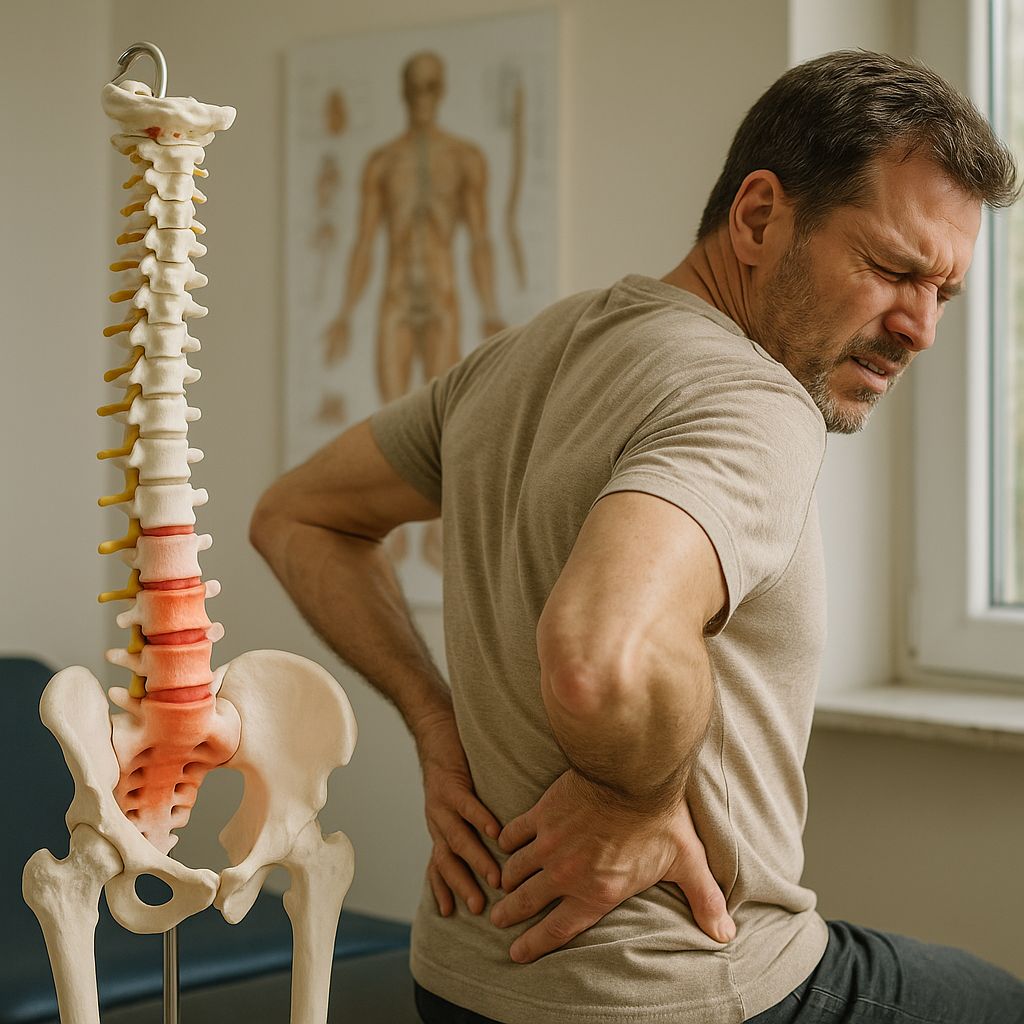
The lumbar vertebrae play a pivotal role in the human spine, forming the foundation for both stability and flexibility. Located in the lower back, these five vertebrae—L1 through L5—are crucial in supporting the upper body's weight and facilitating a wide range of movements. The lumbar region is often the unsung hero of our daily activities, providing the necessary support for tasks as simple as walking and bending. Yet, its significance is most felt when issues arise, such as lower back pain, which is a common ailment affecting millions worldwide.
