgeons (AANS). "Herniated Disc."
- Northeast Spine and Sports. "What Is the Best Treatment for a Herniated Disc?"
- University of Maryland Medical System. "A Patient's Guide to Lumbar Herniated Disc."