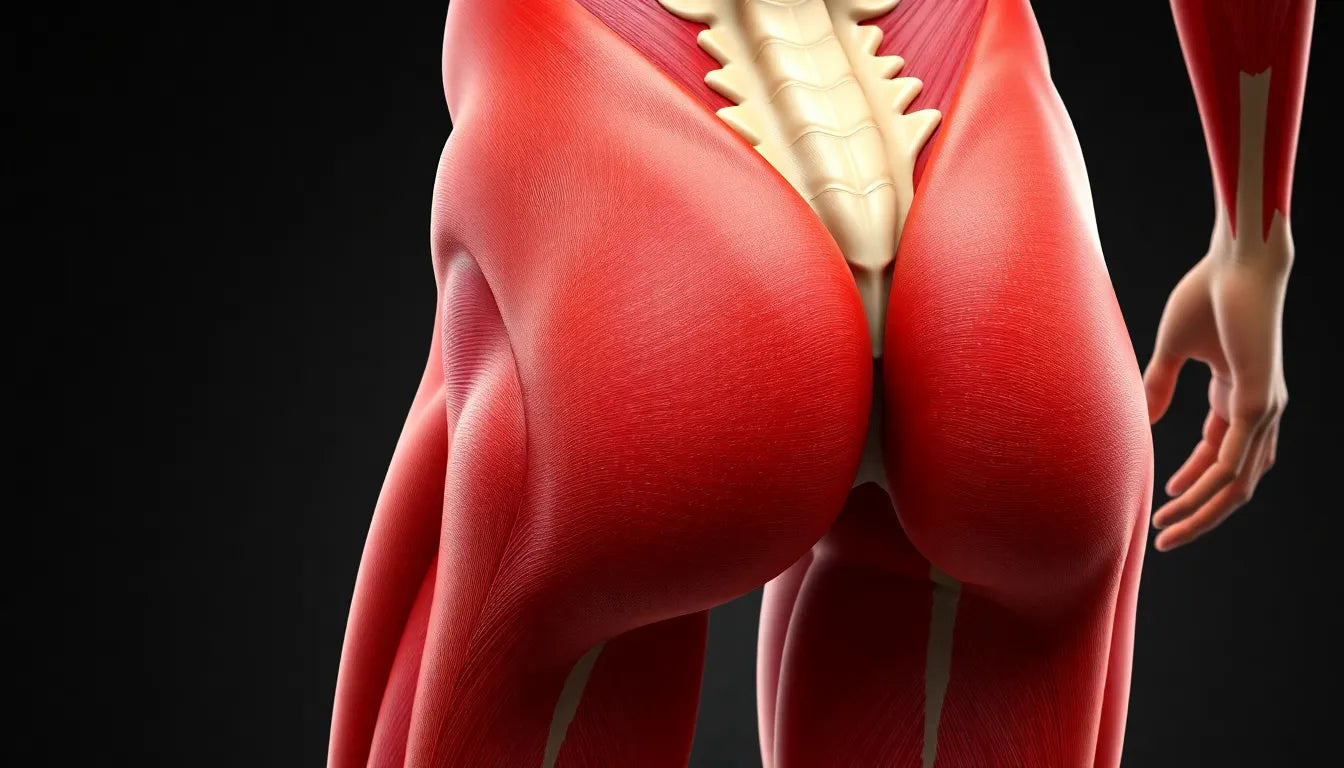
The hip joint is an integral part of our body's architecture, allowing us to move through life with grace and ease. This ball-and-socket joint, where the thigh bone meets the pelvis, is pivotal in supporting our body weight and facilitating a wide range of movements. Yet, many people find themselves grappling with hip pain or discomfort, which can significantly impact their daily activities and overall quality of life.
Understanding the importance of hip joint health
The hip joint plays a crucial role in our everyday mobility. As a primary weight-bearing joint, it endures significant stress during activities such as walking, running, and even standing. Its unique structure allows for multidirectional movement, making it essential for maintaining balance and stability. However, the very demands placed on the hip joint can lead to a variety of issues, from minor discomfort to severe conditions like osteoarthritis.
