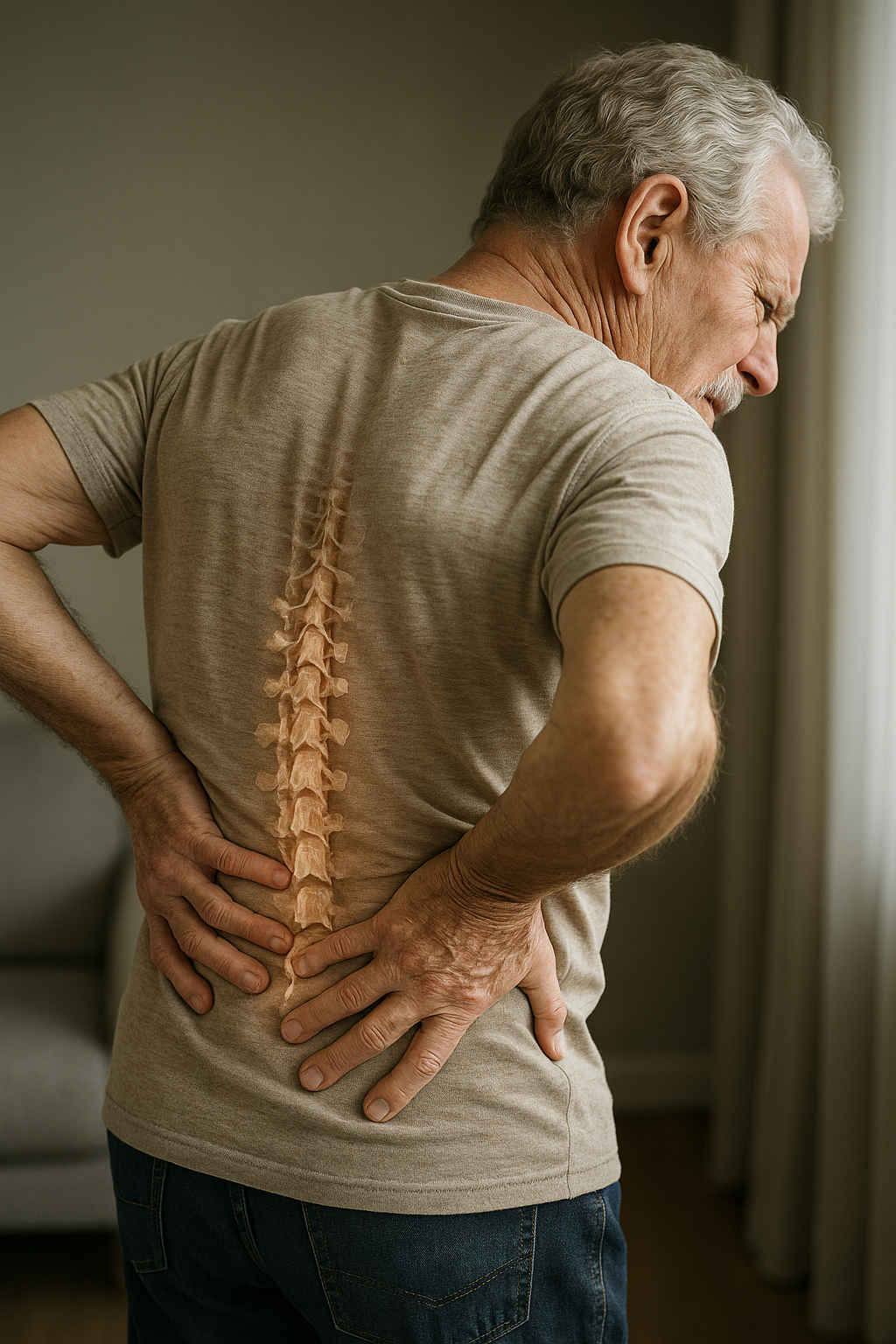
Cervical spinal stenosis is a condition that affects the cervical spine, leading to a range of symptoms that can significantly impact daily life. Understanding these symptoms is crucial for early recognition and effective management, allowing individuals to address the condition before it progresses to more severe stages.
what is cervical spinal stenosis?