Understanding the anatomy of lumbar vertebrae
The lumbar vertebrae are distinct from other regions of the spine due to their size and structure. These vertebrae are larger and more robust, designed to bear the brunt of the body's weight and absorb the stresses of movement. Each vertebra consists of a vertebral body, which is stout and thick, providing a solid base for muscle attachment and force distribution. The lumbar region also exhibits a natural inward curve known as lumbar lordosis, which is vital for maintaining an upright posture and efficient bipedal locomotion.
This curve not only helps in balancing the body but also plays a key role in shock absorption during activities like walking, running, or jumping. The lumbar vertebrae's unique characteristics enable them to withstand significant pressure, making them indispensable to our structural integrity.
The importance of lumbar health
Maintaining the health of the lumbar vertebrae is essential for overall well-being. A healthy lumbar region contributes to a pain-free lifestyle by facilitating smooth movement and reducing the risk of injury. Conversely, poor lumbar health can lead to chronic pain and mobility issues, significantly impacting one's quality of life. Ergonomic solutions, such as proper seating and posture correction, can play a crucial role in minimizing lumbar strain and preventing discomfort.

Lumbar support belt
Supports and stabilises the lower back to combat pain and relieve tension during daily activities.
Incorporating ergonomic practices into daily routines can help maintain the natural curve of the lumbar region, reducing the likelihood of developing back pain. Whether through the use of supportive chairs, adjustable desks, or lumbar cushions, these interventions can provide the necessary support to keep the lumbar vertebrae healthy and functional.
Understanding and caring for your lumbar vertebrae is a step towards a more active and pain-free life. By recognizing their importance and taking proactive measures to support them, you can ensure that your lumbar region remains a strong and reliable foundation for your body.
Detailed anatomy of lumbar vertebrae
The lumbar vertebrae are uniquely designed to handle the immense responsibilities of supporting the upper body and enabling movement. The vertebral bodies of these five vertebrae are notably stout and thick, a testament to their role in bearing significant weight. This robust structure is further characterized by kidney-shaped superior surfaces, which are essential for distributing loads and providing a stable foundation for muscle attachment.
Each lumbar vertebra is composed of several critical components: the vertebral arch, pedicles, laminae, transverse processes, and spinous processes. The vertebral arch forms the posterior part of the vertebra, protecting the spinal cord while providing attachment sites for muscles and ligaments. The pedicles connect the vertebral body to the arch, while the laminae complete the arch's enclosure. Transverse and spinous processes extend from the arch, acting as levers for muscle action and contributing to the spine's overall movement and flexibility.
Functional significance of lumbar vertebrae
The lumbar vertebrae are integral to the spine's function, playing a critical role in weight-bearing and force absorption. They support the body's weight, particularly during activities like lifting and carrying, and are designed to absorb axial forces that occur during movement. This capacity for force absorption is crucial in maintaining spinal integrity and preventing injury.
In terms of movement, the lumbar vertebrae facilitate a range of motions, including flexion, extension, rotation, and lateral bending. This flexibility is vital for performing everyday activities, from bending to tie a shoe to twisting to reach an object. The unique anatomy of the lumbar region allows it to balance stability with mobility, ensuring both support and movement.
Moreover, the lumbar vertebrae play a protective role, safeguarding the spinal cord and facilitating nerve communication pathways. The spinal canal, formed by the vertebral arches, houses and protects the spinal cord, while openings between the vertebrae allow nerves to exit and transmit signals throughout the body.
Clinical relevance of lumbar vertebrae
The lumbar region is often a focal point in clinical settings due to its susceptibility to various conditions. One common issue is spondylolysis, a stress fracture in the vertebra, often occurring at L5. This condition can progress to spondylolisthesis, where a vertebra slips out of place, causing pain and mobility issues.
Lumbar puncture procedures, commonly performed at the L1-L2 level, are another clinical aspect of the lumbar vertebrae. This procedure involves accessing the spinal canal to collect cerebrospinal fluid or administer medication, highlighting the lumbar region's significance in medical diagnostics and treatment.
The health of intervertebral discs, situated between each vertebra, is also crucial. These discs act as shock absorbers, cushioning the vertebrae and maintaining spinal flexibility. However, aging and trauma can lead to disc degeneration or protrusion, contributing to lower back pain and other complications.