Maintaining hip joint health is vital not just for athletes or those leading an active lifestyle, but for anyone who wishes to preserve their mobility and independence as they age. A healthy hip joint can prevent pain, improve function, and enhance the overall quality of life. With hip-related issues being quite common, understanding how to care for this joint is more important than ever.
What this blog will cover
In this blog, we will delve into the anatomy of the hip joint, exploring its complex structure and the role it plays in our body's mechanics. We will also discuss common problems that can affect the hip, offering insights into conditions like osteoarthritis and other ailments that can cause hip pain. Finally, we will provide practical solutions to support hip health, including ergonomic strategies, exercises, and lifestyle modifications that can help you maintain a pain-free hip joint.
By unlocking the secrets to a healthy hip joint, you can transform your daily life, ensuring that your movements remain fluid and pain-free. Stay tuned as we explore these topics in depth, offering you the knowledge and tools needed to keep your hip joint in optimal condition.
Understanding the hip joint: anatomy and functionality
The hip joint is a marvel of biological engineering, designed to support the human body through a spectrum of activities. At its core, the hip is a ball-and-socket joint, a design that allows for extensive multidirectional movement. The ball is formed by the head of the femur (thigh bone), which fits snugly into the acetabulum, a cup-like structure in the pelvis. This configuration provides the hip with remarkable stability and flexibility, crucial for both everyday activities and athletic pursuits.
Key components of the hip joint include the cartilage, ligaments, and synovial fluid. Cartilage covers the surfaces of the femur and acetabulum, reducing friction and absorbing shock during movement. Ligaments, strong bands of tissue, connect bones and stabilize the joint, preventing dislocation. Synovial fluid, a viscous liquid, lubricates the joint, allowing for smooth motion. Additionally, the hip joint is richly supplied with blood vessels and nerves, essential for its health and function.
Biomechanics: the balance of stability and mobility
The hip joint's unique biomechanics enable it to perform weight-bearing and dynamic activities with ease. It supports the body's weight not only when standing still but also during complex movements like walking, running, and jumping. This joint must strike a delicate balance between stability and mobility, a feat achieved through its robust structure and muscular support.
Compared to other joints such as the shoulder, the hip is more stable due to its deeper socket and stronger ligaments. This stability is crucial for maintaining posture and balance. However, it still allows for a wide range of motion, pivotal for activities such as bending, stretching, and rotating the leg. Understanding these mechanics is vital for appreciating the hip's role in daily life and the importance of maintaining its health.
Common hip joint issues: recognizing the signs
Despite its robust design, the hip joint is susceptible to a variety of issues, with osteoarthritis being one of the most prevalent. This degenerative condition involves the breakdown of cartilage, leading to pain, stiffness, and a reduced range of motion. Osteoarthritis can significantly impair mobility, making everyday tasks challenging.
Besides osteoarthritis, other conditions can affect the hip joint, such as labral tears, bursitis, and osteonecrosis. Labral tears involve damage to the ring of cartilage (labrum) that follows the outside rim of the acetabulum. Bursitis is the inflammation of the bursae, small fluid-filled sacs that cushion the hip joint. Osteonecrosis occurs when blood supply to the femur is compromised, leading to bone tissue death. Recognizing the symptoms of these conditions, such as persistent pain or difficulty moving, is crucial for seeking timely medical advice.
Visual aid: hip joint anatomy
For a comprehensive understanding of the hip joint's anatomy, refer to the diagram below. This visual aid highlights the key components discussed, including the femur, acetabulum, cartilage, ligaments, and synovial fluid. By familiarizing yourself with these elements, you can better appreciate the intricate workings of this essential joint and the importance of maintaining its health.

In the next section, we will explore practical solutions for maintaining hip health, including ergonomic strategies, exercises, and lifestyle modifications. These insights will equip you with the knowledge to support your hip joint, ensuring it remains pain-free and functional throughout your life.
Practical solutions for maintaining hip joint health
Ensuring the health of your hip joint involves a combination of ergonomic strategies, targeted exercises, and lifestyle modifications. By integrating these practices into your daily routine, you can significantly reduce the risk of hip pain and enhance your overall mobility.
Ergonomic strategies for daily activities
Adopting ergonomic strategies in your daily life is crucial for maintaining hip joint health. Start by ensuring your work and home environments are designed to support good posture. Use ergonomic chairs that provide adequate support for your lower back and hips, and consider adding cushions for extra comfort. When sitting, keep your knees at a 90-degree angle and your feet flat on the floor to reduce strain on your hips.