Cervical spinal stenosis refers to the narrowing of the spinal canal in the neck region, which can lead to compression of the spinal cord and surrounding nerves. This narrowing can result from various factors, including age-related degeneration, herniated discs, or congenital conditions. The condition is particularly prevalent among individuals over the age of 50, as natural wear and tear on the spine accumulates over time.
As the spinal canal narrows, it can exert pressure on the spinal cord and nerve roots, leading to a variety of symptoms that may affect one's quality of life. These symptoms often vary in severity and can range from mild discomfort to debilitating pain and neurological issues.
why understanding symptoms is important
The objective of this post is to educate readers on the symptoms associated with cervical spinal stenosis, helping individuals identify and understand the severity of their condition. Early detection of symptoms can play a crucial role in managing the condition effectively, preventing further complications, and improving overall well-being.
Recognizing the signs of cervical spinal stenosis early on can lead to timely medical intervention, which may include conservative treatments such as physical therapy, medication, and lifestyle modifications. In some cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to alleviate pressure on the spinal cord and nerves.
By understanding the symptoms and their progression, individuals can make informed decisions about their health and seek appropriate care when needed. This knowledge empowers individuals to take control of their condition and work towards maintaining a better quality of life.
understanding symptom severity in cervical spinal stenosis
Recognizing the symptoms of cervical spinal stenosis and understanding their severity is crucial for effective management and treatment. Symptoms can be classified into stages—mild, moderate, and severe—each indicating the progression and impact of the condition on daily life.
mild stage symptoms
In the mild stage, individuals may experience occasional neck pain and stiffness. These symptoms often result from minimal spinal cord compression and can be easily overlooked. The discomfort is usually intermittent and may not significantly interfere with daily activities. However, ignoring these early signs can lead to progression, making early recognition vital.

Women's Posture Shirt™ - Black
Støtter og aktiverer dine muskler for bedre kropsholdning og smertelindring.
moderate stage symptoms
As cervical spinal stenosis progresses to the moderate stage, symptoms become more persistent and noticeable. Individuals may experience frequent tingling and numbness in the arms and hands. This discomfort can disrupt daily activities, such as typing or lifting objects, and may require adjustments in routine tasks. At this stage, seeking medical advice is recommended to prevent further deterioration.
severe stage symptoms
In the severe stage, symptoms are constant and can significantly impact the quality of life. Individuals may experience weakness in the upper extremities, making it difficult to perform tasks that require strength or coordination. Balance issues and coordination difficulties become more pronounced, affecting the ability to walk or perform hobbies. These symptoms necessitate immediate medical intervention to prevent long-term damage.
core symptom clusters of cervical spinal stenosis
Understanding the core symptom clusters associated with cervical spinal stenosis can help individuals identify specific issues related to the condition. These clusters include neck-focused symptoms, upper extremity symptoms, neurological symptoms, and severe or emergency indicators.
neck-focused symptoms
Neck-focused symptoms typically involve stiffness and pain in the neck and upper back. This discomfort can vary from a dull ache to a burning sensation, often exacerbated by certain neck positions or physical activities. These symptoms may be the first indication of cervical spinal stenosis and should not be ignored.

Men's Posture Shirt™ - White
Fremmer bedre holdning og kan lindre smerter i nakke, skuldre og ryg.
upper extremity symptoms
Upper extremity symptoms include weakness, numbness, and tingling in the arms and hands. These sensations result from nerve compression and can affect the ability to grip objects or perform fine motor tasks, such as buttoning a shirt. Monitoring these symptoms is crucial, as they can indicate the progression of the condition.
neurological symptoms
Neurological symptoms involve balance and coordination problems, making it difficult to walk or perform tasks requiring fine motor skills. These issues arise from spinal cord compression and can significantly impact daily life. Early detection and management of these symptoms are essential to prevent further complications.
severe/emergency indicators
Severe or emergency indicators include loss of bladder or bowel control and paralysis. These critical signs require immediate medical attention, as they indicate significant spinal cord compression. Prompt intervention can prevent permanent damage and improve outcomes.
characterizing pain in cervical spinal stenosis
Pain associated with cervical spinal stenosis can vary in quality and pattern. It may be described as a dull ache, a burning sensation, or an electric-like sensation. The pain can be intermittent or constant, often worsening with specific neck positions or physical activities. Understanding the nature of the pain can help in diagnosing the condition and determining the appropriate treatment plan.