Understanding the anatomy and function of the lumbar vertebrae is essential for recognizing their impact on overall health. By appreciating their role in supporting the body, facilitating movement, and protecting vital structures, individuals can take proactive steps to maintain lumbar health and prevent pain.
Ergonomic and postural considerations for lumbar vertebrae health
In today's fast-paced world, the health of your lumbar vertebrae is more important than ever. Our modern lifestyle, characterized by prolonged sitting and minimal physical activity, can have detrimental effects on the lumbar region. Poor posture and inadequate workstation setups often lead to increased lumbar strain, resulting in discomfort and potential long-term issues.
Ergonomic interventions are crucial for alleviating lumbar strain and promoting spine health. Adjusting your workstation to ensure proper posture is one of the simplest yet most effective strategies. This includes using chairs with lumbar support, positioning computer screens at eye level, and keeping feet flat on the floor. These adjustments help maintain the natural curve of the lumbar spine, reducing the risk of strain and injury.

Men's Posture Shirt™ - Black
Patented shirt with NeuroBand™ tech to stimulate muscles, relieve pain, and improve postural awareness.
Practical strategies for maintaining lumbar health
For desk workers and those in labor-intensive professions, incorporating practical strategies to support lumbar health is essential. Regular breaks to stand, stretch, and walk can significantly reduce the pressure on your lumbar vertebrae. Additionally, incorporating exercises that strengthen the core and lower back can enhance lumbar stability and support.
Using ergonomic aids such as lumbar cushions or adjustable desks can further aid in maintaining proper posture. These tools help support the natural alignment of the spine, preventing the slouching and hunching that often lead to lumbar discomfort.
Real-world application of lumbar vertebrae knowledge
Understanding the anatomy of lumbar vertebrae can directly impact everyday movements and activities. For instance, when lifting heavy objects, it's crucial to bend at the knees and keep the object close to the body to minimize stress on the lumbar region. This simple adjustment can prevent undue strain and potential injury.
Visual comparisons between healthy and compromised lumbar spines can be enlightening. A healthy spine exhibits a natural curve and even spacing between vertebrae, whereas a compromised spine may show signs of misalignment or disc protrusion. Recognizing these differences can motivate individuals to adopt healthier habits and ergonomic practices.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main functions of the lumbar vertebrae?
The lumbar vertebrae primarily support the upper body's weight, facilitate movement, and protect the spinal cord. They enable a range of motions, including flexion, extension, and rotation, while safeguarding nerve pathways.
How can I prevent lower back pain related to lumbar vertebrae?
Prevention strategies include maintaining proper posture, using ergonomic aids such as lumbar supports, and engaging in exercises that strengthen the core and lower back muscles. Regular movement and stretching are also vital.
What are common lumbar spine conditions and their symptoms?
Common conditions include spondylolisthesis, characterized by vertebral slippage, and disc protrusion, which can cause pain and mobility issues. Symptoms often include lower back pain, stiffness, and nerve-related discomfort.
How does aging affect the lumbar vertebrae?
Aging can lead to changes in disc structure, such as dehydration and degeneration, affecting the vertebrae's ability to absorb shock. This can result in reduced flexibility and increased susceptibility to conditions like arthritis.
What ergonomic solutions are most effective for lumbar support?
Effective solutions include using chairs with built-in lumbar support, adjustable desks to promote standing, and lumbar cushions to maintain spinal alignment. These aids help reduce lumbar strain and promote a healthy posture.
Källor
- Standring, S. (2016). "Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice." National Center for Biotechnology Information.
- Healthdirect Australia. (2021). "Lumbar Spine."
- Physiopedia. (2021). "Lumbar Vertebrae."
- University of Maryland Medical Center. (2021). "Anatomy and Function of the Spine."
- TeachMeAnatomy. (2021). "Lumbar Spine."
- Walker, B. R., & Colledge, N. R. (2018). "Davidson's Principles and Practice of Medicine." National Center for Biotechnology Information.