Lumbar support belt
Adjustable belt for back pain relief and lumbar support—ideal for daily comfort and stability.
Incorporating standing desks or taking regular breaks to stand and stretch can also alleviate pressure on your hips. These adjustments not only enhance comfort but also promote better alignment and reduce the risk of joint issues.
Exercises and stretches to strengthen the hip joint
Regular physical activity is essential for strengthening the muscles around the hip joint and improving flexibility. Incorporate exercises such as hip bridges, leg raises, and squats into your routine to target the hip muscles. These exercises help build strength and stability, reducing the likelihood of injury.

37 exercises collected in the ultimate exercise book
E-book with expert-selected exercises for injury prevention, rehab, and body strength.
In addition to strength training, stretching exercises like the hip flexor stretch and piriformis stretch can enhance flexibility and alleviate tension. Aim to incorporate these exercises into your routine at least three times a week for optimal results.
Lifestyle modifications for long-term hip health
Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for reducing stress on the hip joint. Excess weight can exacerbate joint pain and increase the risk of conditions like osteoarthritis. Focus on a balanced diet rich in nutrients that support joint health, including omega-3 fatty acids, calcium, and vitamin D.
Preventive care is also vital. Regular check-ups with healthcare professionals can help identify potential issues early, allowing for timely intervention. By adopting these lifestyle changes, you can support your hip joint health and enjoy a more active, pain-free life.
Visual aid: exercise and stretching guide
To assist you in incorporating these exercises and stretches into your routine, refer to the table below. This guide outlines key exercises and stretches designed to improve hip health, complete with descriptions and recommended repetitions.
| Exercise/Stretch | Description | Repetitions |
|---|---|---|
| Hip Bridge | Lie on your back, bend your knees, and lift your hips towards the ceiling. | 3 sets of 10 reps |
| Leg Raises | Lie on your side and lift your top leg towards the ceiling. | 3 sets of 10 reps per side |
| Hip Flexor Stretch | Kneel on one knee, push your hips forward to stretch the front of the hip. | Hold for 30 seconds per side |
| Piriformis Stretch | Lie on your back, cross one leg over the other, and pull the opposite knee towards your chest. | Hold for 30 seconds per side |
Frequently asked questions
What are the early signs of hip joint problems?
Early signs of hip joint problems include persistent pain in the hip or groin, stiffness, and a reduced range of motion. If these symptoms interfere with daily activities, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional.
How can I prevent hip joint issues?
Preventing hip joint issues involves regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, and making ergonomic adjustments to your environment. Incorporating hip-strengthening exercises and stretches can also play a significant role in prevention.
When should I see a doctor about my hip pain?
Seek medical advice if you experience severe pain, swelling, or if your hip pain persists despite home remedies. A healthcare professional can provide a diagnosis and recommend appropriate treatment options.
Are there non-surgical treatments for hip joint pain?
Yes, non-surgical treatments for hip joint pain include physical therapy, medications like anti-inflammatories, and lifestyle changes such as weight management and exercise. These can effectively manage pain and improve joint function.
How do ergonomic aids help with hip joint health?
Ergonomic aids, such as supportive chairs and cushions, help maintain proper posture and reduce strain on the hips. These aids are designed to enhance comfort and prevent joint stress during daily activities.
Kilder
- Kenhub. "Hip Joint Anatomy."
- Ortho1. "Hip Anatomy."
- NCBI. "Hip Joint Anatomy and Function."
- Heraeus Medical. "Understanding the Hip Joint."
- Physio-pedia. "Hip Anatomy."
- SJRI. "Anatomy of the Hip Joint."
- Grossmont Orthopaedic. "Hip Anatomy."
- MedlinePlus. "Hip Joint Anatomy."
- Arthritis Foundation. "Anatomy of the Hip."
- Cleveland Clinic. "Hip Joint Overview."
- YouTube. "Hip Joint Anatomy Video."
- Bryan Kelly MD. "Normal Anatomy of the Hip Joint."
- Same Day Hip and Knee Surgery. "Anatomy and Function of the Hip."