By recognizing the symptoms of cervical spinal stenosis and understanding their severity, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their condition and seek appropriate medical care. Early detection and intervention are key to preventing further complications and maintaining a good quality of life.
monitoring symptom onset and progression
Cervical spinal stenosis symptoms often develop gradually over time, progressing from mild discomfort to more severe manifestations. This progression can occur over weeks, months, or even years, depending on individual circumstances and underlying causes. It is crucial for individuals to monitor these symptoms closely, as early recognition and intervention can prevent the condition from worsening.
Regularly assessing the frequency and intensity of symptoms such as neck pain, tingling in the arms, and coordination difficulties can help determine when to seek medical evaluation. Keeping a symptom diary can be an effective way to track changes and provide valuable information to healthcare providers.
activity-specific symptom triggers
Understanding which activities exacerbate cervical spinal stenosis symptoms can aid in managing the condition effectively. Certain movements and positions can intensify symptoms, making it important to identify and avoid these triggers when possible. Below is a table highlighting common activities that may worsen symptoms:
| Activity | Potential Impact |
|---|---|
| Prolonged sitting | Increases neck stiffness and pain |
| Lifting heavy objects | Exacerbates upper extremity symptoms |
| Repetitive neck movements | Aggravates neck pain and tingling sensations |
| High-impact sports | Worsens balance and coordination issues |
By identifying these triggers, individuals can make lifestyle adjustments to minimize discomfort and prevent symptom progression. Incorporating ergonomic tools and supportive devices can also help alleviate strain on the cervical spine during daily activities.
when to seek emergency care
While many symptoms of cervical spinal stenosis can be managed with conservative treatments, certain warning signs indicate the need for immediate medical intervention. Sudden loss of motor function, severe pain that does not respond to medication, or the onset of paralysis are critical indicators that require urgent attention.
Additionally, experiencing a sudden loss of bladder or bowel control is a severe symptom that necessitates emergency care. These signs suggest significant spinal cord compression and, if left untreated, can lead to permanent damage.
Frequently Asked Questions
What causes cervical spinal stenosis?
Cervical spinal stenosis is commonly caused by age-related degeneration, which leads to the narrowing of the spinal canal. Other causes include herniated discs, congenital spinal abnormalities, and traumatic injuries that affect the neck region.
How is cervical spinal stenosis diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves a combination of medical history evaluation, physical examination, and imaging tests such as MRI or CT scans. These methods help assess the extent of spinal canal narrowing and nerve compression.
Can cervical spinal stenosis be treated without surgery?
Yes, many cases can be managed with non-surgical treatments, including physical therapy, medication, and lifestyle modifications. These approaches aim to alleviate symptoms and improve mobility without invasive procedures.
What are the potential complications if left untreated?
Untreated cervical spinal stenosis can lead to chronic pain, permanent nerve damage, and significant impairment in daily functioning. Severe cases may result in paralysis or loss of bladder and bowel control.
How can I manage symptoms at home?
Home management strategies include performing neck exercises, using ergonomic aids, and making lifestyle adjustments to reduce strain on the neck. Maintaining good posture and avoiding activities that exacerbate symptoms are also beneficial.
Kilder
- RWJBarnabas Health. "Cervical Spinal Stenosis."
- Epstein, N. E. (2009). "Cervical Myelopathy: A Review." Surgical Neurology International.
- Goodman Campbell Brain and Spine. "Cervical Spinal Stenosis."
- Southeast Texas Spine Institute. "The Best Ways to Treat Cervical Stenosis."
- UCSF Health. "Cervical Stenosis."
- Cary Templin, MD. "Cervical Stenosis."
- Neurosurgeons of New Jersey. "Cervical Stenosis Emergency Signs."
- Mayo Clinic. "Spinal Stenosis: Diagnosis & Treatment."
- Merck Manuals. "Cervical Spinal Stenosis."
- NewYork-Presbyterian. "Spinal Stenosis Treatment."
- Cleveland Clinic. "Spinal Stenosis."
- Massachusetts General Hospital. "Cervical Spinal Stenosis."
- Mayo Clinic. "Spinal Stenosis: Symptoms & Causes."
- Commons Clinic. "Innovations in Spinal Stenosis."
- Precision Health. "Cervical Spinal Stenosis."
- WebMD. "Spinal Stenosis."
- Kaiser Permanente. "Cervical Spinal Stenosis."